STA¶
约 2498 个字 13 行代码 20 张图片 预计阅读时间 8 分钟
Abstract
- Sequential Clocking
- Static Timing Analysis
- Design Constraints
Sequential Clocking¶
- 绝大部分数字电路都采用 Synchronous 同步电路的设计方法,使用 Sequential Elements 时序元件。同步设计消除了竞争,同时可以通过流水线提高吞吐。
- 这里假定所有的寄存器都是 D-Flip Flops,时钟上升沿触发。
-
Timing Paramters
-
\(t_{cq}\),从时钟边沿到数据输出的时间(从 D 到 Q 端)
Timing Diagram
注意 tcqLH 和 tcqHL 不一定相同(这里我们不区分
) ,一般从上升 / 下降 50% 时开始计时。
-
\(t_{setup}\),在时钟上升沿到来之前,数据需要提前到达一段时间,以确保正确采样。
Timing Diagram

-
\(t_{hold}\),在时钟上升沿到来之后,数据需要保持一段时间,以确保正确采样。
Timing Diagram

-
-
Timing Constraints
- 在同步逻辑中,有两个主要问题:
- Max Delay:数据不能在下一个时钟上升沿之前从一个寄存器到另一个寄存器。原因是 slow data path,也称为 Setup path。
- Min Delay:数据在相同的时钟周期内会通过多个寄存器。原因是 short data path,也称为 Hold path。
-
Setup (Max) Constraint \(t_{launch} < T + t_{capture}\)
-
数据必须在下一个时钟上升沿的建立时间之前,到达下一个寄存器的 D 端。我们将其称为发射和捕获。

-
可以划分为两条路径。一个是 Capture Path 捕获路径,一个是 Launch Path 发射路径。

注意这里加上了 clock skew,即第二个时钟到达的时间晚于启动时钟到达时间的时间差。
-
决定了最大频率,如果发现 setup 失败,我们可以减慢时钟(即延长周期)
-
-
Hold (Min) Constraint \(t_{launch} > t_{capture}\)
-
此时两个寄存器看到的都是同一个时钟上升沿,出现 hold 违例的关键在于数据到的太快了,下一个寄存器要在新的数据到来之前把上升沿时的数据保存(需要 \(t_{hold}\) 时间
) 。
-
可以得到下面的公式,其本质就是描述数据到 D 的时间和时钟到 CLK 的时间的关系:

-
与时钟周期无关,如果出现 hold 违例,you can throw your chip away!
-
-
关键是看两个路径,一个是数据什么时候到寄存器 D 端(launch path
) ,一个是时钟上升沿什么时候到寄存器的时钟端口(capture path) 。
- 在同步逻辑中,有两个主要问题:
Static Timing Analysis¶
- STA checks the worst case propagation of all possible vectors for min/max delays.
- 优点:快,exhaustive,不需要功能向量。
- 缺点:不检查电路功能正常性,需要定义时序要求 / 例外(如果定义错误,garbage in => garbage out
) 。 - 局限:只对同步设计有用,无法处理组合回环,不能处理异步事务,不检查毛刺等情况。
-
Timing Paths: A path is a route from a Startpoint to an Endpoint.
- Startpoint (SP): 触发器的时钟端口、输入端口(Primary Inputs, PI)
- Endpoint (EP): 触发器的输入端口(除了时钟
) 、输出端口(Primary Outputs, PO) ,内存 / 硬宏
Example
path 主要取决于 FF 的数量,同一个 FF 可以既作为 SP,又作为 EP(feedback path
) 。
-
Four categories of timing paths: reg2reg, in2reg, reg2out, in2out

-
Goals of Static Timing Analysis: 知道所有违背时序约束的路径、严重程度、以及它们的位置。
-
Algorithm
- 基本假设:设计是同步的,pin-to-pin delay model(即每个门有单个固定的延时
) ,以拓扑序的方式遍历电路(因此忽略了逻辑正确性) 。 -
路径表示:
- Vertices: Wires, 1 per gate output and 1 for each SP and EP
- Edges: Gates, input pin to output pin, 1 edge per input with a delay for each edge.
- 最后添加 Source/Sink 节点,添加 0 权重的边到每个 SP / 从每个 EP 出发。
Example

-
我们基于节点分析,找到相对于该节点最差的路径。
- Arrival Time at a node (AT): the longest path from the source to the node.
- Required Arrival Time at node (RAT): the latest time the signal is allowed to leave the node to make it to the sink in time.


