Inter-Process Communication¶
约 675 个字 4 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Processes within a host may be independent or cooperating.
Reasons for cooperating processes:
- Information sharing
- Computation speedup
- Modularity
- Convenience
进程保护的太好了,需要有互相通信的手段。
Models of IPC
- Shared memory
- Message passing
- Signal
- Pipe
- Socket
IPC Communication Models¶
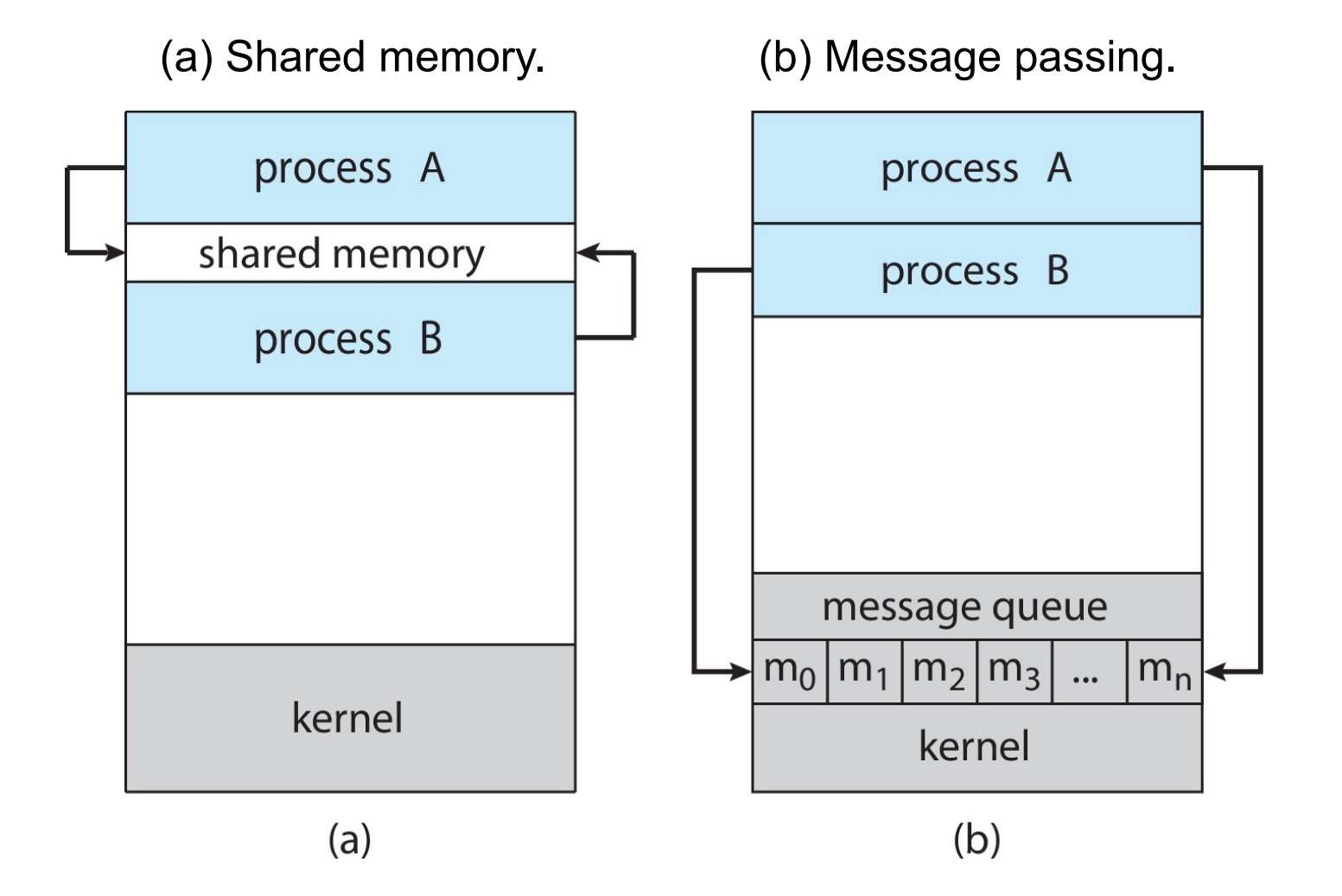
- Message-passing
需要内核空间支持- useful for exchanging small amounts of data
- simple to implement in the OS
- sometimes cumbersome for the user as code is sprinkled with send/recv operations
- high-overhead: one syscall per communication operation
- Shared memory
非内核空间- low-overhead: a few syscalls initially, and then none
- more convenient for the user since we’re used to simply reading/writing from/to RAM
- more difficult to implement in the OS
Shared Memory¶
Processes need to establish a shared memory region.
