Pipelining¶
约 2402 个字 6 行代码 34 张图片 预计阅读时间 8 分钟
Abstract

What is pipelining?
How is the pipelining Implemented?
What makes pipelining hard to implement?
What is pipelining?¶
从两个角度进行加速:对每一条的指令进行加速;对一段程序的执行进行加速
Pipelining is an implementation technique whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution; it takes advantage of parallelism that exists among the actions needed to execute an instruction.
机制上,先进行分段,每一段用不同的部件,就可以并行执行。我们用 Buffer 存放了临时的结果,有人放有人取
假设一条指令的执行分为下面三段:
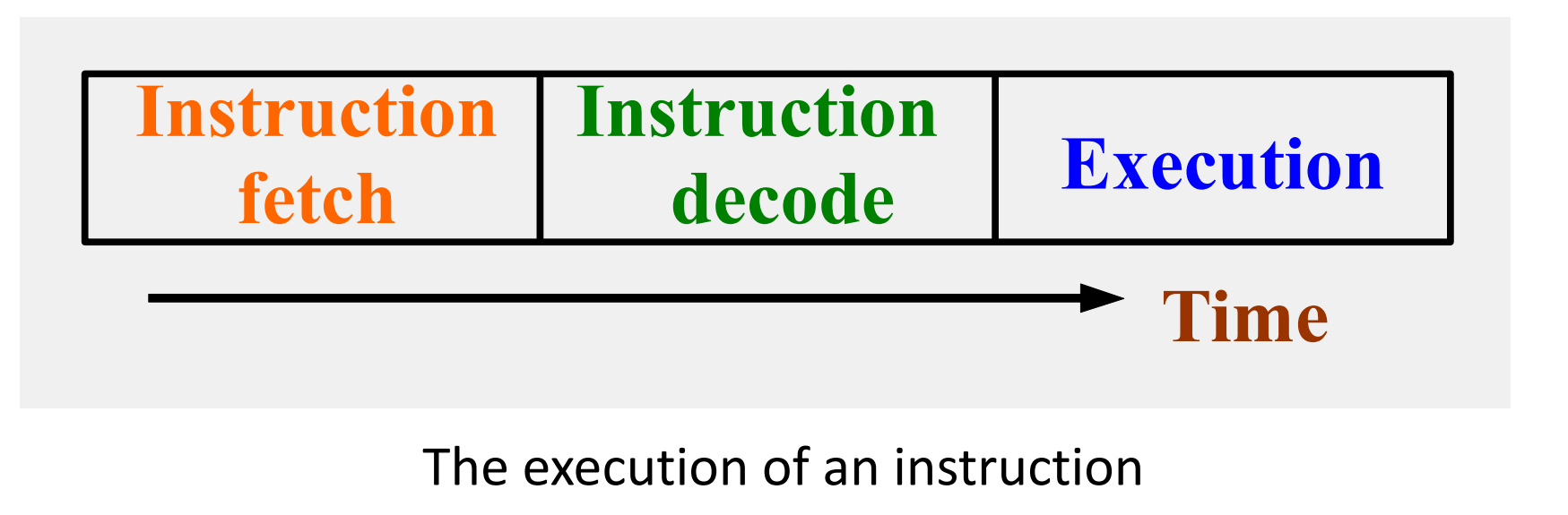
那么我们执行的模式可以有下面三种:
Three modes of execution
- Sequential execution
- Single overlapping execution
- Twice overlapping execution
Sequential execution¶
没有流水线的时候,每一条指令顺序执行,执行时间就是每一条指令的每个阶段时间求和。
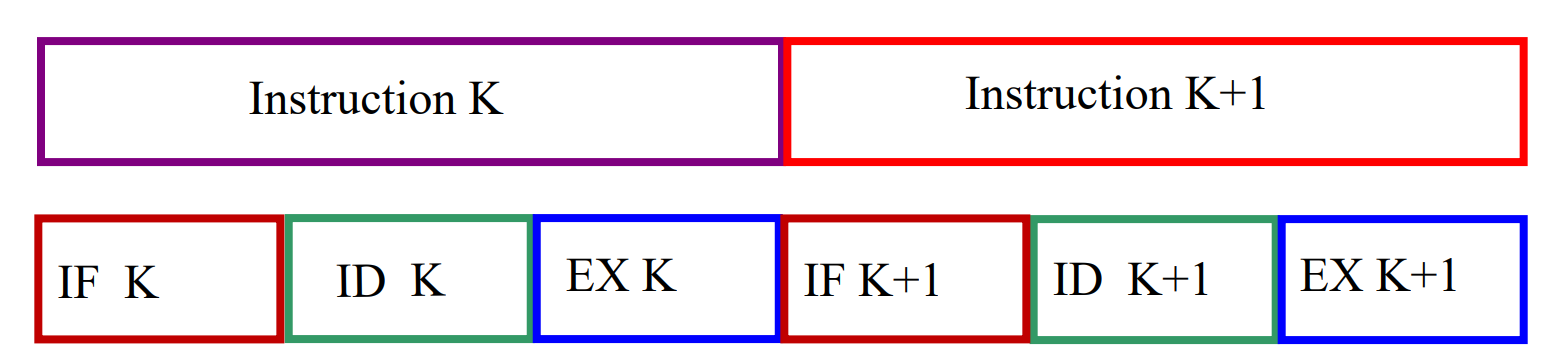
Overlapping execution¶
重叠执行时,如果不同阶段时间不一致,如 ID 阶段时间较长,那么需要等待,浪费资源;如 EX 阶段时间较长,那么产生冲突,执行部件不够。


因此理想情况是让三个阶段的时间相等。
-
Single
好处:时间缩短 ⅓,但提高了硬件开销,而且有冒险。

-
Twice
好处:时间缩短 ⅔,但需要更复杂的硬件,而且需要单独的 FETCH DECODE EXE 部件。
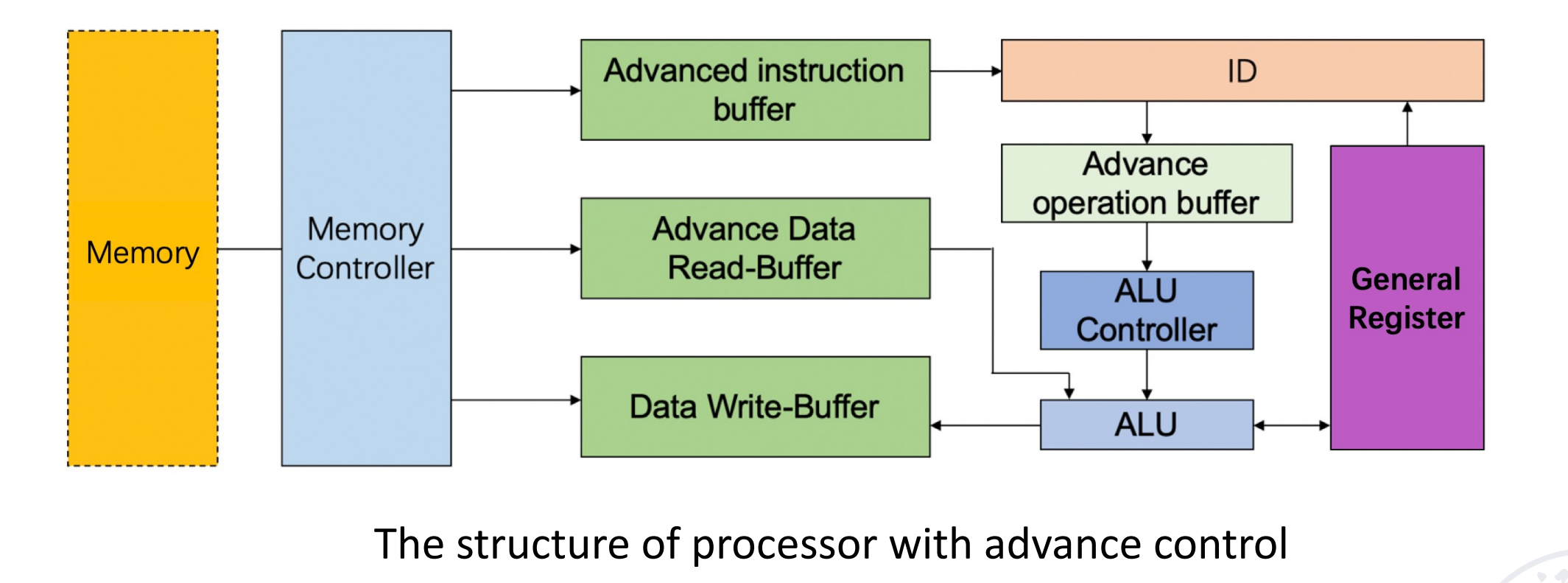
如何实现重叠?- buffer
Adding instruction buffer between memory and instruction decode unit.
添加 buffer 之后,IF 阶段时间变得很短,此时可以和 ID 阶段合并(把二次重叠变为了一次重叠)。
但如果合并后 IFID 和 EX 阶段时间不一致,也会有执行部件的浪费。
如何平滑速度的差异?- buffer
Common features: They work by FIFO, and are composed of a group of several storage units that can be accessed quickly and related control logic.
