File System Interface¶
约 1578 个字 14 张图片 预计阅读时间 5 分钟
File concept¶
如何使用大规模存储和 IO?后来有了文件系统,对磁盘提供了抽象。
-
File system presents abstraction of disk。
- File <-> Track/sector
-
How to use file system?
- How to use file?
- How to use directory?
- How to implement file system?
- How to implement file?
- How to implement directory?
File is a contiguous logical space for storing information.
- data: character, binary, and application-specific
- program
- special one:
procfile system - use file-system interface to retrieve system information.
File Attributes¶
- Name – only information kept in human-readable form
- Identifier – unique tag (number) identifies file within file system
- Type – needed for systems that support different types
- Location – pointer to file location on device
- Size – current file size
- Protection – controls who can do reading, writing, executing
- Time, date, and user identification – data for protection, security, and usage monitoring
这些信息是目录结构 (directory structure) 的一部分,也存在磁盘上。 可能有其他属性,例如 checksum,这些会存到 extended file attributes 里。
Example

modify 是修改文件内容 content data,change 是修改文件 Metadata 的时间。
File Operations¶
- create:
- space in the file system should be found
- an entry must be allocated in the directory
- open: most operations need to file to be opened first
- return a handler for other operations
-
read/write: need to maintain a pointer
-
reposition within file – seek
将 current-file-position pointer 的位置重新定位到给定值,例如文件开头或结尾。
-
-
close
- delete
- Release file space
- Hardlink: maintain a counter - delete the file until the last link is deleted
-
truncate: empty a file but maintains its attributes
把文件的所有 content 清空,但保留 metadata。
其他操作可以通过上面这些操作实现。如拷贝就是 create+read&write。
Open Files¶
Several data are needed to manage open files:
- Open-file table: tracks open files
- File pointer: pointer to last read/write location, per process that has the file open
- File-open count: counter of number of times a file is open – to allow removal of data from open-file table when last processes closes it
- Disk location of the file: cache of data access information
- Access rights: per-process access mode information
文件可能被并发访问,我们需要锁。有 Shared lock 和 Exclusive lock,以及两种锁的机制 mandatory lock(一旦进程获取了独占锁,操作系统就阻止任何其他进程访问对应文件)和 advisory lock(进程可以自己得知锁的状态然后决定要不要坚持访问
File Types¶
识别不同的文件类型:
-
as part of the file names - file extension
