I/O Systems¶
约 649 个字 8 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Overview¶
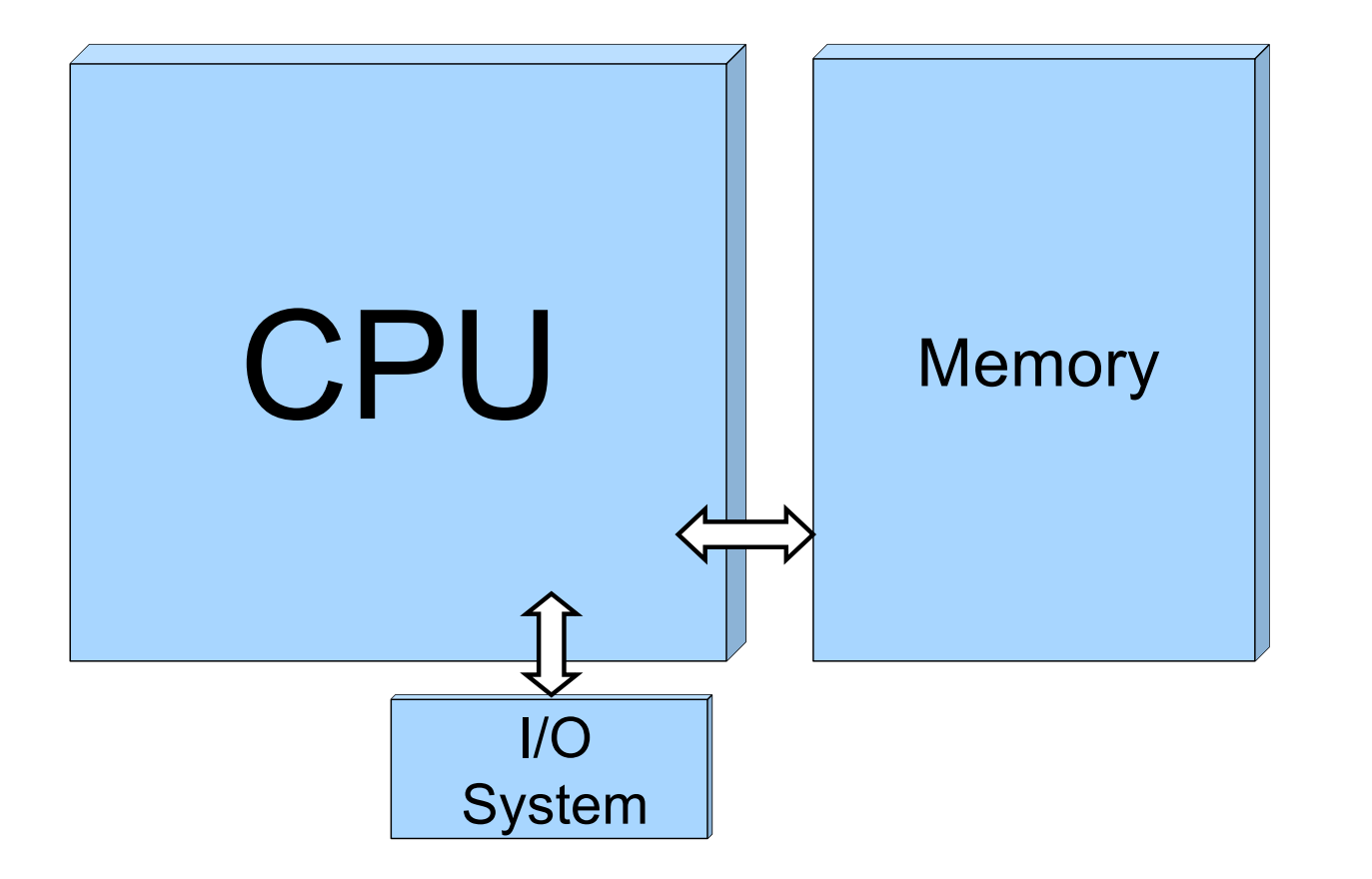
I/O management is a major component of OS design and operation.
- important aspect of computer operation
-
I/O devices vary greatly
IO 设备差异很大,如网卡、鼠标键盘、显示器。
-
new types of devices frequently emerge
下图里除了处理器和内存,均是外设。

I/O Hardware¶
Common concepts: signals from I/O devices interface with computer
-
bus
用来做设备和 CPU 的互连。
-
port
- controller
I/O access can use polling or interrupt.
-
Some CPU architecture has dedicated I/O instructions.
