Placement¶
约 2047 个字 29 行代码 21 张图片 预计阅读时间 7 分钟
Abstract
- Introduction
- Random Placement
- Simulated Annealing
- Analytic Placement
- Cost Function
- Calculation
- Recursive Partitioning
- Placement Legalization
- Placement in Practice
Introduction¶
- netlist: connected gates + wires in your technology.
- Floorplanning 过后,我们已经有一个布局图,里面有 pre-placed blocks,现在要做的是把 std cells 的具体位置确定下来。
-
Chip Size
-
在实际设计中,small cells 占主导地位。因此我们通常将芯片大小看作 equivalent small gates,大的 hard macro 可以被认为是很多个小门。因此当我们说芯片大小时,我们通常指的是 small gates 的数量。
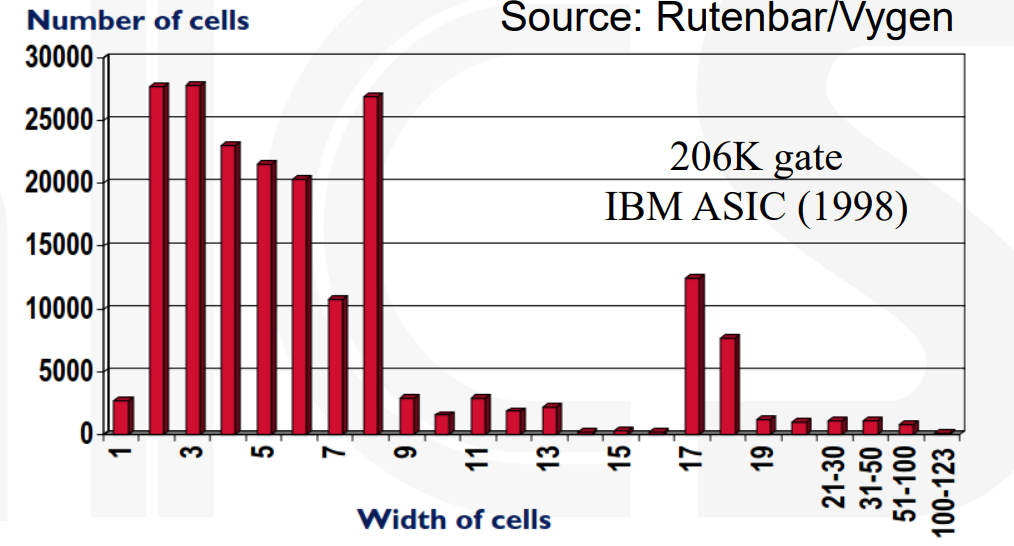
-
Instances 是我们要 placement 的对象,经验得到 Instances 约为 #Gates / 4..5
Gates == Equivalent NAND2 gates
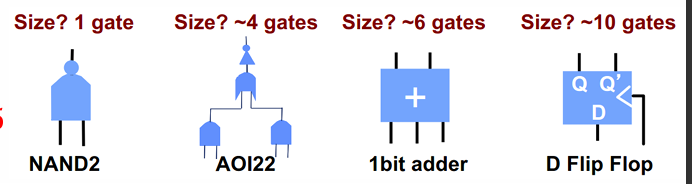
-
-
Placement
-
Placement is the stage of the design flow, during which each instance (standard cell) is given an exact location.
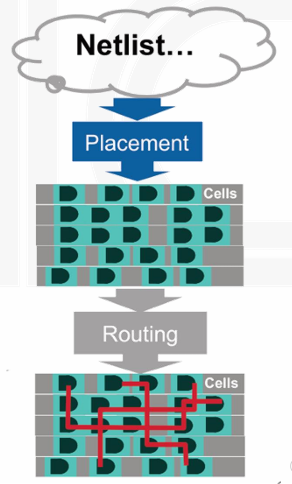
-
输入是 netlist,floorplan 和 technology constraints,输出是 all cells located in the floorplan。
