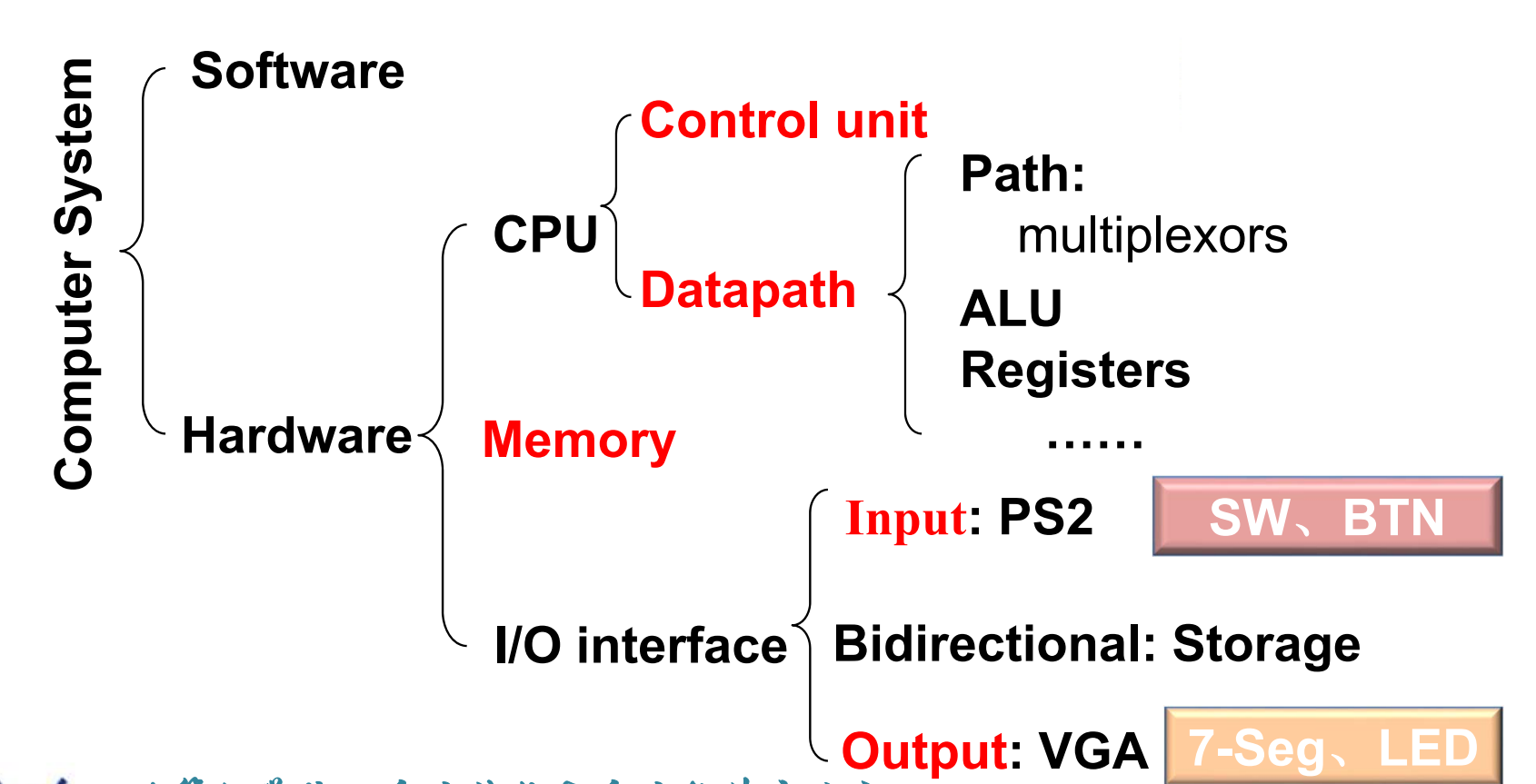
Computer Abstractions and Technology¶
约 548 个字 3 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
8 Ideas in Computer Architecture¶
- Moore's Law
The integrate circuit resource double every 18-24 months. -
User abstraction to simplify design
- Lower-level details are hidden to higher levels
- Instruction set architecture -- the interface between HW and SW.
- Make the common cases fast
- Performance via Parallelism
- Performance via Pipelining
- Performance via Prediction
- Hierarchy of memory
- Dependability via redundancy
Performance¶
- Response time: How long it takes to do a task.
- Throughput ( 吞吐量 ): Total work done per unit time.
Define \(Performance = \dfrac{1}{Execution\ Time}\)
Execution time¶
- Elapsed Time
Total response time, including all aspects e.g. Processing, I/O, OS overhead, idle time. - CPU Time
Discounts I/O time, other jobs’ shares
这里我们只考虑 CPU 时间
CPU Clocking¶
- Clock period: duration of a clock cycle.