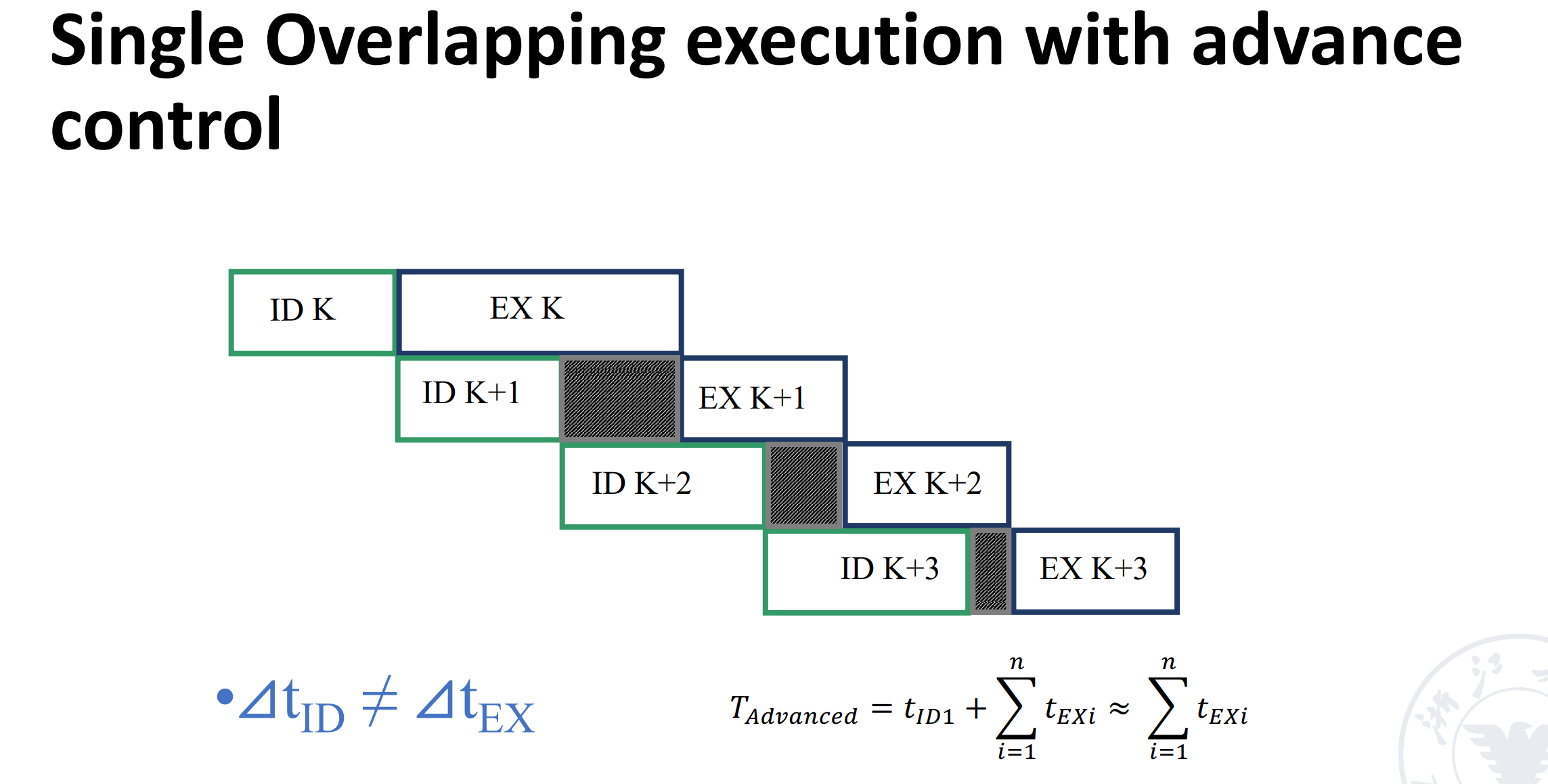
可以看到,添加 buffer 之后,ID 阶段不用等待 EX 阶段技术才能进行下一条的译码,因为 ID 阶段的结果已经存放在 buffer 中了。
Classes of pipelining¶
Characteristics of pipelining
- Single function pipelining: only one fixed function pipelining.
-
Multi function pipelining: each section of the pipelining can be connected differently for several different functions.
不同运算,用到流水线中不同的段,这样实现了不同的功能。Example
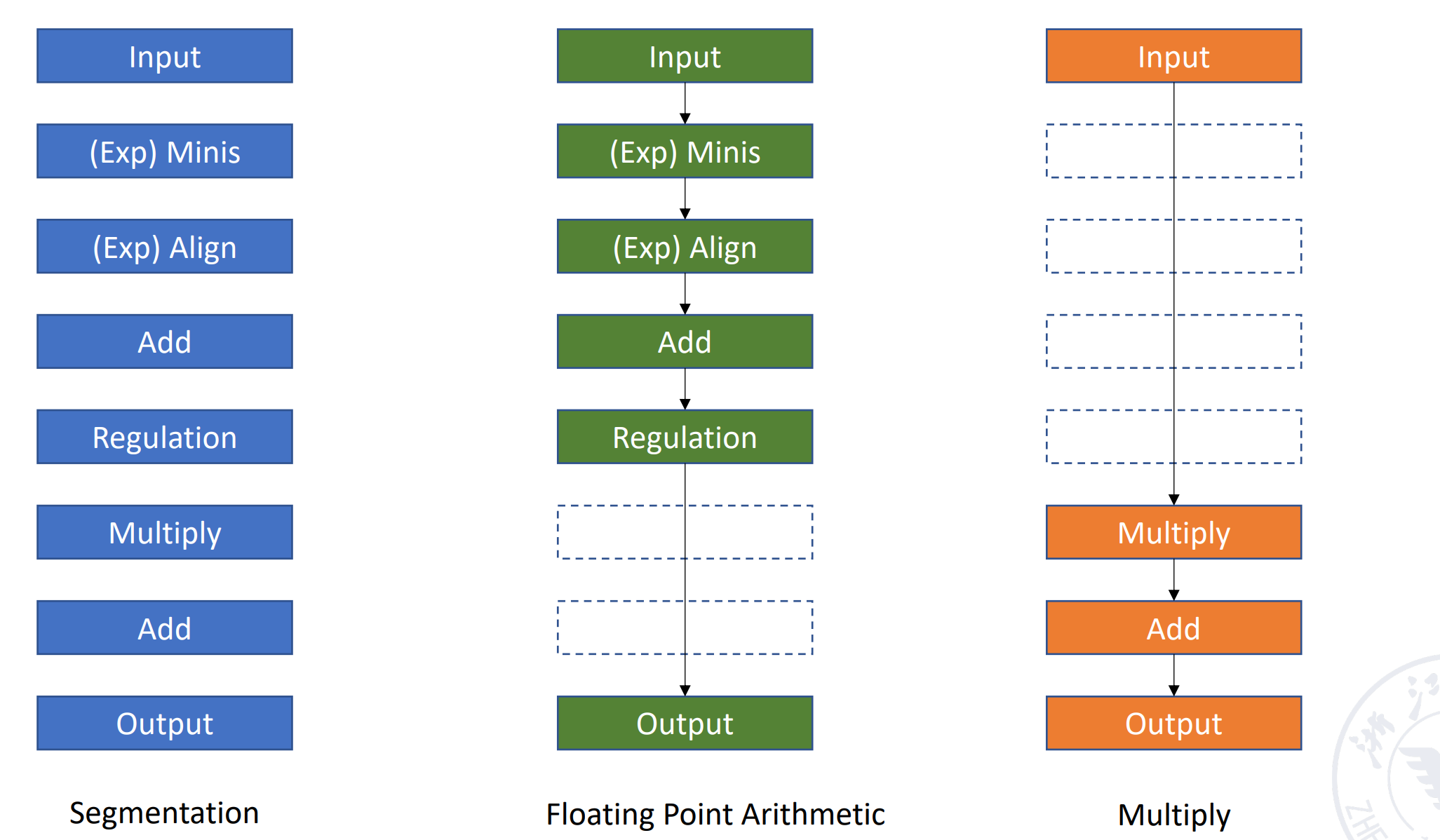
针对多功能流水线的划分 :
- Static pipelining
静态流水线:同一个时刻流水线只能做一个功能。
例如在刚刚的例子中,流水线要么做浮点加法,要么做乘法。 -
Dynamic pipelining
动态流水线:同一个时刻流水线可以做多个功能。Example
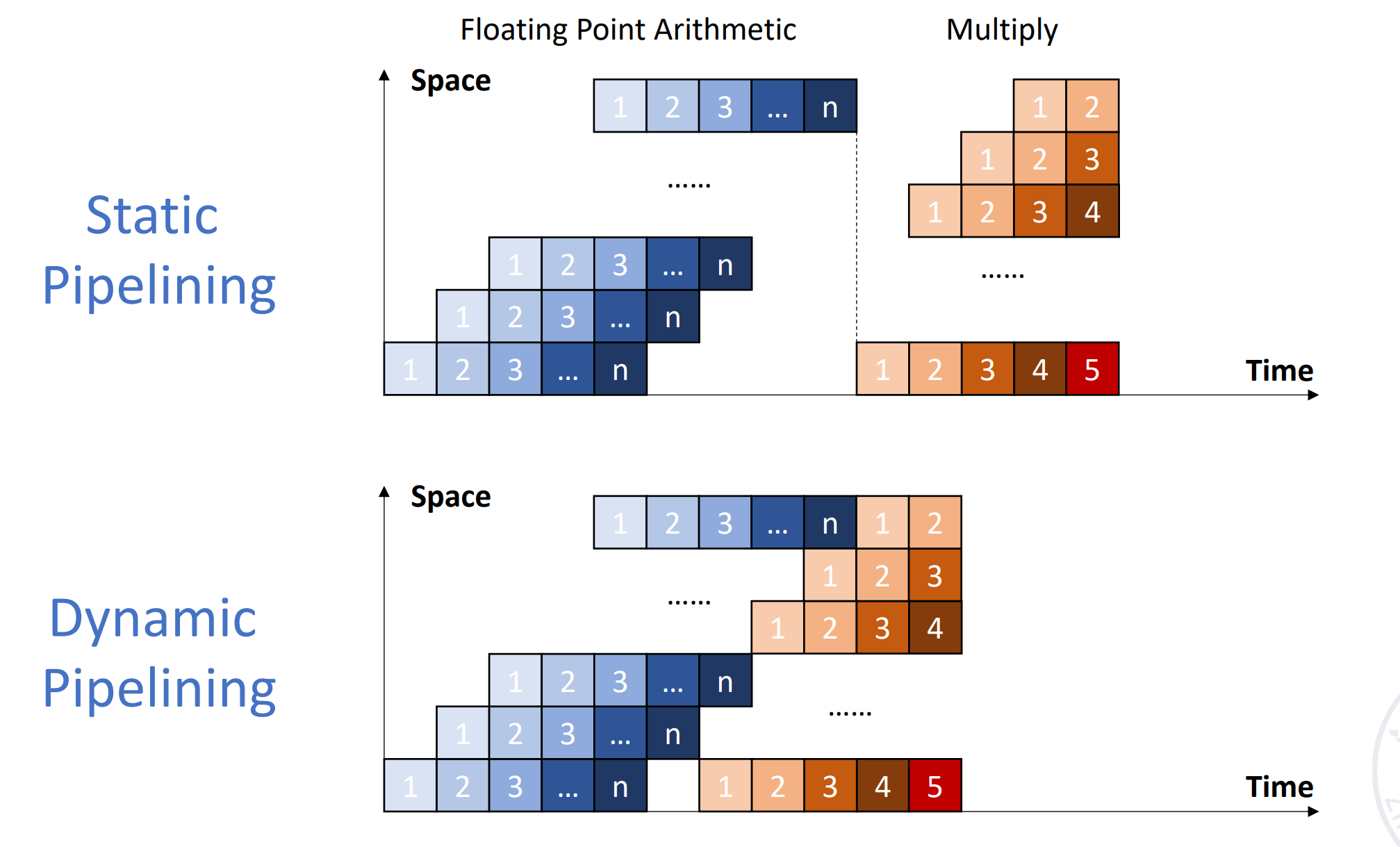
可以不用等浮点加法第 n 条结束,就可以开始浮点乘法。
- Static pipelining
还可以从不同粒度分类:
- Component level pipelining (in component - operation pipelining)
- Processor level pipelining (inter component - instruction pipelining)
- Inter processor pipelining (inter processor - macro pipelining)