例如规定只有扩展名是 .com, .exe, .sh 的文件才能执行。
-
magic number of the file
在文件开始部分放一些 magic number 来表明文件类型。例如 7f45 4c46 是 ASCII 字符,表示 ELF,代表 elf 文件格式。
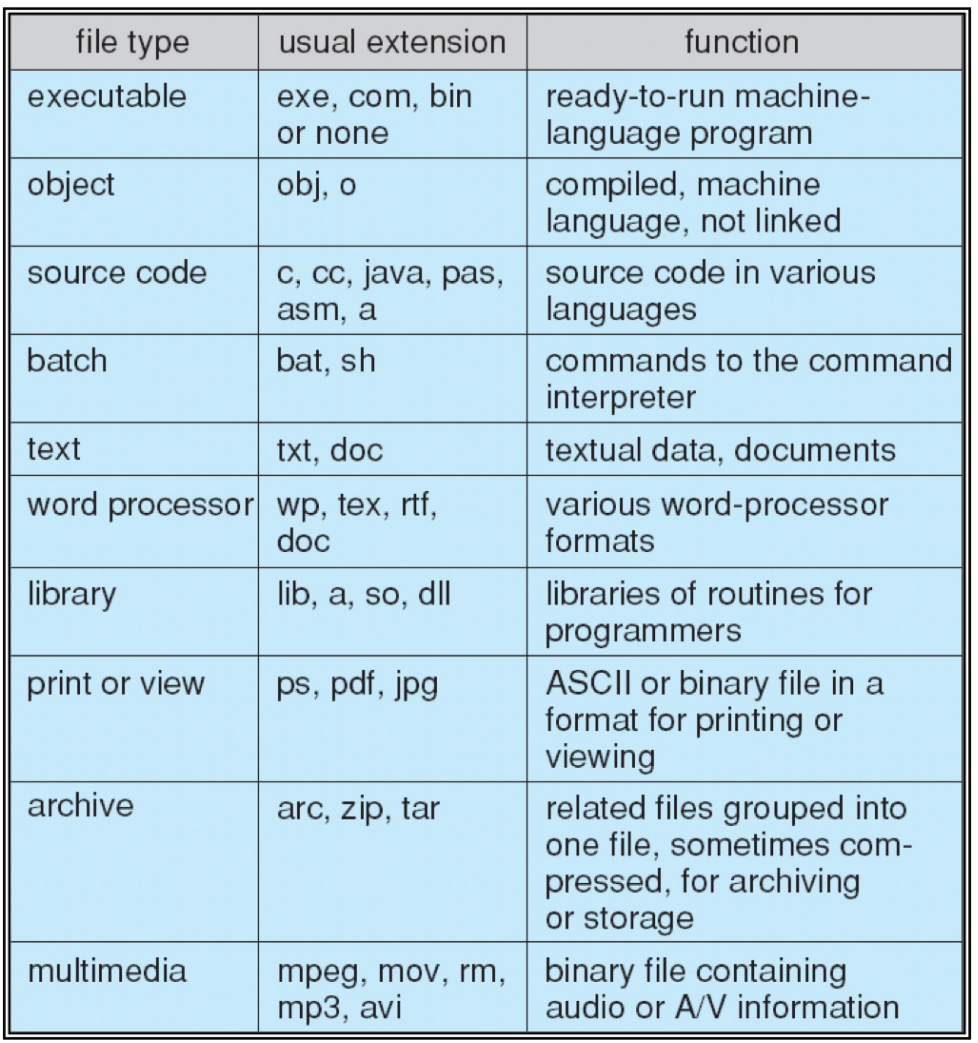
File Structure¶
A file can have different structures, determined by OS or program
- No structure: a stream of bytes or words
-
Simple record structure
- Lines of records, fixed length or variable length
-
Complex structures
Access Methods¶
-
Sequential access
-
a group of elements is access in a predetermined order
每次都只能从头开始访问。
-
-
Direct access
-
access an element at an arbitrary position in a sequence in (roughly) equal time, independent of sequence size.
可以跳到任意的位置访问,也称为随机访问。
-

在直接访问的方法之上,还有可能提供索引,即先在索引中得知所需访问的内容在哪里,然后去访问。也有可能使用多层索引表。
Directory structure¶
Disk can be subdivided into partitions
- partitions also known as minidisks, slices
-
different partitions can have different file systems
一个文件系统可以有多个 disk,一个 disk 可以有多个 partition,一个 partition 又有自己的文件系统。
-
disk or partition can be used raw. (without a file system)
partition 也可以不对应一个文件系统。
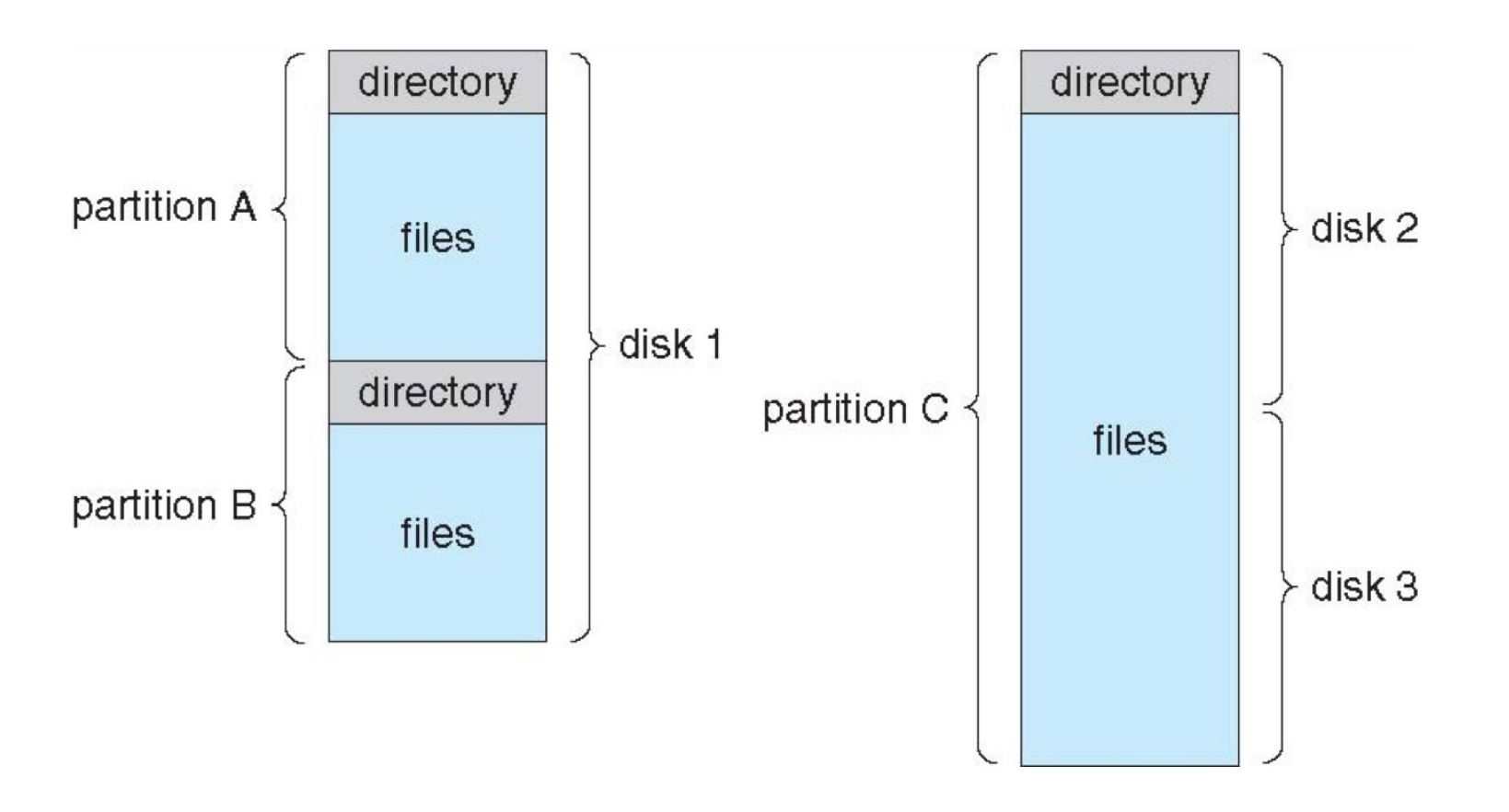
Directory is a collection of nodes containing information about all files.