- Goal:
- Provide legal location of entire netlist
- Enable detailed route of all nets
- Meet timing, area, and power targets
-
-
Placement Flow
- 通常大部分 EDA 工具会将 Placement 任务划分为两个阶段:
- Global placement,快速地将设计中的所有 cell 分配到芯片上的各个区域或 bin 中,目标是尽量减少不同区域之间的连接。
- Detailed placement,为每个 instance 提供一个合法的位置,同时尽量最小化 wirelength(或者其他目标
) ,尽量保证 uncongested。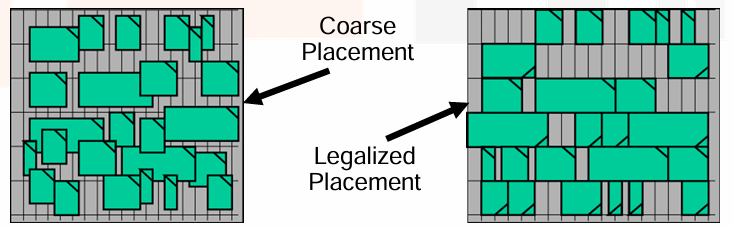
- 通常大部分 EDA 工具会将 Placement 任务划分为两个阶段:
Info
为什么我们需要在 Placement 阶段重点关注 wirelength?这就有点像综合重点会关注时序,明明后续有静态时序分析工具。布局也是类似的,其需要为后续的 router 服务,其一般内部有一个简化版的 router 估计工具,其目的最核心的在于没有违反电路规则的情况下,最小化互连线的长度。这也是 Placer 最核心的出发点,其基于这个出发点进行布局。
Random Placement¶
- Problem Formulation
- Given a netlist, and fixed-shape cells (small, standard cell), find the exact location of the cells to minimize area and wire-length
- row-based, no hard-macros
- Modules
- Usually fixed, equal height (exception: double height cells)
- Some fixed (I/O pads)
- Connected by edges or hyperedges
-