还可以分为线性 / 非线性:
- Linear pipelining
-
Nonlinear pipelining
非线性,功能部件可能多次使用,造成回路Example
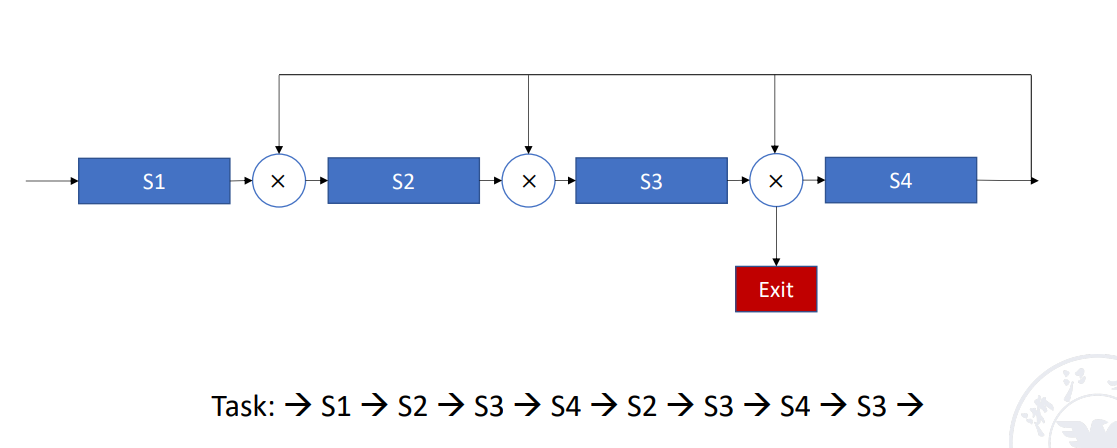
还可以分为顺序 / 乱序:
- Ordered pipelining
- Disordered pipelining
进来和流出的顺序不一样。后面的指令与前面的指令无关,则可以先出来,不能则要等待。
还可以分为标量 / 向量处理器:
- Scalar processor
- Vector pipelining processor: The processor has vector data representation and vector instructions. It is the combination of vector data representation and pipelining technology.
Performance evaluation of pipelining¶
Throughput¶
流水线希望我们单位时间内处理的任务越多越好,即提高吞吐率。
Throughput(TP) \(TP=\dfrac{n}{T_K}<TP_{max}\)(实际上 TP 会有损耗)
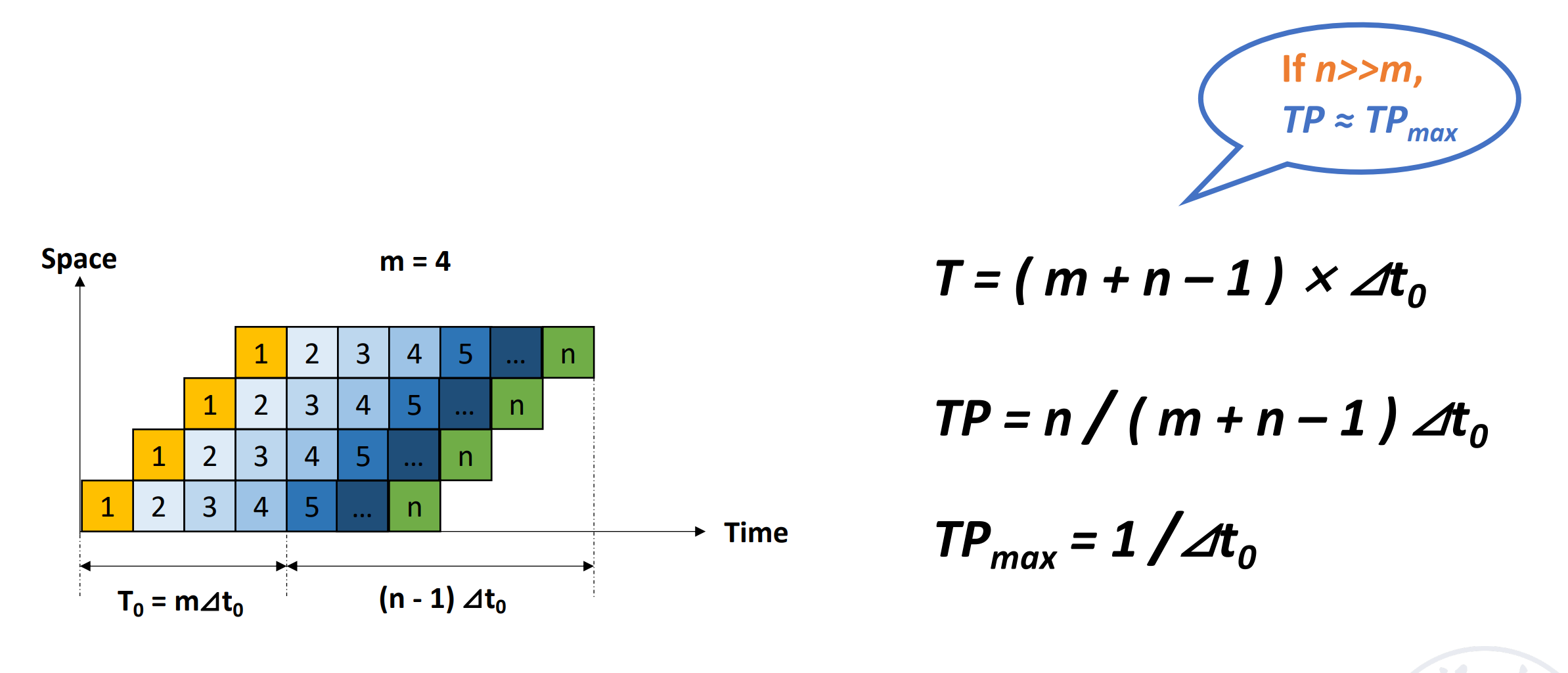
\(TP=\dfrac{n}{n+m-1}TP_{max}\)
- if \(n>>m, TP\approx TP_{max}\)
Suppose the time of segments are different in pipelining, then the longest segment in the pipelining is called the bottleneck segment.