文件名的集合

Operations Performed on Directory¶
- Create a file: new files need to be created and added to directory
- delete a file: remove a file from directory
- List a directory: list all files in directory
- Search for a file: pattern matching
- Traverse the file system: access every directory and file within a directory
Single-Level Directory¶
我们设计的 directory,要能快速定位文件;要兼顾效率、便于使用、便于按一些属性聚合。
A single directory for all users:
存在 Naming problems and grouping problems,如果两个用户想用相同的文件名,无法实现。
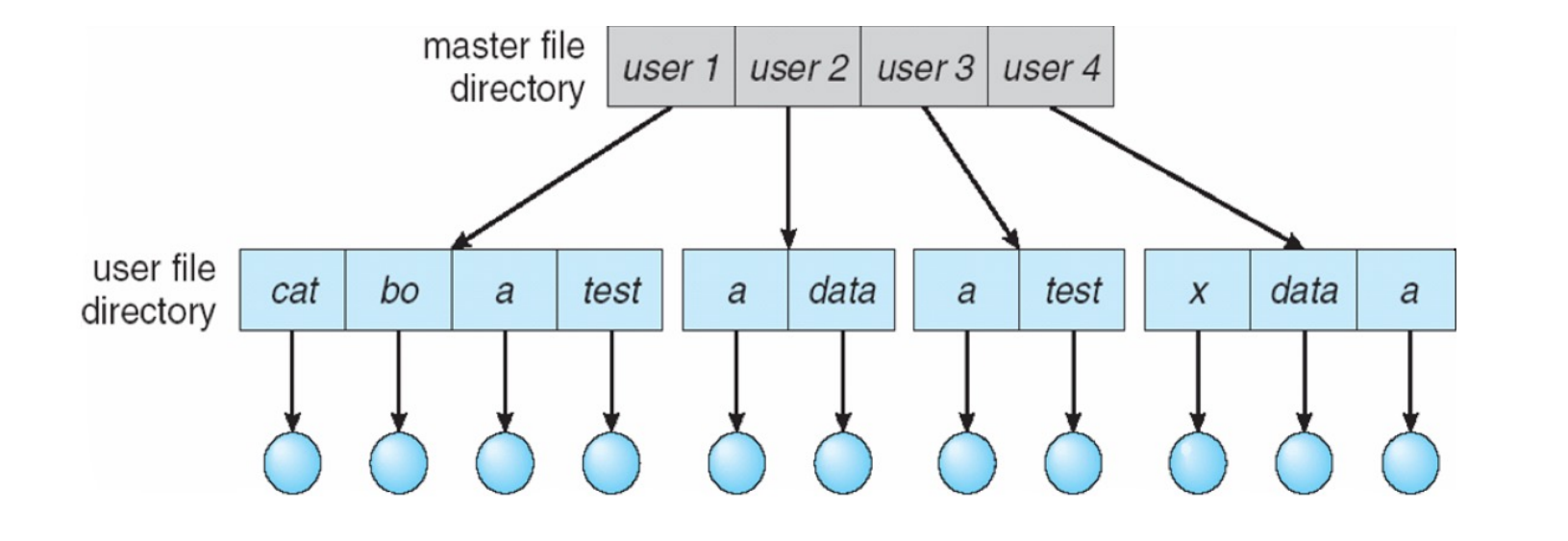
Two-Level Directory¶
Separate directory for each user
- Different user can have the same name for different files
- Each user has his own user file directory (UFD), it is in the master file directory (MFD).
- Efficient to search
Tree-Structured Directories¶
Files organized into trees
- efficient in searching, can group files, convenient naming
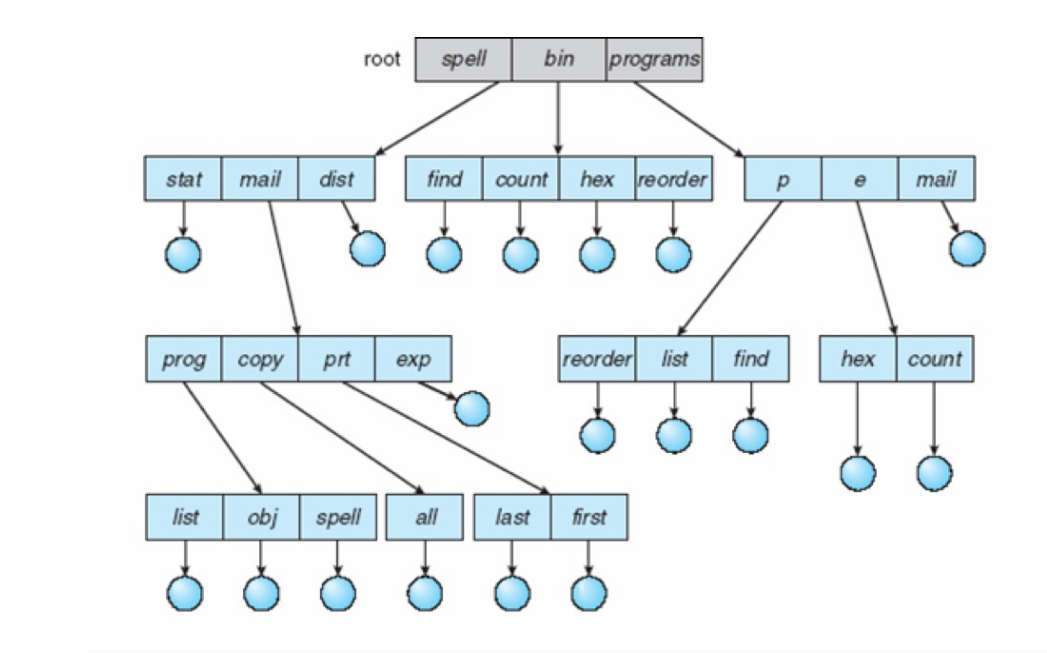
如果所需目录不在当前目录,那么用户就必须提供一个路径名 (path name) 来指定。
File can be accessed using absolute or relative path name
- absolute path name:
/home/alice/.. - relative path is relative to the current directory (pwd)
操作:
- Creating a new file: touch
- Delete a file: rm
- Creating a new subdirectory:
mkdir <dir-name> - Delete directory:
- If directory is empty, then it’s easy to handle
- If not