如 x86 里有
in,out。 -
Devices are assigned addresses for registers or on-device memory
-
direct I/O instructions
扩展性差,现在使用的少。
-
memory-mapped I/O
把外设映射到内存地址空间,这样就可以用内存访问指令来访问外设。
-
Polling¶
CPU 主动询问设备,是否需要服务。
For each I/O operation:
-
busy-wait if device is busy (status register)
- Cannot accept any command if busy
-
send the command to the device controller (command register)
- read status register until it indicates command has been executed
- read execution status, and possibly reset device status
Polling requires busy wait.
busywait 需要锁,会 sleep。所以如果设备很快那么轮询是合理的;如果设备很慢那么会很低效。
Interrupts¶
Interrupts can avoid busy-wait
- device driver (part of OS) send a command to the controller (on device), and return
- OS can schedule other activities
- device will interrupt the processor when command has been executed
- OS retrieves the result by handling the interrupt
Interrupt-based I/O requires context switch at start and end.
如果中断发生的频率很高,那么上下文切换会浪费很多 CPU 时间。

- Interrupt is also used for exceptions
- protection error for access violation
- page fault for memory access error
- software interrupt for system calls
- Multi-CPU systems can process interrupts concurrently
- sometimes a CPU may be dedicated to handle interrupts
- interrupts can also have CPU affinity
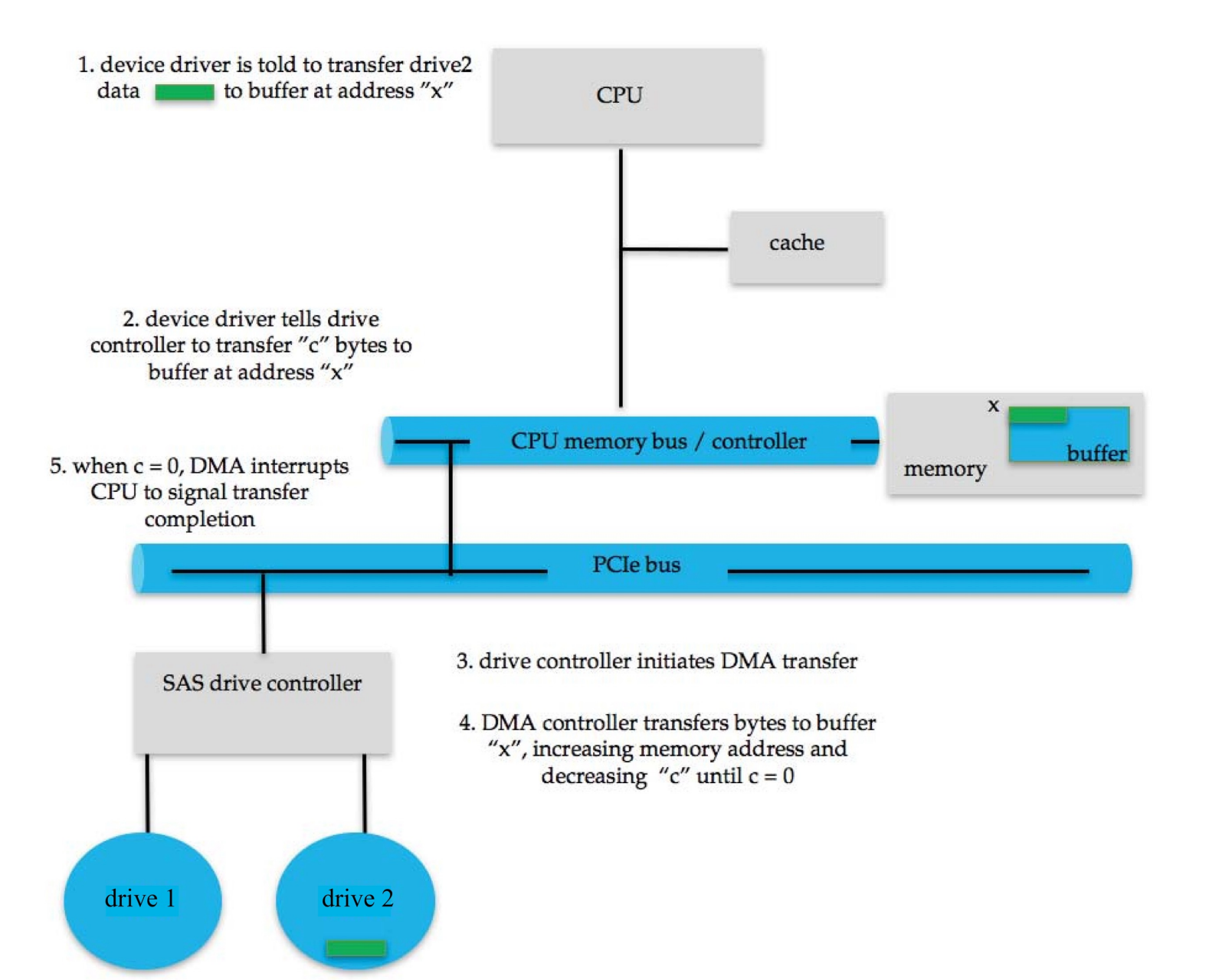
Direct Memory Access¶
DMA transfer data directly between I/O device and memory.