Example
- \(M = 4\)
- Time of S1, S3, S4: \(\delta t\)
- Time of S2: \(3\delta t\) (Bottleneck)
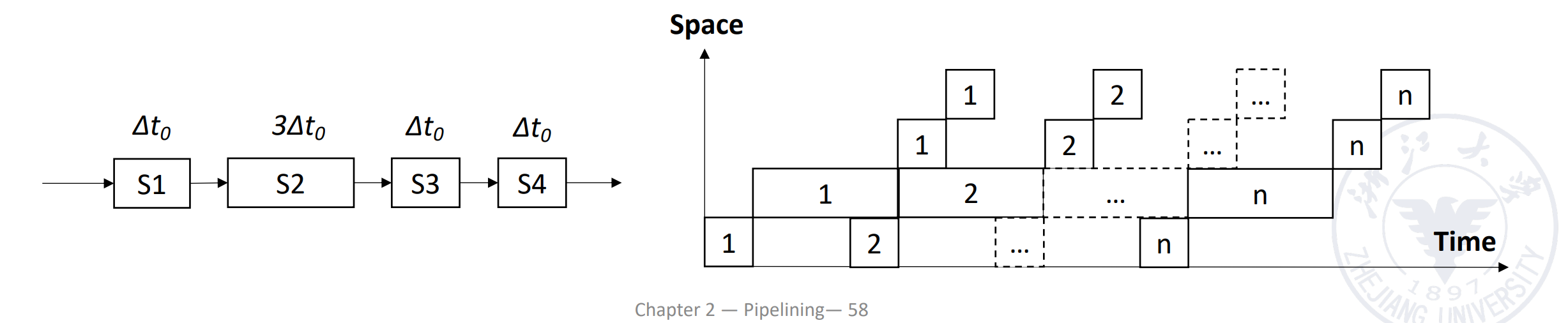
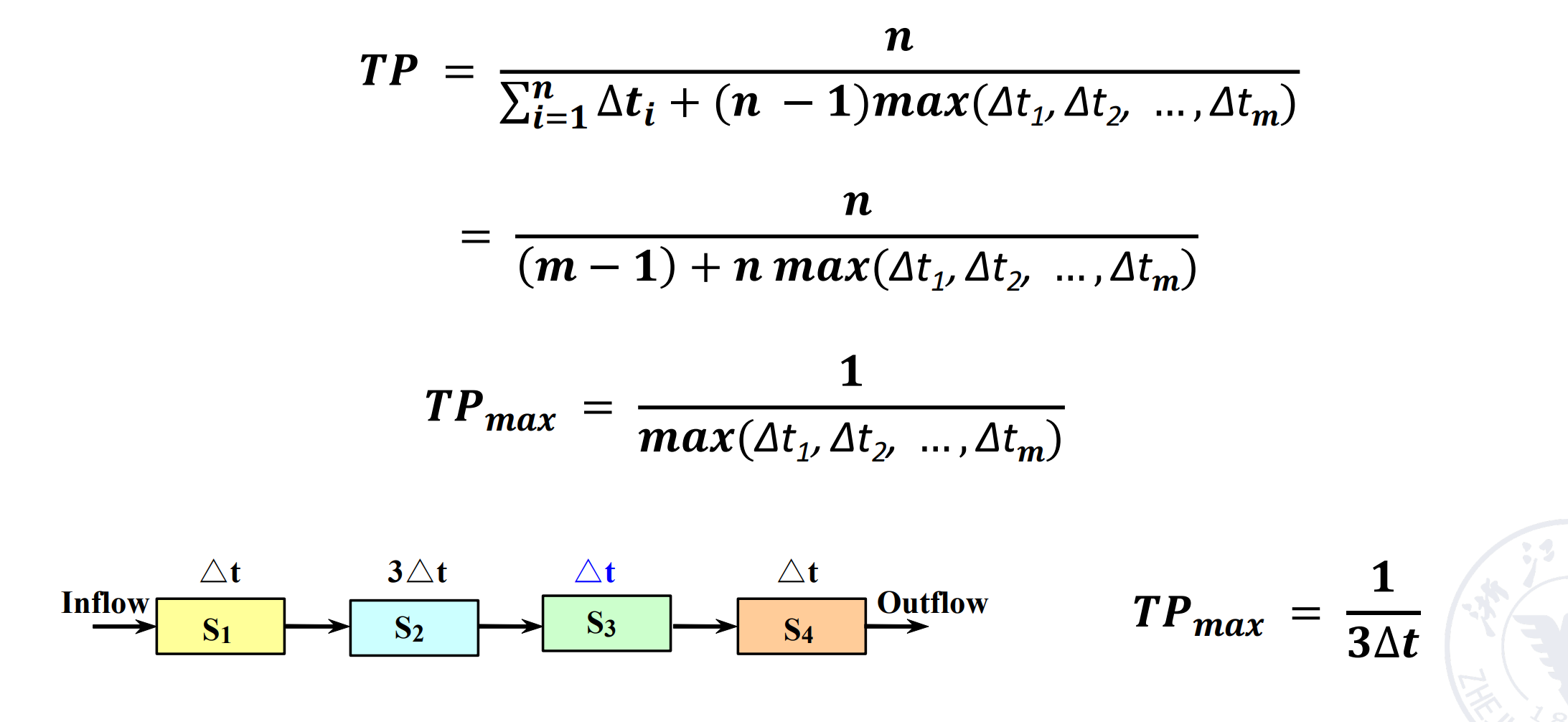
可以看到 \(TP_{max}\) 只和瓶颈段的时间有关
Common methods to solve pipeline bottleneck¶
-
Subdivision
把瓶颈段分成若干段执行

-
Repetition
在瓶颈段多使用几个部件

Speedup¶
\(S_p = \dfrac{n\times m \times \delta t_0}{m(m+n-1)\delta t_0} = \dfrac{n}{m+n-1}\)
- if \(n>>m, S_p\approx m\)
Efficiency¶
效率,从计算机部件的角度:纵轴代表使用的不同的功能部件。效率指的是我们真正使用这个部件占整个时空的百分比。

\(\eta = \dfrac{n\times m \times \delta t_0}{m(m+n-1)\delta t_0} = \dfrac{n}{m+n-1}\)
- 注意效率得到的结果应该是百分比,之前的吞吐量、加速比都是没有量纲的数。
- if \(n>>m, \eta\approx m\)
Pipeline Performance¶
Vector Calculation in Static Pipeline
现在有两个向量 A 和 B,我们要计算 A 点乘 B,通过下面的动态双功能流水线运算。
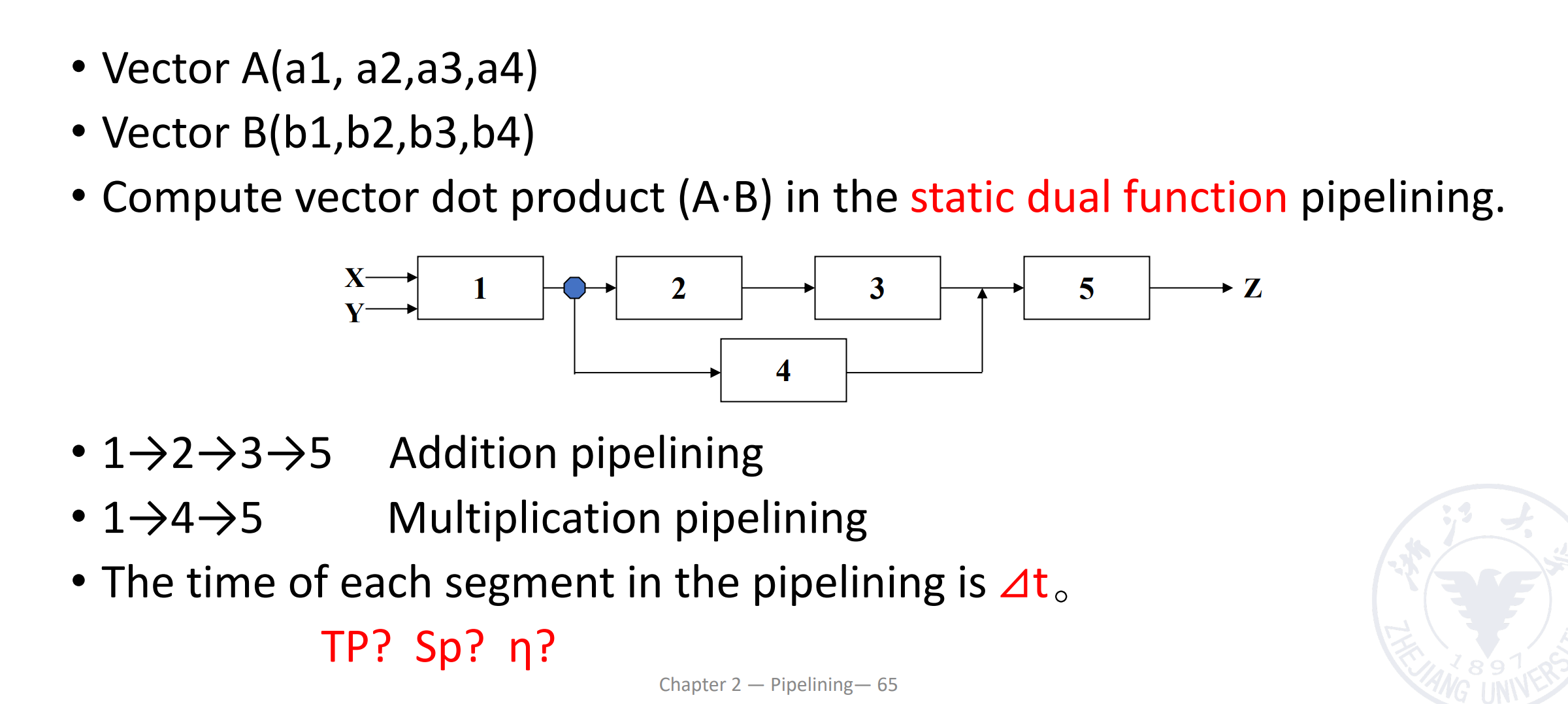
注意到这里是静态流水线,同一时刻只能做一类事情,需要先完成一种操作再完成另一种。这里我们需要先做乘法,排空,再做加法。做加法时,第三个乘法的结果需要等前两个乘法的结果相加后,再计算。
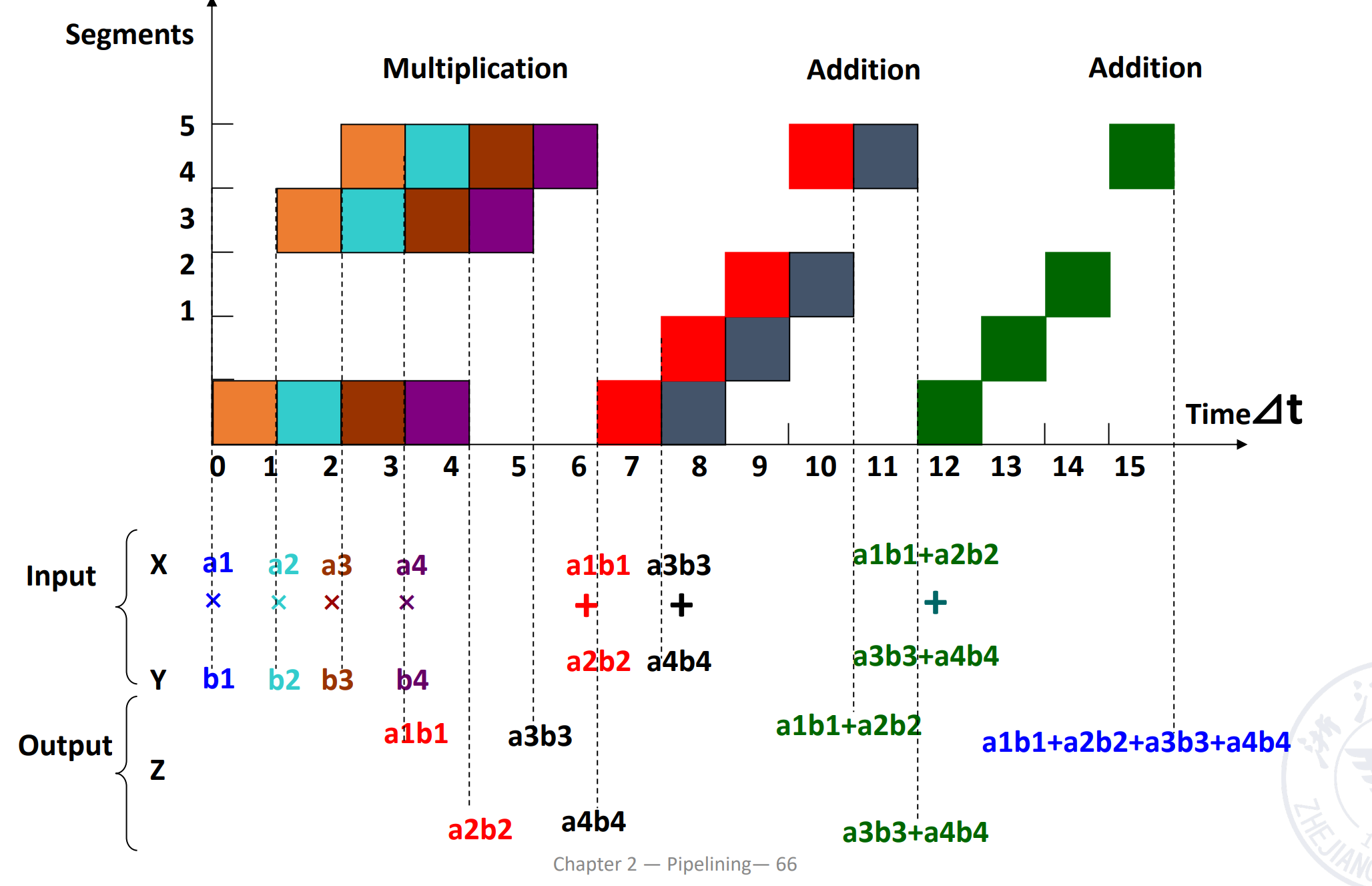