- Option I: directory cannot be deleted, unless it’s empty
- Option II: delete all the files, directories and sub-directories
sudo rm -rf /
这里不能 share 一个文件(即多个指针指向同一个文件
Acyclic-Graph Directories¶
allow links to a directory entry/files for aliasing (no longer a tree)
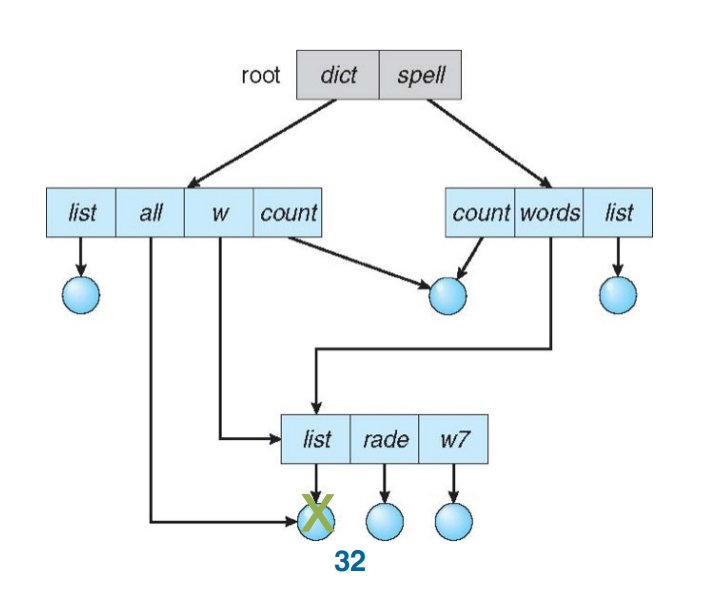
-
Dangling pointer problem:
e.g., if delete file
/dict/all,/dict/w/listand/spell/words/listare dangling pointers.- Solution: back pointers/reference counter
- Back pointers record all the pointers to the entity, a variable size record
-
Or count # of links to it and only (physically) delete it when counter is zero
如果一个文件被删除,那么它的 reference counter 就会减一,当减到 0 时,才真正删除。
- Solution: back pointers/reference counter
General Graph Directory¶
Allowing arbitrary links may generate cycles in the directory structure.
允许目录中有环。
-
allow cycles, but use garbage collection to reclaim disk spaces
如果没有外界目录指向一个环,那么就把这个环都回收了。
-
every time a new link is added use a cycle detection algorithm

File System Mounting¶
A file system must be mounted before it can be accessed.
- mounting links a file system to the system, usually forms a single name space.
- the location of the file system being mounted is call the mount point.
- a mounted file system makes the old directory at the mount point invisible.