Simple Placer
-
假设简单的网格(方形,pin 在边上固定
) 。所有的 gate 大小都相同,网格的每个格子可以放一个 gate。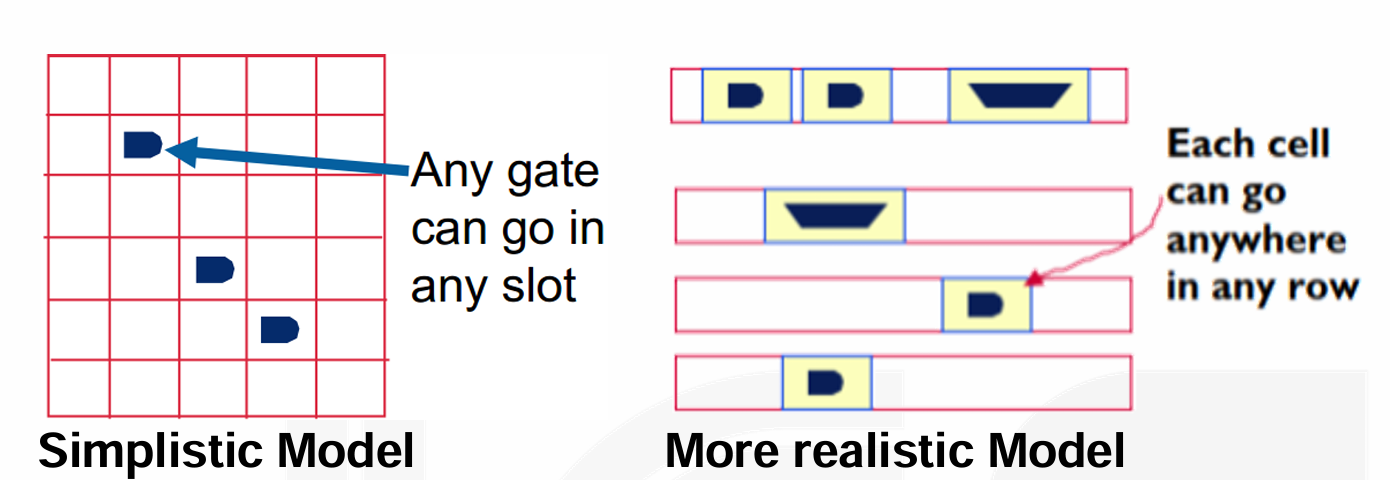
-
bounding box wirelength estimator: Half-Perimeter Wirelength (HPWL),其核心思想在于找一个最小的矩形框,把所有的 point 给包住,基于这个矩形框,我们就可以评估相应的 net 长度了。
- HPWL 是实际 wirelength 的下界,主要特点是简单、评估快、和实际布线长度误差 10% 左右。
HPWL
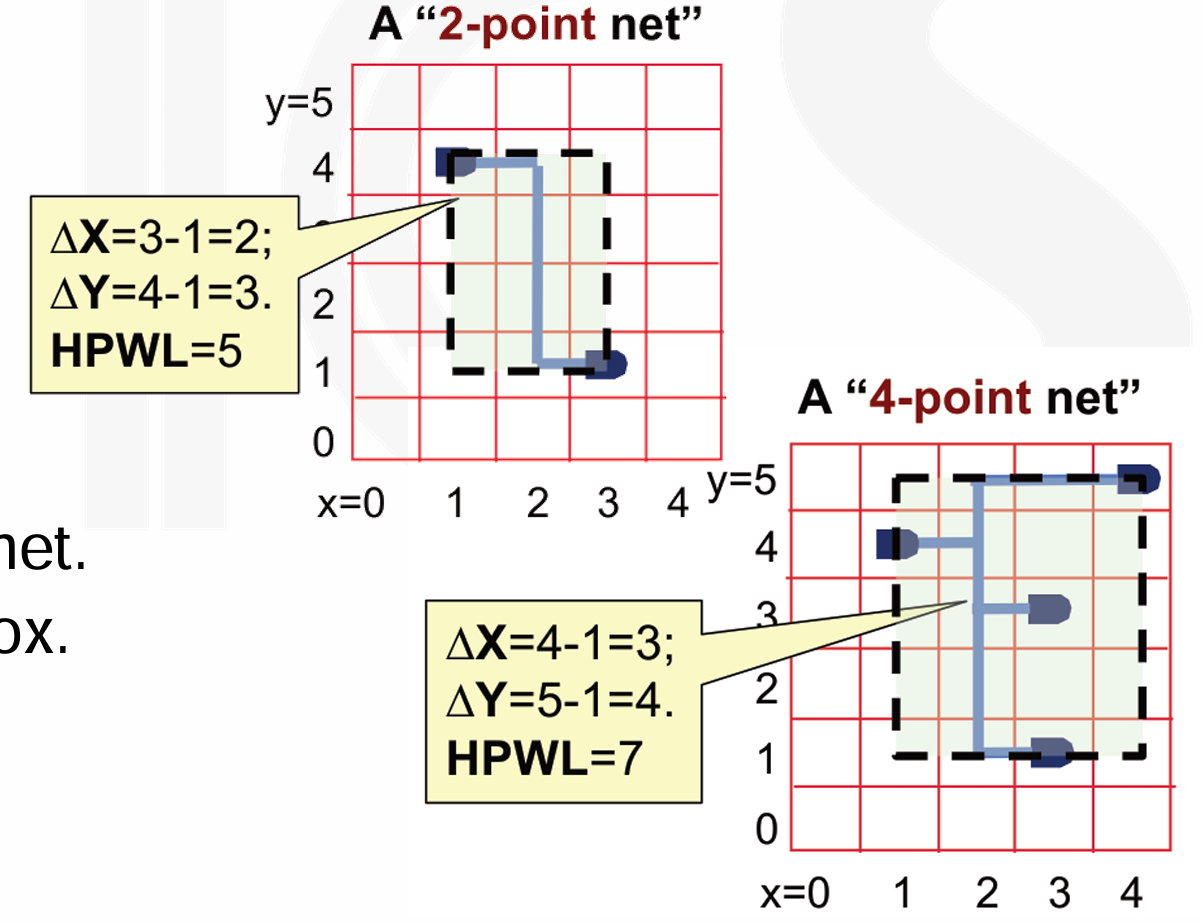
Net
在 Layout 中,我们把线叫做 net,这些线是 netlist 的一部分。netlist 就是映射在具体工艺上的 gates+wires。我们根据这些 net 连接了多少个东西,称其为 “x-point net”。比如上图中的 2-point net 和 4-point net。
在 VLSI 中,走线都必须是 XY 两个方向的,也就是不能像散落的绳子一样,随意拐弯。
-
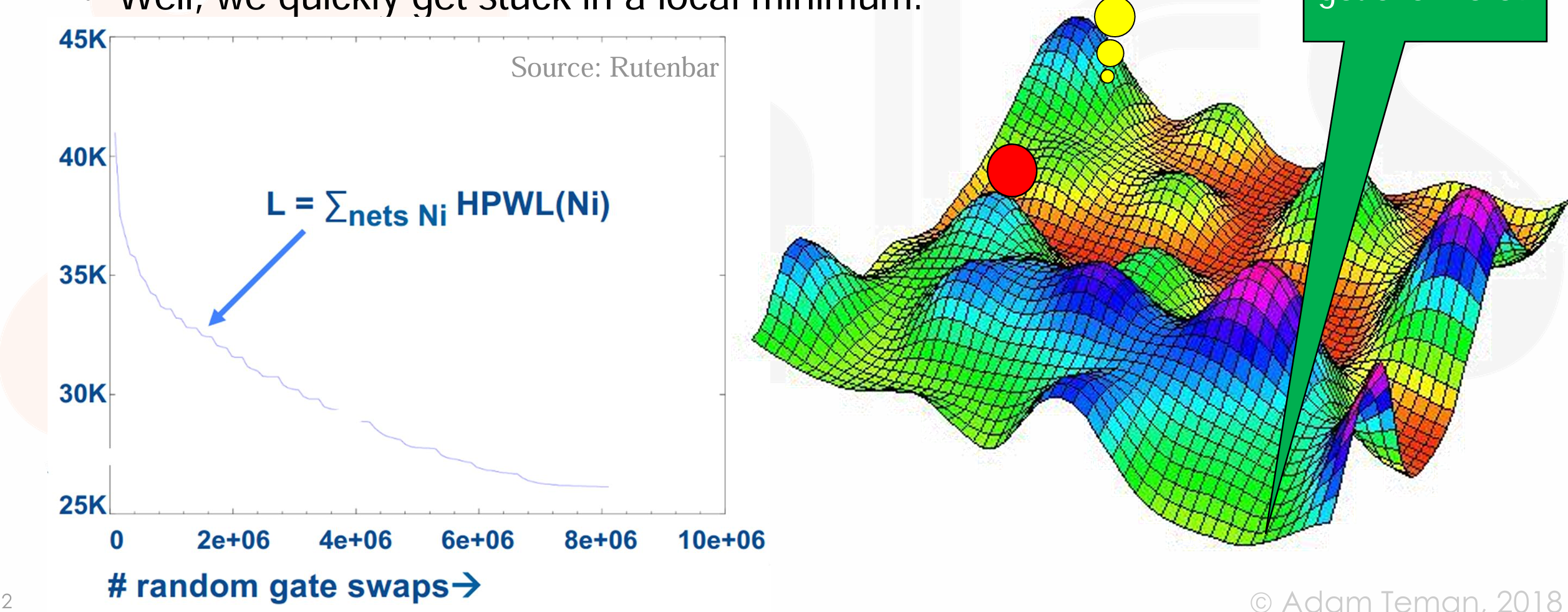
Algorithm: 随机选取一对门,尝试交换,如果 wirelength 减少则保留 swap,否则撤销。直到 wirelength 停止减少。
// Random initial placement foreach(gate Giin netlist) place Giin random (x,y) not occupied. // calculate initial HPWL L=0 foreach(net Niin netlist) L= L+ HPWL(Ni) // random iterative improvement while (overall HPWLis improving) pick two random gates Gi, Gj swap Giand Gj evaluate ΔL= new HPWL–old HPWL if (ΔL < 0) then keep the swap if (ΔL > 0) undo the swap -