得到 \(T_p=7/15\delta t, S_p = 1.6, \eta=32%\)
Vector Calculation in Dynamic Pipeline
动态流水线,可以在前一个功能还没有做完的时候执行另一个功能,不需要排空。

这里当两个乘法的结果算出来之后,就可以执行对应的加法。
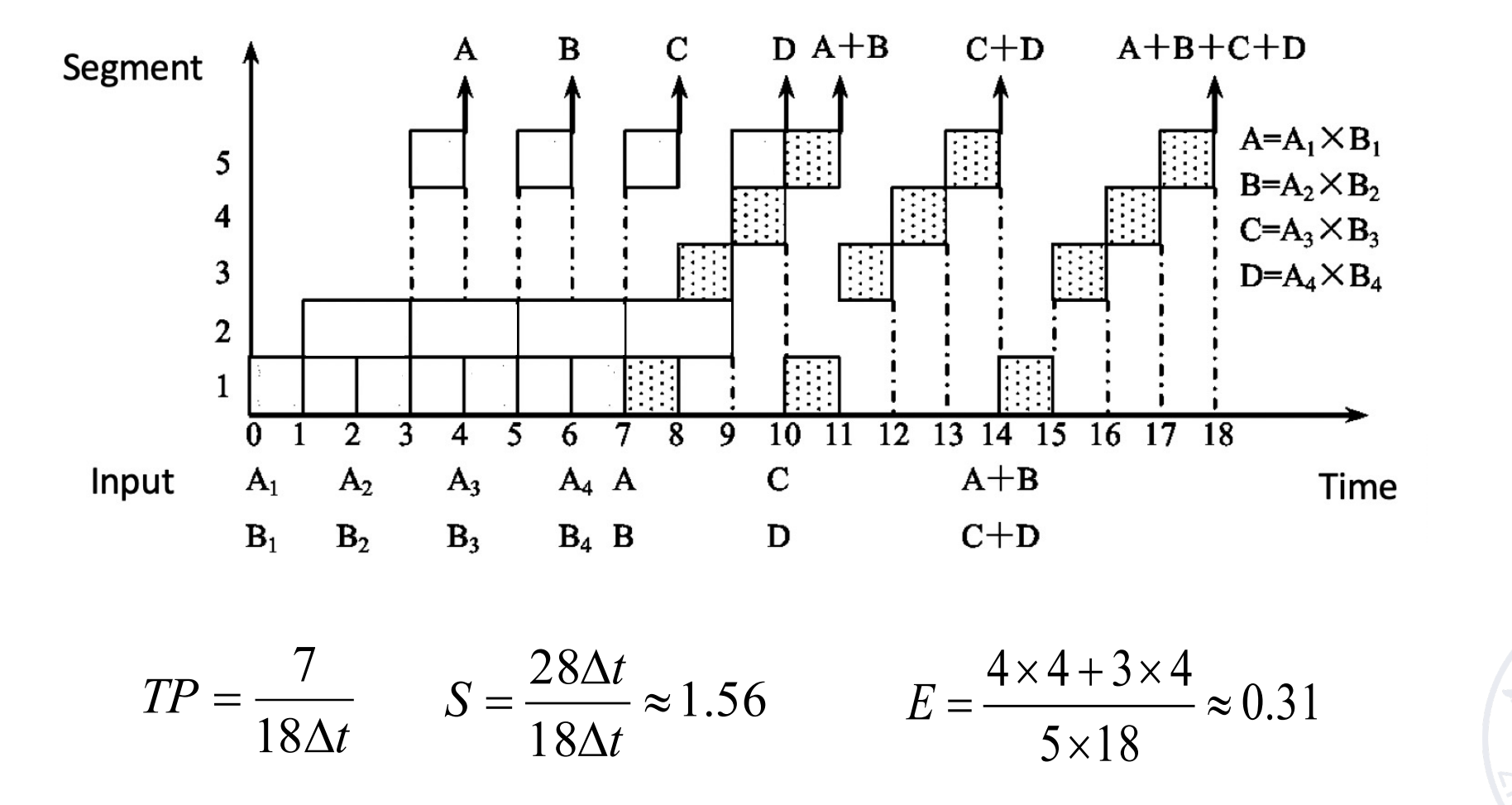
流水线的段数 m 不是越多越好。
Too many stages:
- Lots of complications
- Should take care of possible dependencies among in-flight instructions
- Control logic is huge
流水线的性能有关:动态(不需要排空,但需要硬件支持)还是静态,流水线段数,代码质量(冒险)
Hazards of Pipelining¶
Hazards
- Situations that prevent starting the next instruction in the next cycle.
-
Structure hazards
A required resource is busy.
-
Data hazard
Need to wait for previous instruction to complete its data read/write.
-
Control hazard
Deciding on control action depends on previous instruction.
Structure Hazards¶
对结构的争用,如 memory.
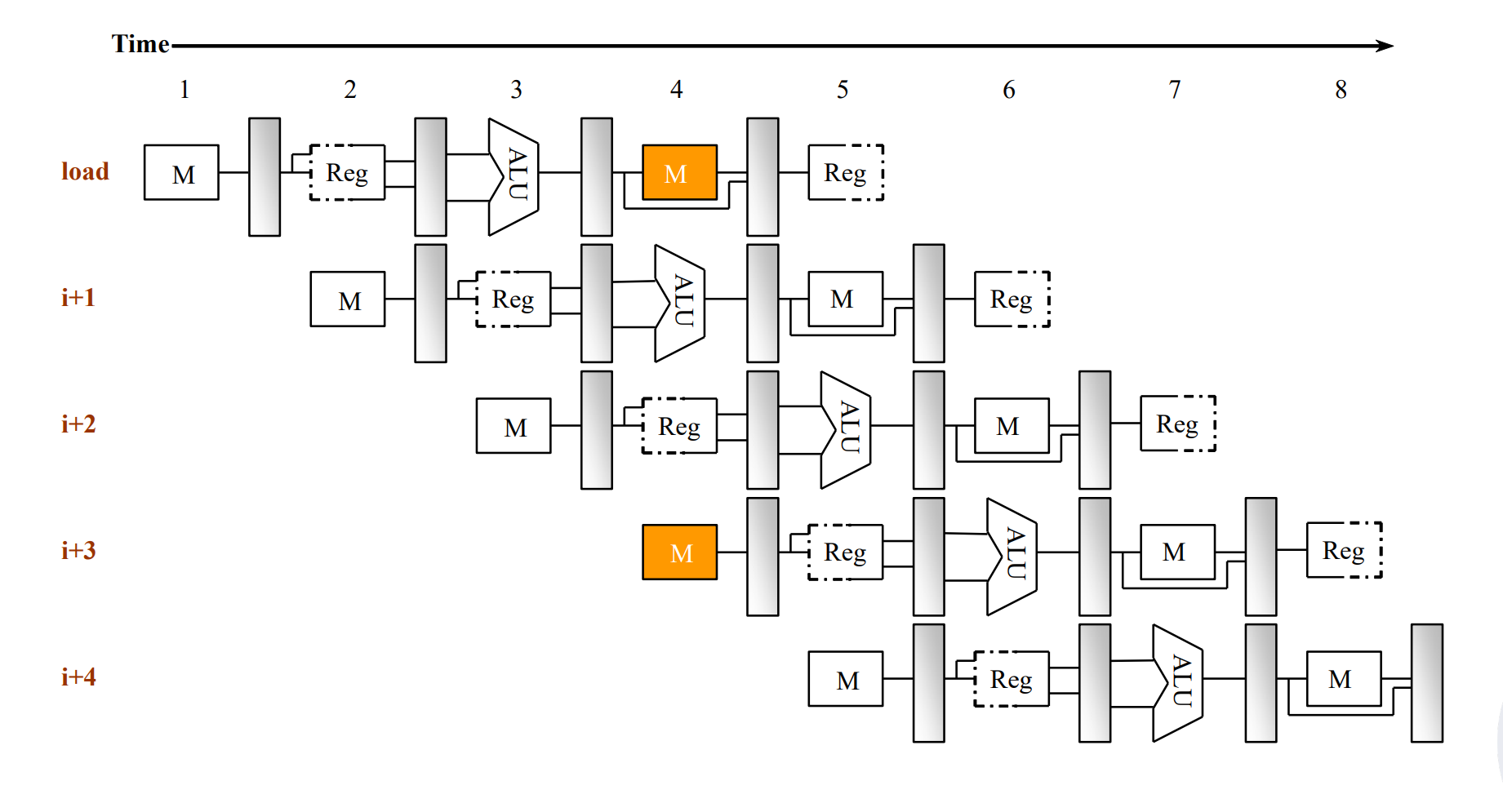
一般加 bubble,或者加硬件。
Data Hazards¶
An instruction depends on completion of data access by a previous instruction.