GPU 访问内存也算 DMA,只要不经过 CPU 就算。
Application I/O Interface¶
I/O system calls encapsulate device behaviors in generic classes.
- in Linux, devices can be accessed as files; low-level access with
ioctl.
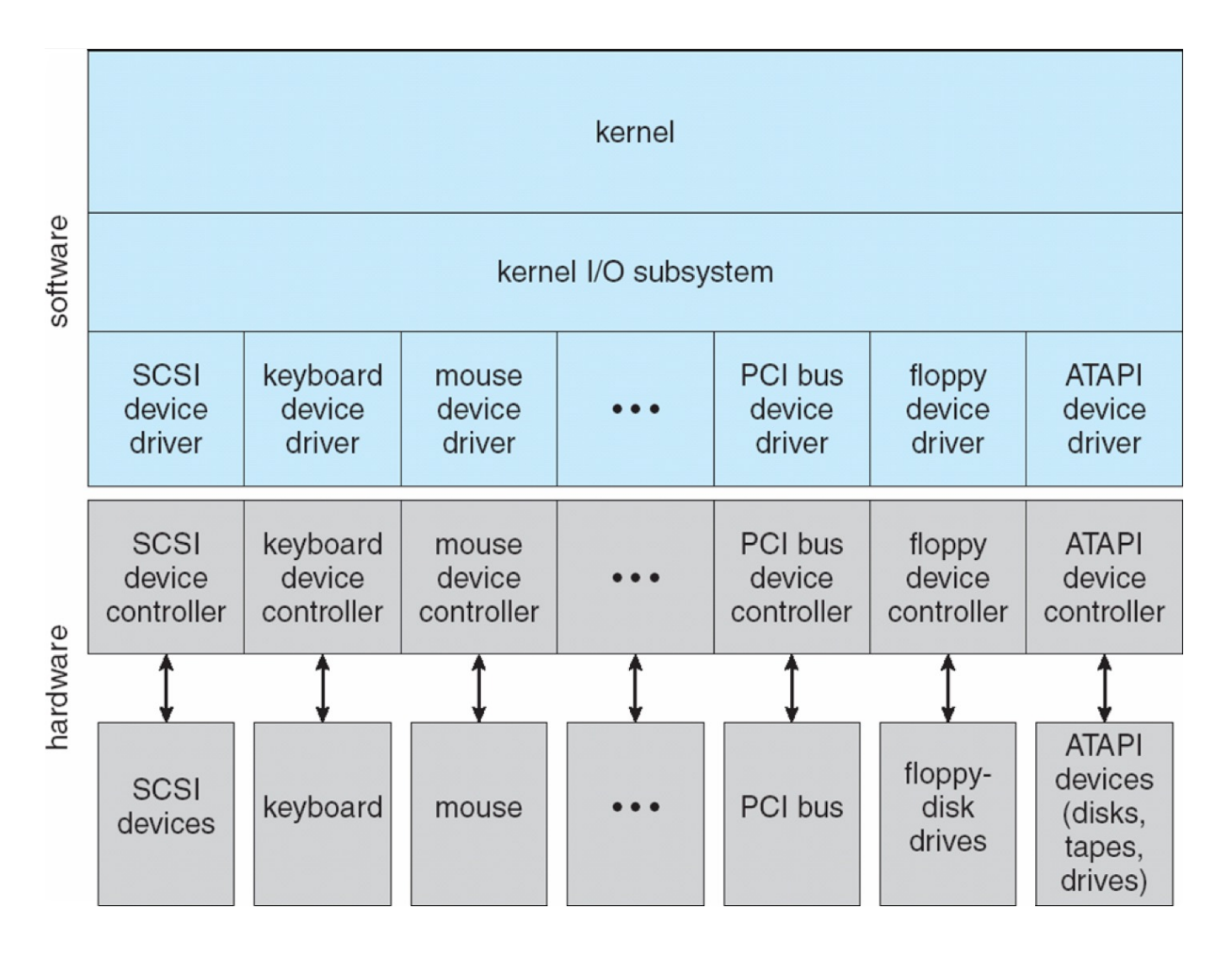
Device-driver layer hides differences among I/O controllers from kernel.