producer/consumer example

Example

ipcs -a 可以查看当前 IPC 的状态。
存在问题:不安全。任何人拿到 share_id 都可以把共享内存 attach 到自己进程上,可以观察到其他进程的数据、甚至做 DOS 攻击。
而且很 cubersome,会发生各种 error 需要处理
Message Passing¶
Two fundamental operations:
- send: to send a message (i.e., some bytes)
- recv: to receive a message
If processes P and Q wish to communicate they
-
establish a communication “link” between them
This “link” is an abstraction that can be implemented in many ways (even with shared memory!!)
-
place calls to
send()andrecv() - optionally shutdown the communication “link”
Implementing Message-Passing¶
Implementation of communication link
- Physical:
- Shared memory
- Hardware bus
- Network
-
Logical:
-
Direct or indirect
-
Direct
有一个 P 和 Q,直接发信息。如果有 n 个进程,需要建立 \(C_2^n\) 个连接。
-
Indirect
有一个 mailbox,发信息相当于发给一个 mailbox。如果有多个进程,我们需要确定是由哪个进程接收信息。
-
-
Synchronous or asynchronous
-
Synchronous: Blocking is considered synchronous
即我们发信息,如果接收者没收到信息,发送者就堵塞着不走;我们收信息,如果发送者没有发送信息,接送者就堵塞着不走。
-
Asynchronous: Non-blocking is considered asynchronous
- 异步效率更高,同步时效性更高。
- Automatic or explicit buffering
- Zero capacity - no messages are queued on a link. Sender must wait for receiver.
- Bounded capacity - finite length of n messages. Sender must wait if link full.X
- Unbounded capacity - infinite length. Sender never waits.
-
-
Pipes¶
-
Ordinary pipes
没有名字,只能通过
fork()来传播。- Producer writes to one end (the write-end of the pipe)
- Consumer reads from the other end (the read-end of the pipe)
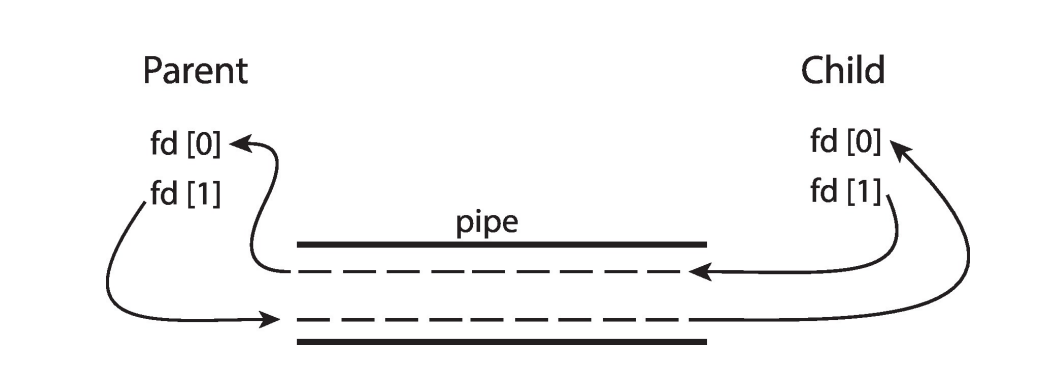
注意
fd[0]是 read-end,fd[1]是 write-end(对于双方都是) -
Named pipes
可以把名字通过网络 / 文件传播,这样就能交互
。 (可以使用mkfifo创建 named pipes)
In UNIX, a pipe is mono-directional.
要实现两个方向一定需要两个 pipe。
Client-Server Communication¶
广义上的 IPC,因为是跑在两个物理机器上的交互。
- Sockets
-
RPCs
所有的交互都是和 stub 通信,stub 会和远端的 server 通信。 存在网络问题,如丢包。
-
Java RMI
RPC in Java
Takeaway¶
Takeaway
- Communicating processes are the basis for many programs/services
- OSes provide two main ways for processes to communicate
- shared memory
- message-passing
- Each way comes with many variants and in many flavors
- Signals, Pipes, Sockets, RPCs, RMIs, etc.