可以加 bubble, 或者通过 forwarding 前递数据,但并不是所有的情况都可以解决。
-
Read after write: RAW
Forwarding 解决这种类型的冒险。
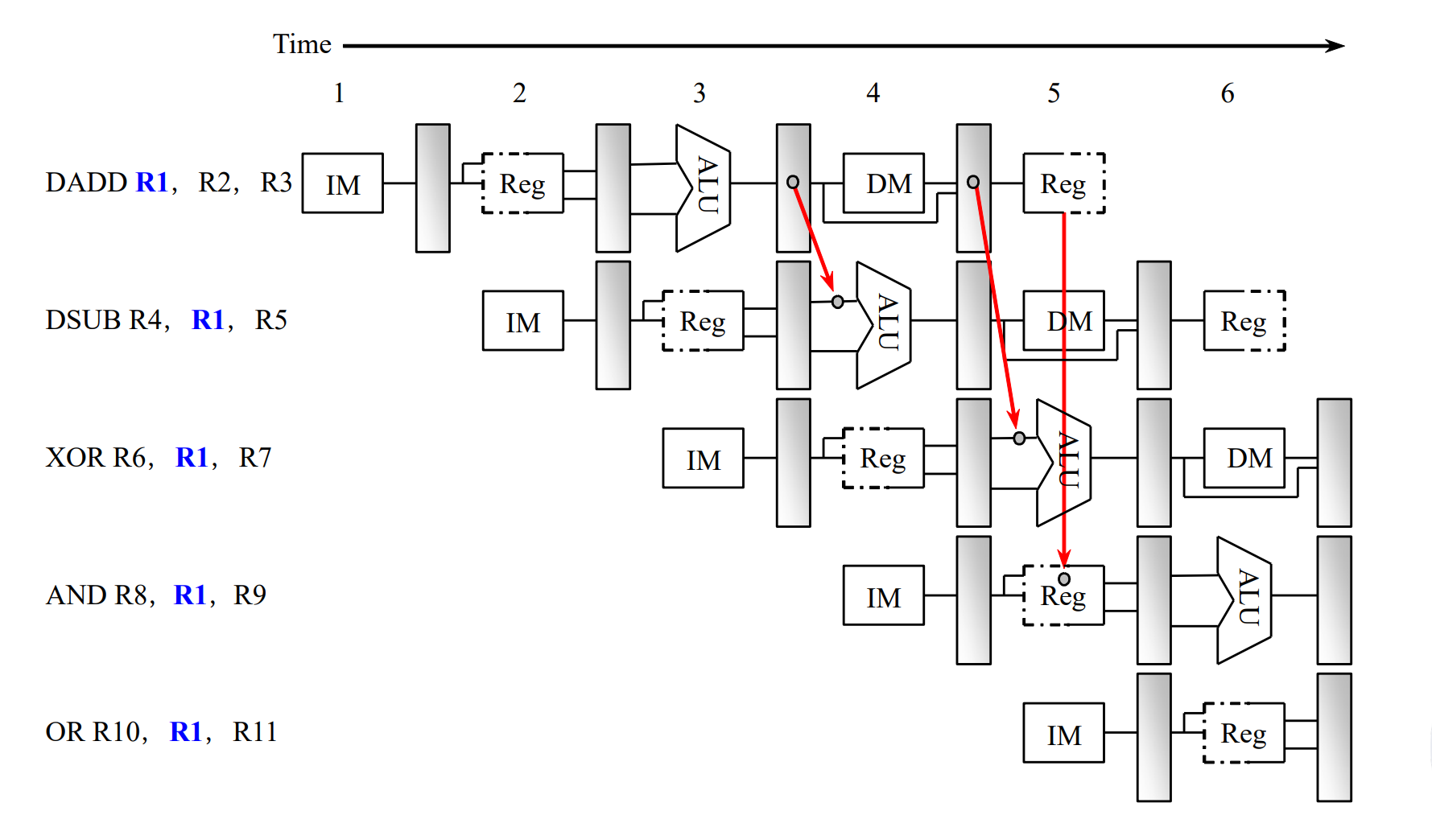
-
Write after read: WAR
Name Dependences(在乱序流水线中可能出现冒险)
-
Write after write: WAW
Name Dependences
但是并不是所有的 RAW 都可以通过 Forwarding 解决,如 Load-use Hazard.
有的时候,我们可以对指令进行调度,改变指令的顺序,从而避免 stall 的情况。
Code Scheduling to Avoid Stalls

- 静态调度:程序还没有运行,编译器为我们优化了代码,改变执行顺序。
- 动态调度:程序运行时,处理器为我们优化了代码,改变执行顺序。
Control Hazards¶
为了减少分支指令带来的 stall,我们使用分支预测的技术。
- Static branch prediction
- Based on typical branch behavior
- e.g. 循环,if-else 语句
- Predict backward branches taken
- Predict forward branches not taken
- Dynamic branch prediction
- Hardware measures actual branch behavior
- e.g. 根据历史记录(如上一次分支的结果
) ,预测下一次的分支
- e.g. 根据历史记录(如上一次分支的结果
- Assume future behavior will continue the trend
- Hardware measures actual branch behavior
Data Hazards: Forwarding vs. Stalling¶
Control Hazards¶
在 RISC-V 中,有无条件跳转 jal, jalr 和有条件跳转 beq, bne, blt, bge, bltu, bgeu。
可以在 ID 阶段就算出要跳转的目标地址,同时预测分支的结果。只有预测错误时才需要 stall 来 flush 掉之前的结果,预测成功不需要 stall。
Static Branch Prediction¶
-
Prediction taken
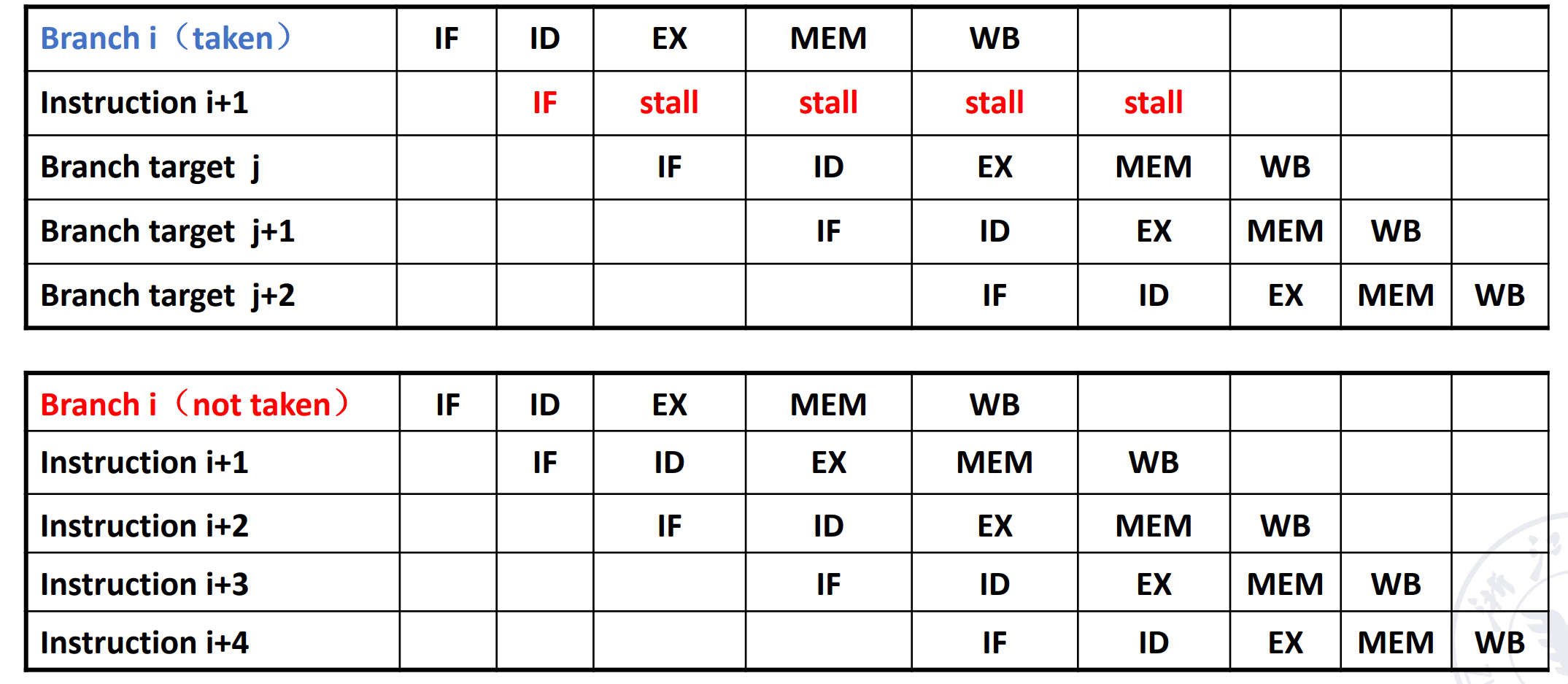
-
Prediction not taken
-
Delayed Branch
The behavior of a delayed branched is the same whether or not the branch is taken.