问题:容易陷入局部最优。
-
-
Simulated Annealing 模拟退火
- Idea: 晶格的最低能态是当所有原子排列整齐时。因此如果我们有一个混乱的晶体,要先加热让他能四处移动,随后慢慢冷却,最终能找到最低能态。
-
Algorithm: 随机交换,如果 HPWL 减少则保留,否则以一定概率保留(与温度有关
) ,如果 HPWL 降低了就降低温度。 -
SA 不能找出最优结果,但是很好地避免了局部最优,很多 EDA 算法会利用 SA。每次运行的结果可能不同,NOT how placer work today.
Analytic Placement¶
- Analytic Placement 是将布局问题转化为一个数学优化问题,通过求解成本函数的最小值来确定电路元件的最佳位置。这种方法的关键在于将成本函数表达为电路元件坐标的函数,并利用数学工具(如微积分)来找到这个最小值。
Cost Function¶
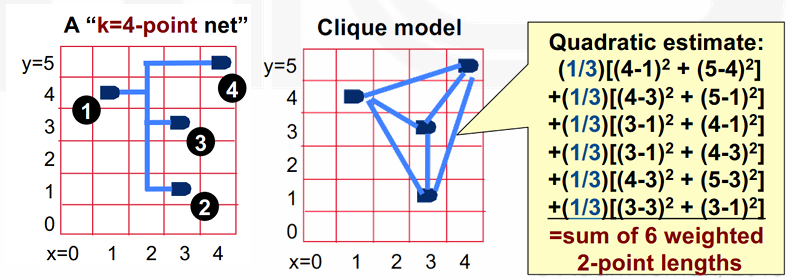
- HPWL 不可微,因此这里我们定义了一个新的线长模型,Quadratic wirelength \(L=(x_1 - x_2)^2 + (y_1 - y_2)^2\).
- 对于 \(k\) 个点,我们使用全连接团模型,即任意两个门之间都有一个连接,共 \(k(k-1)/2\) nets。
- 为了补偿这种模型的偏差,我们可以通过将每个新网络的权重设为 \(1/(k-1)\) 来进行调整。
-
注意这里的 gates 都是 dimensionless 无量纲。
Example
Calculation¶
-
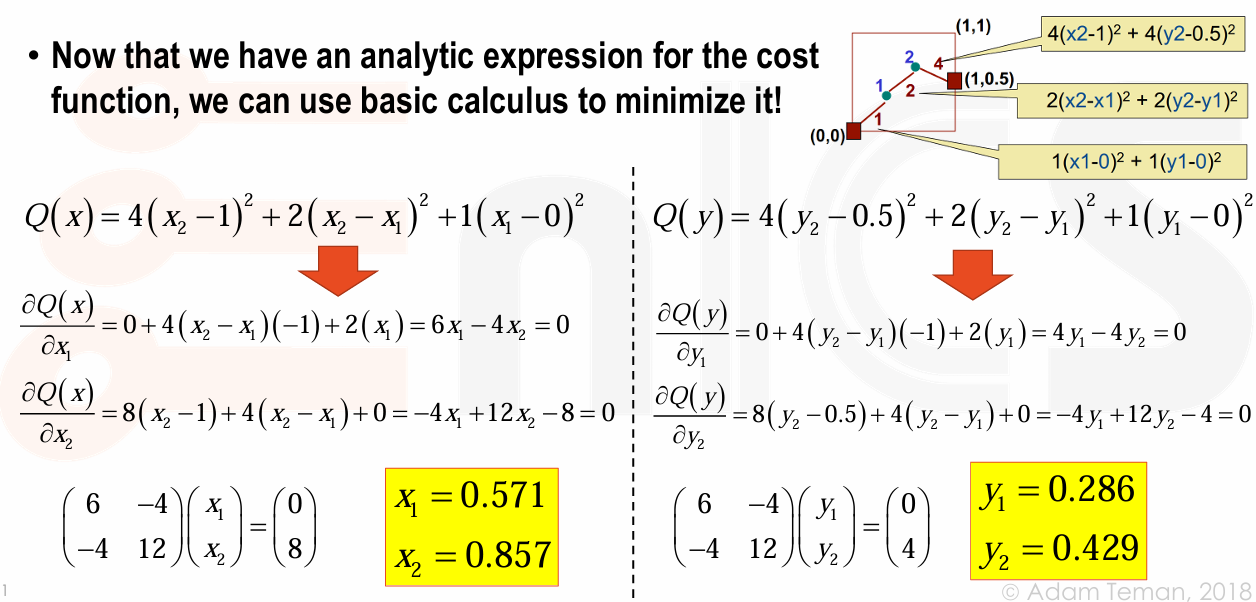
假设 point 坐标 \((x_i,y_i)\)(未知
) ,net 有预先定义好的权重 \(w_i\),pads 是固定在边上的 pins。Example
看到 x 和 y 是没有交叉项的,因此分开计算。通过偏导求得相应的局部最优解。
-