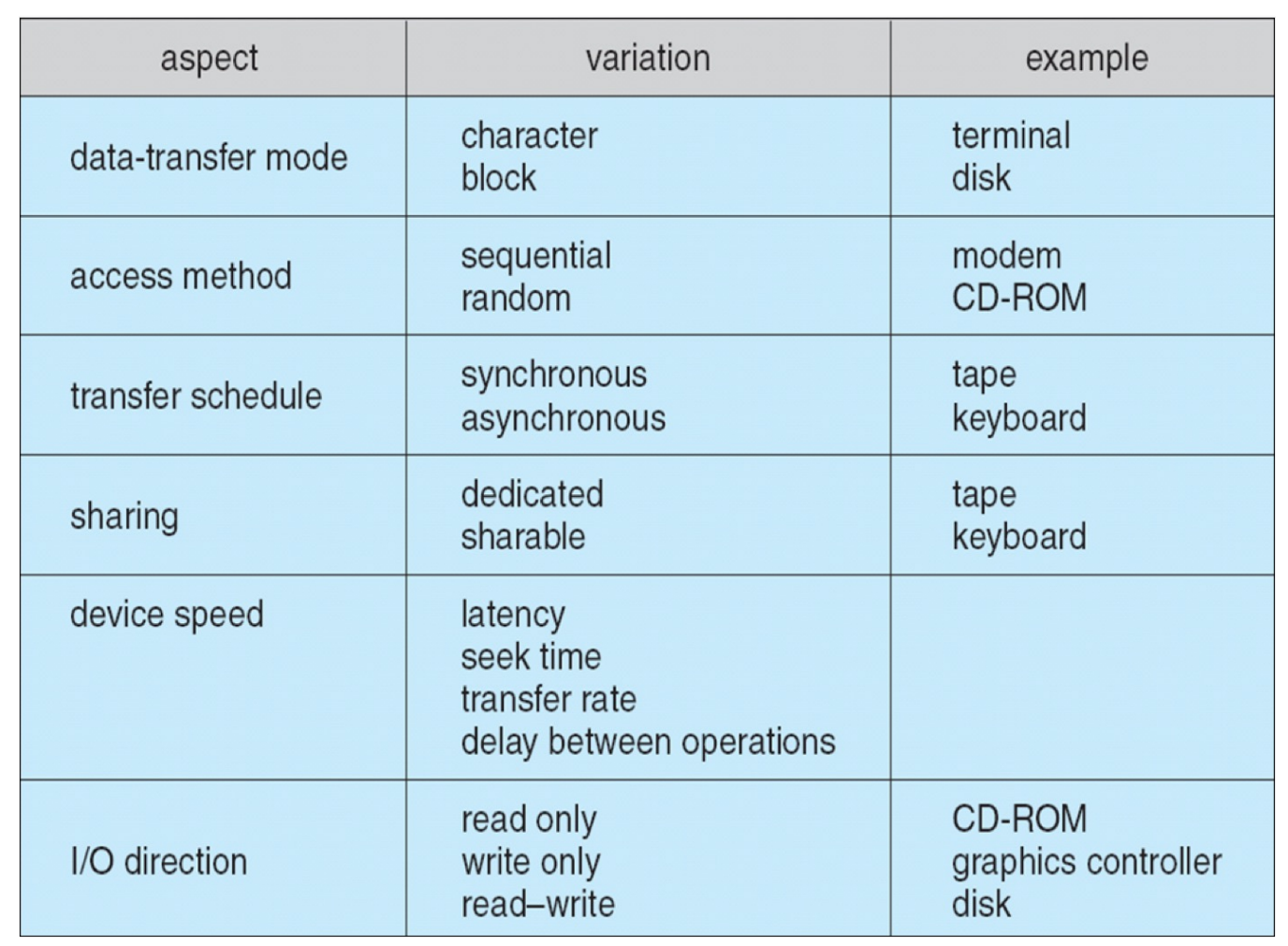
Devices vary in many dimensions
如果想对设备发起控制、命令,会使用 ioctl 这个系统调用。
设备可以被大致分为:
-
Block and Character Devices
以块为单位访问数据。支持 read, write, seek 操作。可以通过内存映射访问,也有 DMA。
其中 character I/O 指逐个字节传输(Stream
) 。 -
Network Devices
socket
-
Clocks and Timers
provide current time, elapsed time, timer.