即无论分支是否发生,分支后面的指令都要执行。(延时槽)
Is delay slot a really good design?
RISC-V 和微架构绑定不深,而且延迟槽也有弊端。
Dynamic Branch Prediction¶
Use dynamic prediction
- Branch prediction buffer (aka branch history table)
- Indexed by recent branch instruction addresses
- Stores outcome (taken/not taken)
-
To execute a branch
-
Check table, expect the same outcome
把之前大家的结果存在一个表里,通过历史判断未来,根据之前的分支结果预测这次。
-
Start fetching from fall-through or target
- If wrong, flush pipeline and flip prediction
-
Branch History Table(BHT)¶
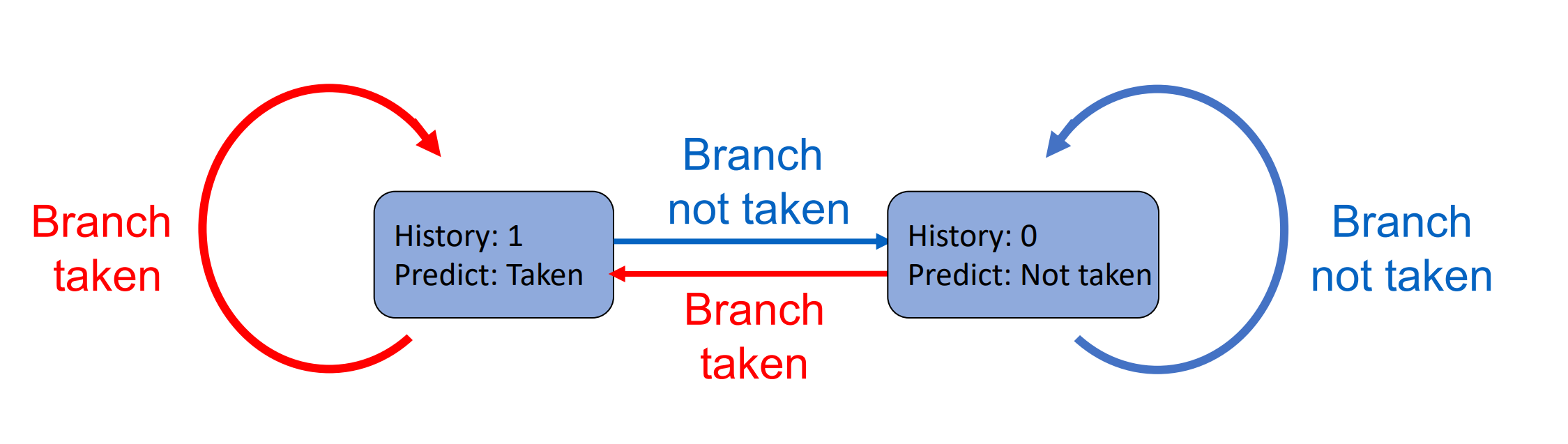
- 1-Bit Predictor
-
2-Bit Predictor
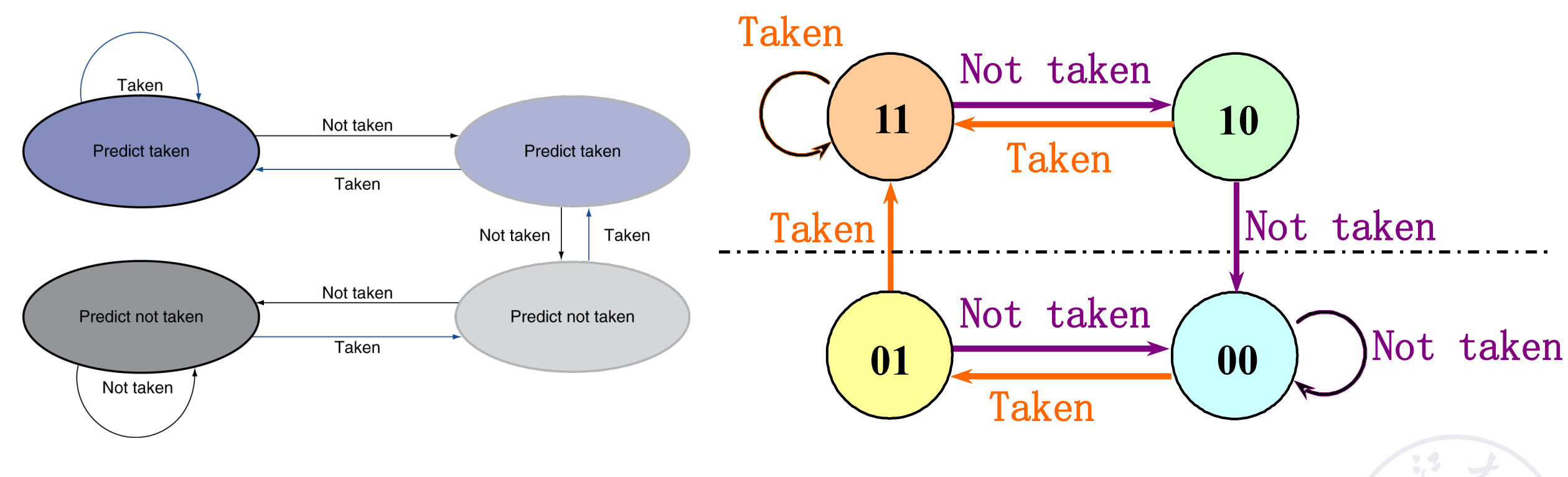
实际上两位的效果已经很好,而且资源开销不小,因此我们一般不会再提升位数。
Advanced Techniques for Instruction Delivery and Speculation¶
-
Increasing Instruction Fetch Bandwidth
-
Branch-Target Buffers(BTBs)
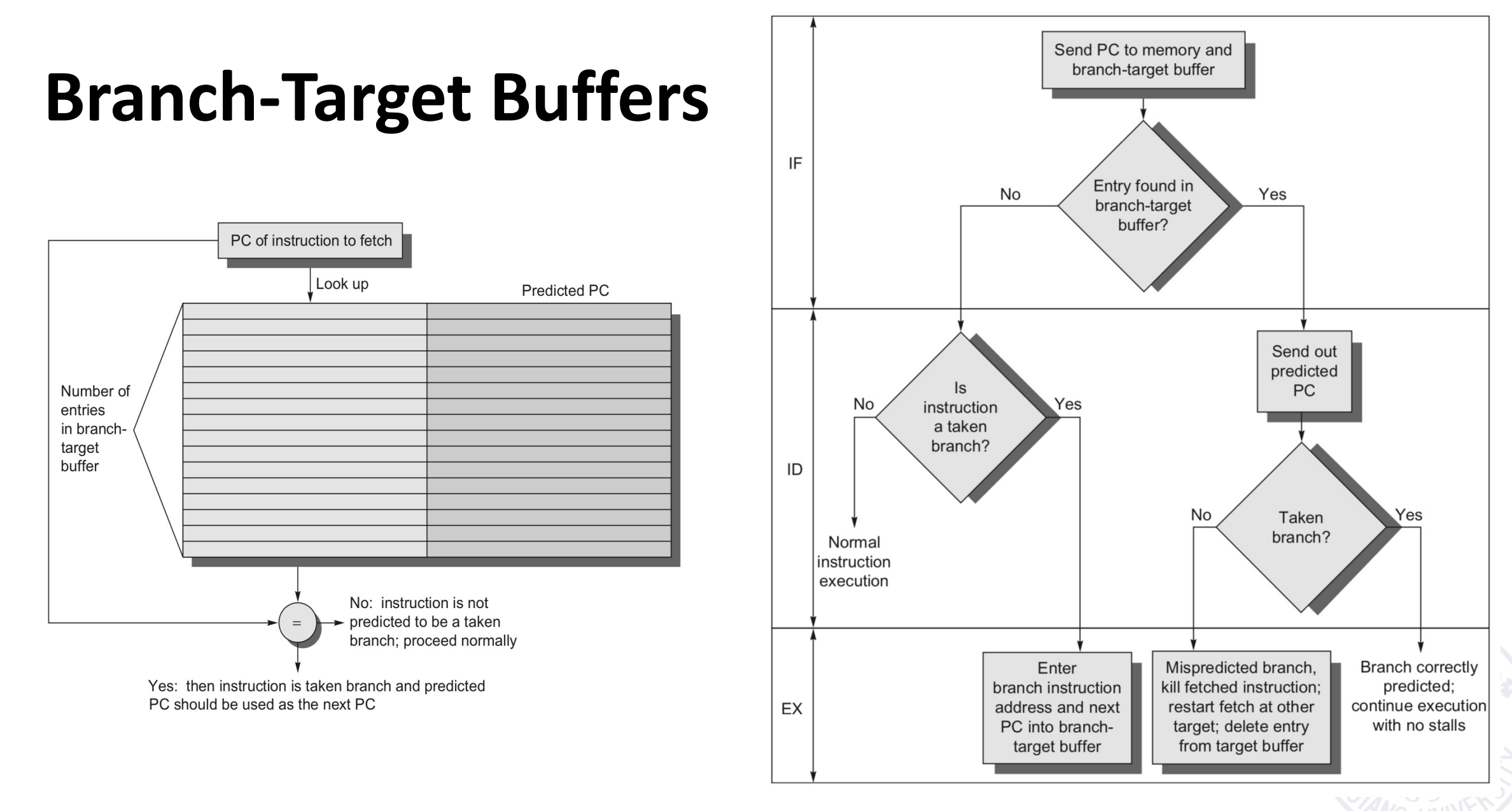
类似于 TLB,放分支预测的目标地址。如果有跳转的分支指令不在表中,就加入;如果有表中的分支指令不发生跳转,就去掉。

-
-
Specialized Branch Predictors: Predicting Procedure Returns, Indirect Jumps, and Loop Branches
- Integrated Instruction Fetch Units
-
Benefit
- Get instructions at branch target faster
- It can provide multiple instructions at the branch target once, which is necessary for the multi processor;
- branch folding
- It is possible to achieve unconditional branching without delay, or sometimes conditional branching without delay