观察到,使用二次线长模型进行布局时,电路元件(点)会被放置在一条直线上,这样的布局可以最小化弹簧权重,即权重较大的连接会有较短的线长。
-
代数上,可以通过下面的方式来构造矩阵:
- connectivity matrix C, \(C_{i,j}=C_{j,i}=\left\{\begin{matrix} 0,& i=j \\ 0,& \text{no net}_{i,j} \\ w_{i,j},& \text{net}_{i,j} \end{matrix}\right.\)
- A matrix, \(A_{i,j}=\left\{\begin{matrix} \sum\limits_{j}^NC_{i,j} + w_{j, pads},& i=j \\ C_{i,j},& i\neq j \end{matrix}\right.\)
- b vector, \(b_{x,i} = \left\{\begin{matrix} w_ix_i,& \text{pad}(x_i,y_i,w_i) \\ 0,& \text{no pad} \end{matrix}\right., b_{y,i} = \left\{\begin{matrix} w_iy_i,& \text{pad}(x_i,y_i,w_i) \\ 0,& \text{no pad} \end{matrix}\right.\)
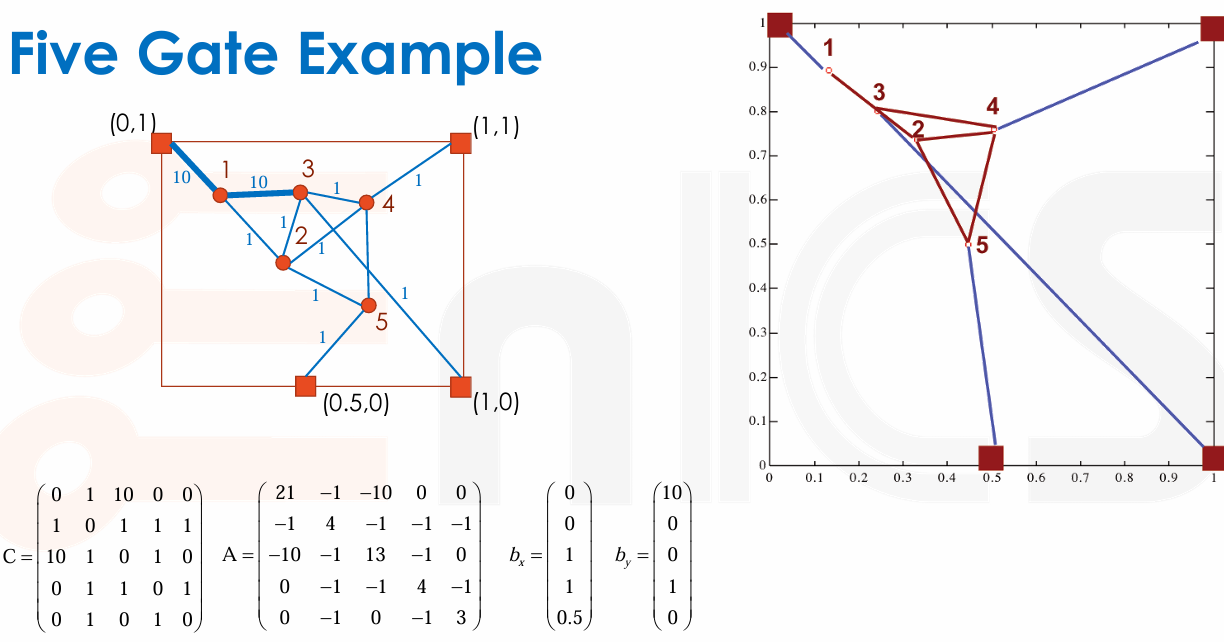
Five Gate Example
Recursive Partitioning¶
-
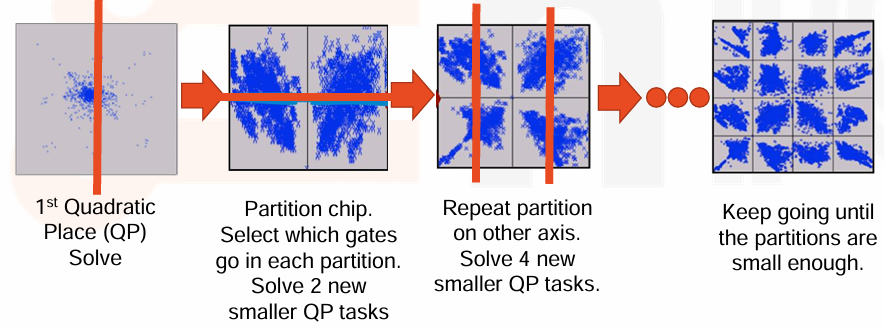
Problem – Gate Clustering
- 使用二次线长会导致一个问题,即所有的门电路都想要放在同一个地方,不能充分利用布局。
-
解决方法就是 Recursive Partitioning,将整个电路分成多个子部分,然后对每个子部分进行单独布局。这些子部分可以进一步划分,直到每个子部分的大小和复杂性适合进行有效的布局。
-
Recursive Partitioning
- Partition
- Divide the chip into new, smaller placement tasks.