用时钟周期代替具体的秒数。 - Clock frequency(rate): cycles per second.
\[
\begin{align*}
CPU\ Time &= CPU\ Clock\ Cycles \times Clock\ Cycle\ Time \\
&=\dfrac{ CPU\ Clock\ Cycles}{Clock\ Rates}
\end{align*}
\]
Performance improved by
- Reducing number of clock cycles
- Increasing clock rate
- Hardware designer must often trade off clock rate against cycle count
\[
\begin{align*}
Clock\ Cycles &= Instruction\ Count \times Cycles\ per\ Instruction(CPI)\\
CPU\ Time & = Instruction\ Count \times CPI\times CPI\ Cycle\ Time\\
& = \dfrac{Instruction\ Count \times CPI}{Clock\ Rate}
\end{align*}
\]
CPI is determined by CPU hardware.
如果不同指令有不同的 CPI, 我们可以用 Average CPI.
综上 , \(CPU\ Time = \dfrac{Instructions}{Program}\times \dfrac{Clock\ Cycles}{Instruction}\times \dfrac{Seconds}{Clock Cycle}\)
Performance depends on
- Algorithm: affects IC, possibly CPI
- Programming language: affects IC, CPI
- Compiler: affects IC, CPI
- Instruction set architecture
Incredible performance improvement¶
Uniprocessor¶
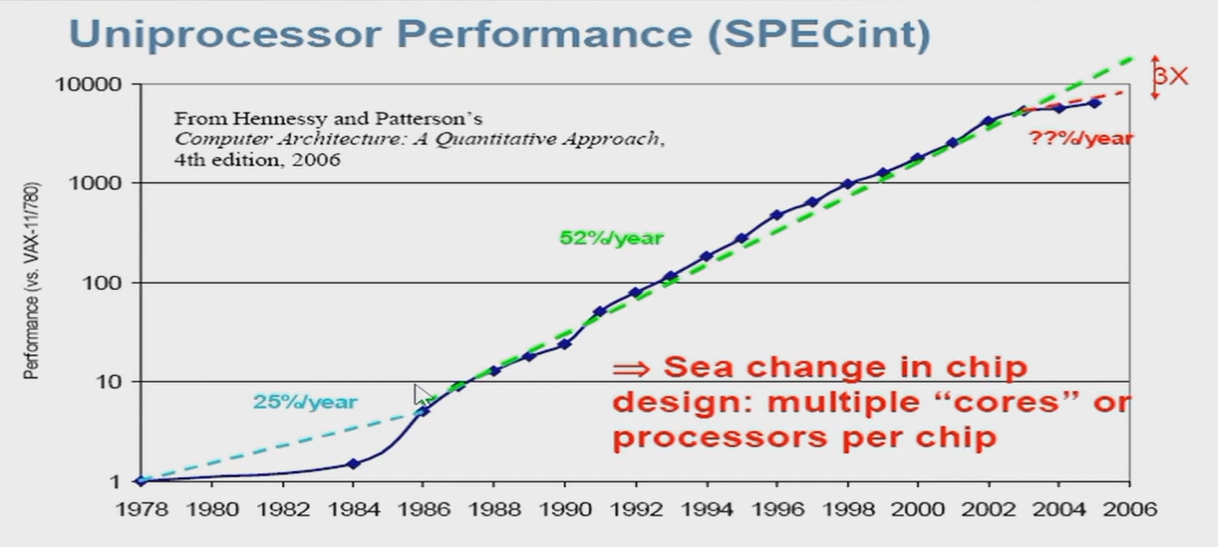
Three Walls
- Power Wall
\(Power = Capactive\ load \times Voltage^2\ Frequency\)

主频提高了很多,但功耗并没有得到这么多的提升,因为我们降低了工作电压 (5V-1V)
现在工作电压不能再降低了(否则泄漏电流占比太大),因此我们不能再提高功率了。
Memory Wall
Memory 的性能增长不如 CPU 的性能增长,大部分时间花在读写内存了,影响整体性能。
ITP Wall
difficulty to find enough parallelism in the instructions stream of a single process to keep higher performance processor cores busy.
指令集并行程度
Multiprocessors¶
requires explicitly parallel programming.
- Amdahl's Law: Improve an aspect of a computer and expecting improvement in overall performance.
实际上, \(T_{improved}=\dfrac{T_{affected}}{improvement\ factor}+T_{unaffected}\). e.g. 对某一方面优化 90%, 并不能使 CPU 整体性能优化 90%.
Corollary: make the common case fast. - Low Power Not at Idle.
机器在没有工作时也有功耗损失。 - MIPS as a Performance Metric
- MIPS: Millions of Instructions Per Second
- 这个参数需要在其他参数一致时,才有比较意义。不同的 ISA 之间不能仅凭 MIPS 比较。