Schedule of Nonlinear pipelining¶
对于非线性流水线,功能部件可能经历多次,有调度问题。
Question
纵轴代表不同的功能部件,横坐标表示拍数。即每一拍需要用到的功能部件。

算法:
-
Initial conflict vector
二进制表示,第几拍是不能使用的。将几个二进制数取并集。
-
Conflict vector
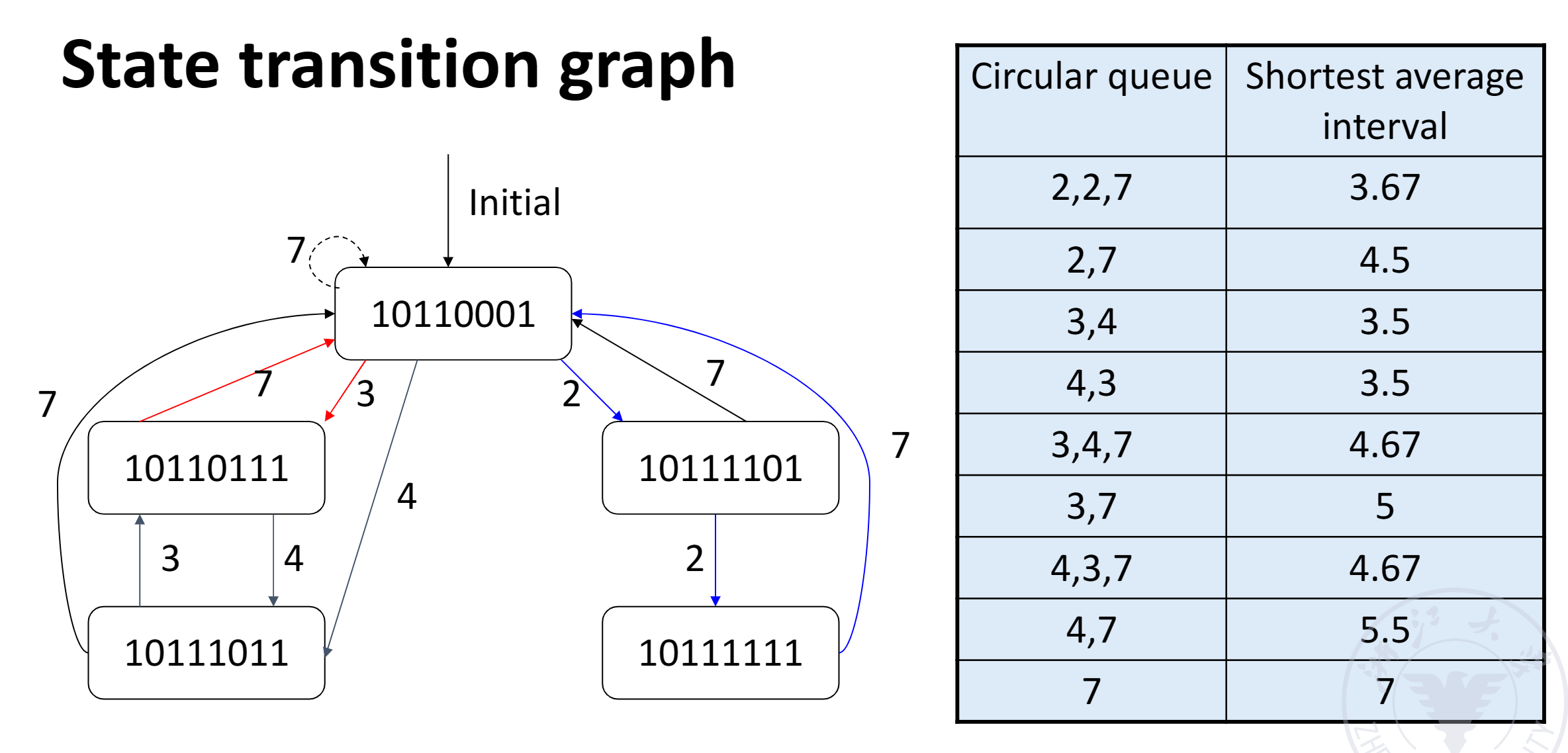
- State transition graph
- Circular queue
- Shortest average interval
Example
-
Initial conflict vector
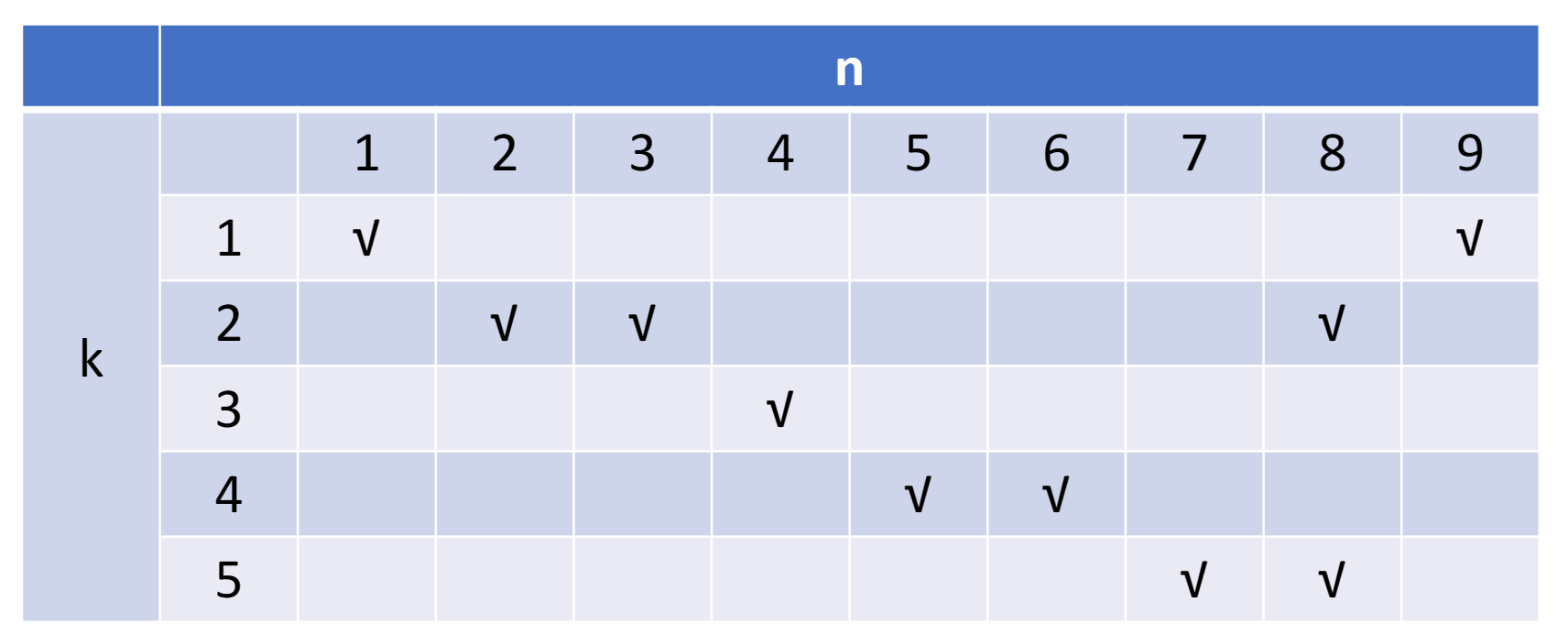
对每一个部件分开来看
- 第一个部件,隔 8 拍会产生冲突;第二个部件:1,5,6;第三个部件:无;第四、五个部件:1
- 将对应二进制数的第 1、5、6、8 位设为 1,其他位为 0,得到了初始的冲突向量 10110001。
-
Conflict vector

对于第三列,隔两拍进下一条指令,我们就把冲突向量向右移两位(高位补 0
) ,得到了新的冲突向量,并和本来的冲突向量或起来得到 CCV。 (注意这里最左侧的一列表示向右移动了多少次)找到了一个循环调度:2-2-7
-
State transition graph
Summary¶
Summary
- How the instruction is executed
- Sequential execution
- Overlap once
- Second overlap
- Pipeline
- Classification of pipelines
- Single function, multi-function
- Static, dynamic
- Linear, non-linear
- In-order, out-of-order
- Performance indicators of the pipeline
- Throughput rate
- Speedup ratio effectiveness
- Factors affecting the performance of the pipeline
- Pipeline design
- Type of instructions
- Instructions related
- Data dependence
- Name dependence
- Control dependence
- Dynamic Branch Prediction
- Branch History Table (BHT)
- Branch-Target Buffer (BTB)
- Non-linear pipeline scheduling problem