- Divide it in half!
- Assignment
- Assign gates into new, smaller region.
- Sort the gates and distribute to each half,排序后将其中一半分配给一个区域,另一半分配给另一个区域。
- Containment
- Formulate new QP matrix that keeps gates in new regions,即重新计算 placement 矩阵。
- Create “pseudo pads”
- Every gate and pad NOT inside the partition R is modeled as a pad on the boundary of R,为了确保不会有任何一个 gate 被放在 partition 之外,我们会在 partition 的边界上放置若干 pseudo pad。
- Propagate the pseudo pads to the their nearest point on R.
Example
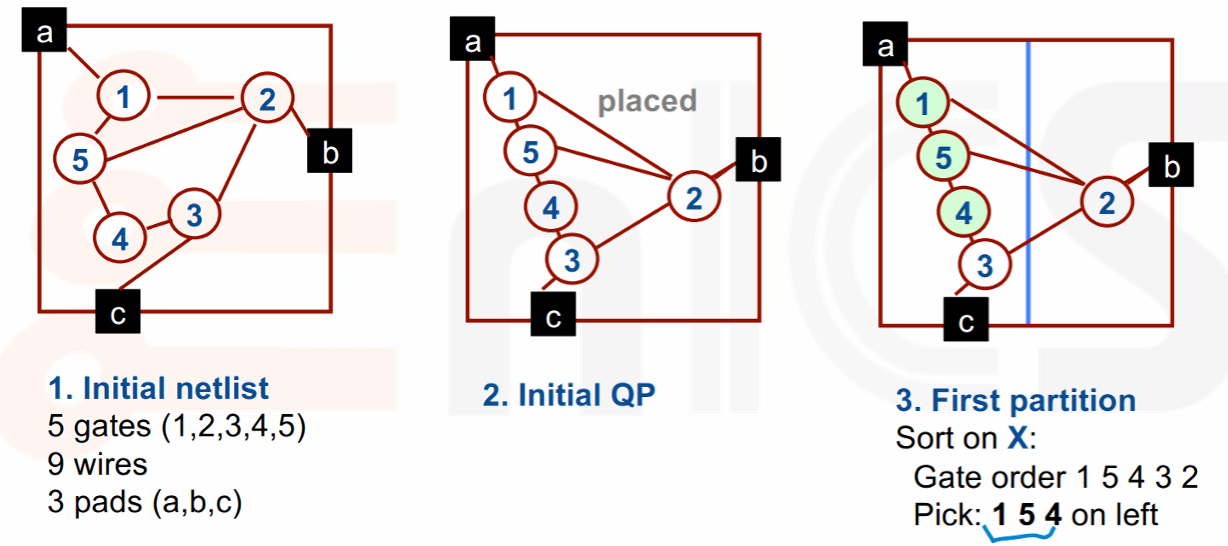
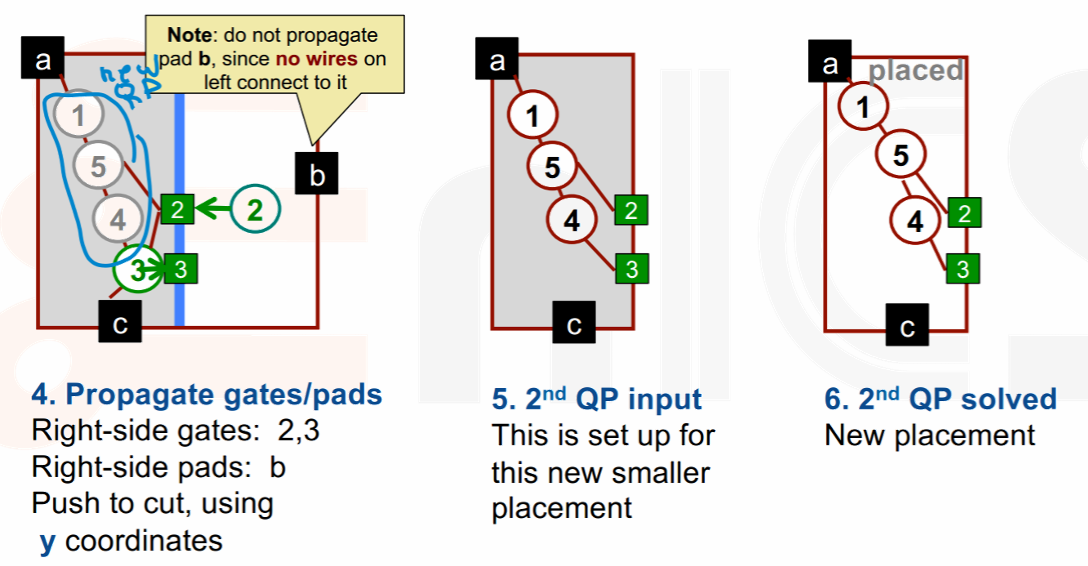
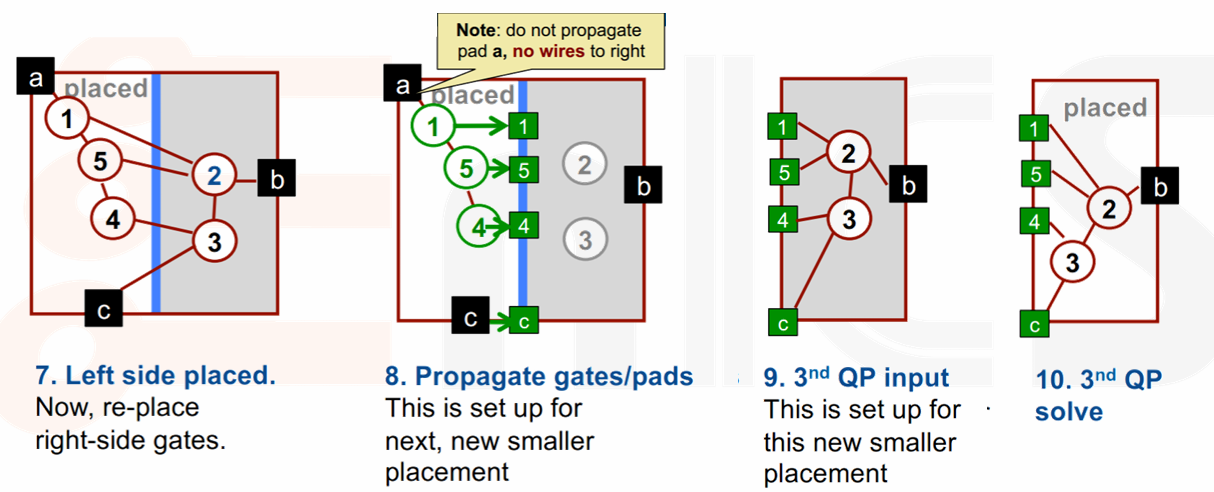
- Partition
Placement Legalization¶
- 通常我们会一直递归划分,直到每个区域只有很少量的 gates (10-100),但是在这些区域里可能还是有 overlap。
- 在实际的布局中,我们需要让门摆放在 precise rows 上,这就是 legalization。
- 比如某个实例 Q 的坐标是(1.3, 5.2