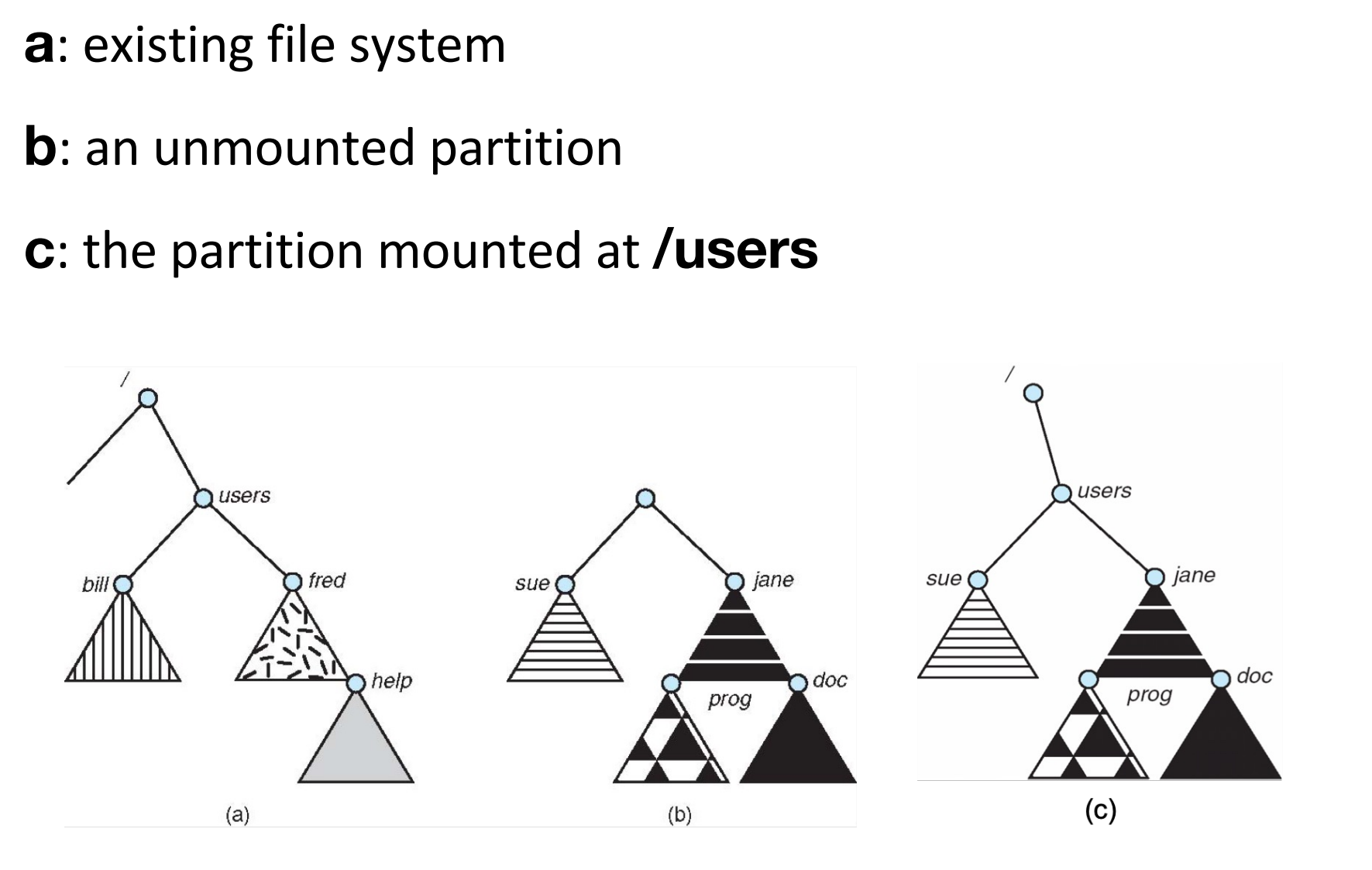
Mounting a file system

File Sharing¶
share 文件需要有一定的保护。
-
User IDs identify users, allowing protections to be per-user.
允许某些用户访问。
-
Group IDs allow users to be in groups, permitting group access rights.