-
memory-mapped file access
Kernel I/O Subsystem¶
- I/O scheduling
- Buffering - store data in memory while transferring between devices.
- Caching: hold a copy of data for fast access.
- Spooling: A spool is a buffer that holds the output (device’s input) if device can serve only one request at a time.
- Device reservation: provides exclusive access to a device.
- OS needs to protect I/O devices.
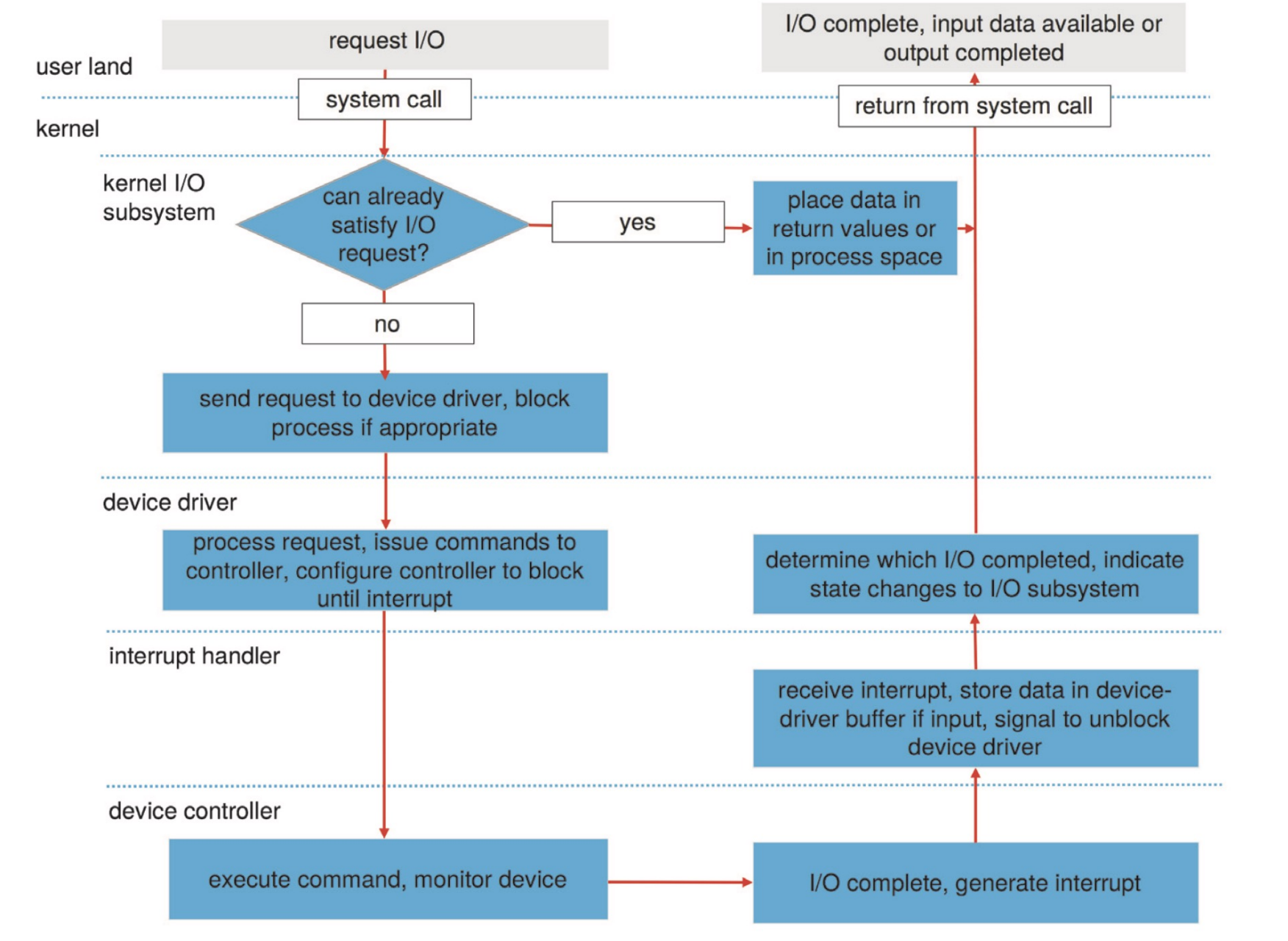
Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations¶
Performance¶
I/O is a major factor in system performance.
Improve Performance
- Reduce number of context switches
- Reduce data copying
- Reduce interrupts by using large transfers, smart controllers, polling
- Use DMA
- Use smarter hardware devices
- Balance CPU, memory, bus, and I/O performance for highest throughput
- Move user-mode processes / daemons to kernel threads