) ,他可能需要对齐到行,变成(1.3,5) 。 - 可以使用 SA 来做这件事。
- 比如某个实例 Q 的坐标是(1.3, 5.2
Placement in Practice¶
- 之前都是基于 wirelength 最小化的优化目标,实际上还要考虑 timing 和 congestion,以及后续的时钟树和功耗优化。
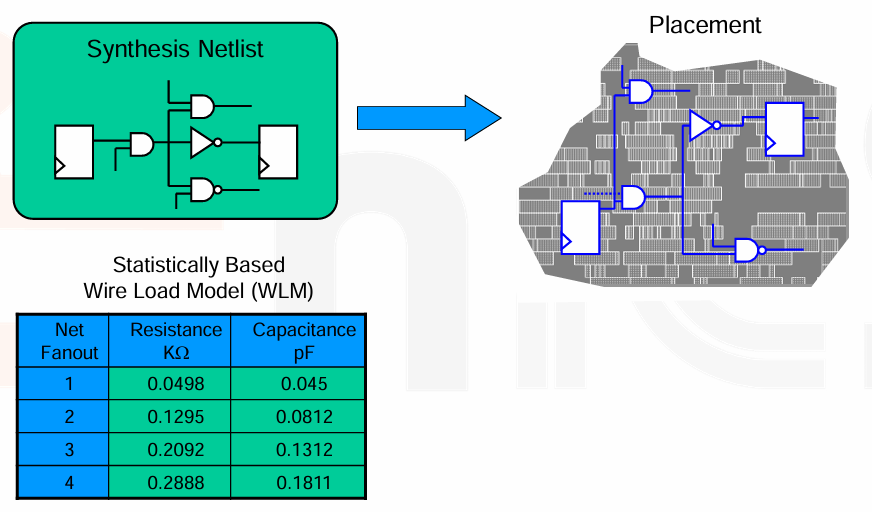
Timing-Driven Placement¶
- 尝试将 critical path 相关的 cell 放在一起,从而减少相关的 net RC 参数,进而优化时序。
- RCs 是基于 Virtual Route (VR),即不考虑 layers 和 via 的因素。
Congestion-Driven Placement¶
-
Congestion
-
Congestion occurs when the number of required routing tracks exceeds the number of available tracks,某些实例附近连线太多,导致 tracks 不够用。
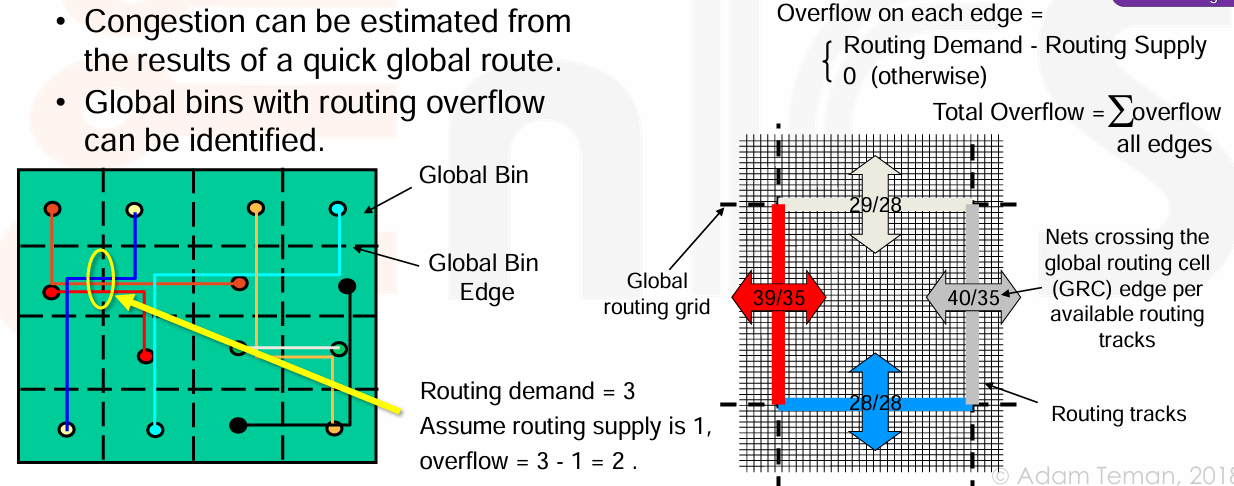
-
如果 congestion 不是很严重,实际布线可以通过 detour 的方式(即从旁边绕行
) ,但这样会导致使用 VR 估计的 RC delay 更加不准确。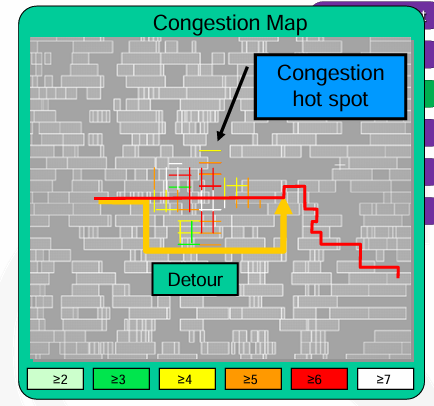
-
在 congestion 严重的区域可能会导致布线失败。
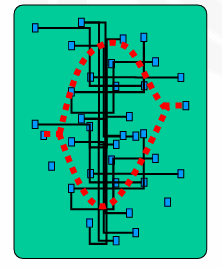
-
-
Congestion Reduction
- The tool tries to evaluate congestion hotspots and spread the cells (lower utilization) in the area to reduce congestion.
-
The tool can also choose cell location based on congestion, rather than wire-length.
Example

-
Strategies to Fix Congestion, 修改布局
- Mark areas for low utilization,降低利用率这样可以减少 congestion。
- Top-level ports
- Changing to a different metal layer
- Spreading them out, re-ordering or moving to other sides
- Macro location or orientation,macro 和 port 是 placement 前固定的锚点。
- Alignment of bus signal pins
- Increase of spacing between macros
- Add blockages and halos
- Core aspect ratio and size
- Making block taller to add more horizontal routing resources,这样可以有更多 track。
- Increase of the block size to reduce overall congestion
- Power grid
- Fixing any routed or non-preferred layer
Placement in Innovus¶