允许某些组的用户访问。
在分布式系统里,文件可以通过网络来共享。
Protection¶
文件的所有者 / 创建者应该能控制文件可以被谁访问,能被做什么。
Types of access
- read, write, append
- execute
- delete
- list
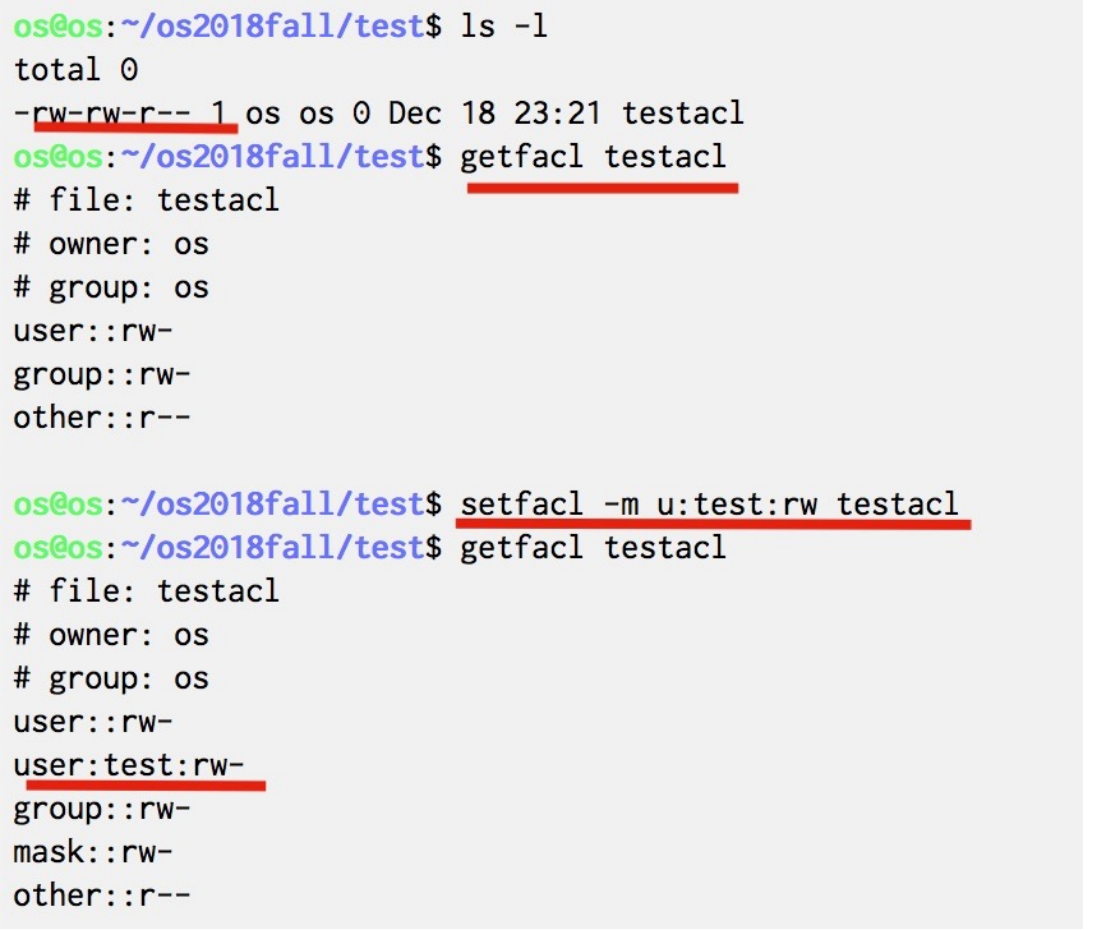
给每个文件和目录维护一个 Access Control List (ACL),指定每个用户及其允许的访问类型。 优点是可以提供细粒度的控制,缺点是如何构建这个列表,以及如何将这个列表存在目录里。
Unix Access Control

Example
Takeaway¶
!! Summary "Takeway" * File system * File operations * Create, open, read/write, close * File type * File structure * File access * Directory structure * Single level, two-level, tree, acyclic-graph, general graph * Protection * ACL
- How to use file system?
- How to use file?
- How to use directory?
- How to implement file system?
- How to implement file?
- How to implement directory?