Example
SLACK = RAT - AT,如果 SLACK < 0,说明路径违背了时序约束。沿着 SLACK 相同的点,即可得到 critical path。

- 基本假设:设计是同步的,pin-to-pin delay model(即每个门有单个固定的延时
-
False Path,即有些路径在逻辑上不会出现。我们需要手动设置。
Example
如下图,这里是两个 MUX,同时他们的选择信号是相反的,因此不会同时选择上面或者下面的路径。因此我们可以设置这两条路径为 False Path。

Design Constraints¶
- 综合工具是基于约束条件去做综合。这个约束条件需要我们自己提供,通常我们采用 SDC 语法。该语法是 TCL 语言的超集。
- Collections
-
SDC 中的 collection 和 TCL 中的 list 类似,但有所不同:collection 的元素本质上是指针,指向你想要的元素。想使用具体的元素,应该用下面的语法。

-
Design Objects¶
- Design: A circuit description that performs one or more logical functions (i.e. Verilog module).
- Cell: An instantiation of a design within another design (i.e. Verilog instance).
- Called an instin Stylus Common UI.
- Reference: The original design that a cell "points to" (i.e. Verilog sub-module)
- Called a modulein Stylus Common UI.
- Port: The input, outputor inoutport of a Design.
- Pin: The input, outputor inoutpin of a Cell in the Design.
- Net: The wire that connects Portsto Pins and/or Pinsto each other.
- Clock: Port of a Designor Pin of a Cellexplicitly defined as a clock source.
- Called a clock_treein Stylus Common UI.

- SDC helper functions
- 注意这里所有函数返回的是 collections,而不是 TCL lists。函数只会在综合之后生效(否则还没有端口信息
) 。 -
"get" & "all" commands:
[get_ports string] # returns all ports that match string [get_pins string] # returns all cell/macro pins that match string. [get_nets string] # returns all nets that match string. [all_inputs] # returns all the primary inputs (ports) of the block. [all_outputs] # returns all the primary outputs (ports) of the block. [all_registers] # returns all the registers in the block.
- 注意这里所有函数返回的是 collections,而不是 TCL lists。函数只会在综合之后生效(否则还没有端口信息
Clock Definitions¶
- 涉及到时钟的信号一定要声明好,否则会被视为普通信号,从而不会进行相应的时序分析。
- 定义时钟
create_clock –period 20 –name my_clock [get_ports clk],周期 20ns,get_ports表明时钟源。 - 定义派生时钟:
create_generated_clock –name gen_clock -source [get_ports clk] –divide_by 2 [get_pins FF1/Q],由设计中某个现有的时钟信号生成,其源时钟是设计中的 clk 端口,该派生时钟是源时钟的一半频率,并且这个派生时钟用于作用名为 FF1 的触发器的输出引脚 Q。 set_ideal_network命令是用来指定一个网络(通常是时钟或复位信号)应该被综合工具视为理想网络。这意味着这个网络被假设为没有延迟和抖动,并且具有无限的能力来驱动负载。在实际的硬件实现中,时钟网络总是会有一定的延迟和抖动,因此set_ideal_network命令不适用于描述真实世界的时钟行为。-
set_clock_transition命令用于指定时钟信号在逻辑电平之间转换的时间。这个转换时间通常被称为时钟的边沿斜率(edge slope) ,它表示时钟信号从低电平跳变到高电平或从高电平跳变到低电平时所需的时间。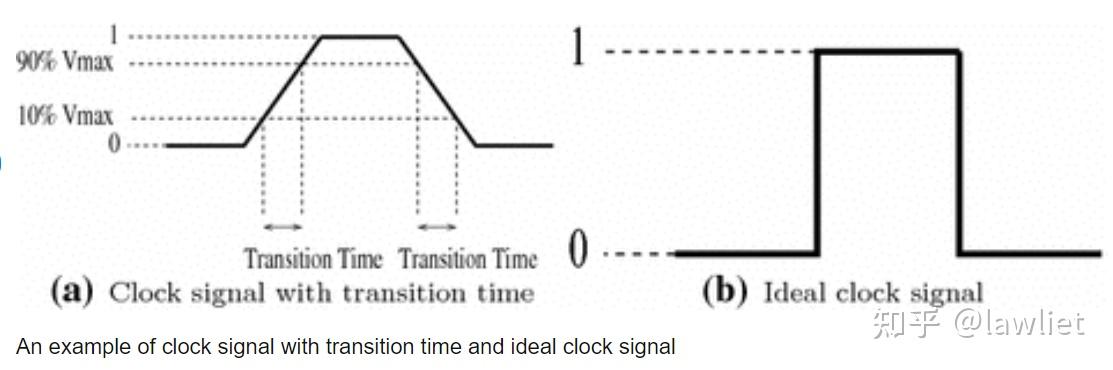
-
set_clock_uncertainty命令用于指定时钟信号的不确定性。时钟不确定性是由于时钟信号在传播过程中的各种因素(如时钟偏斜、时钟抖动、环境噪声等)导致的时钟边沿到达时间的不确定性。 set_propagated_clock命令用于指定一个时钟信号是一个已传播的时钟。已传播的时钟通常是指在设计中通过时钟网络传播后的时钟信号,它可能包含了时钟树综合(clock tree synthesis)后的延迟。
I/O Constraints¶
- 把时钟约束好以后,reg2reg 的路径已经解决。剩下的三种路径需要定义输入输出约束(即延迟
) 。 - 第一种定义方式,直接说明延时。
set_input_delay 0.8 –clock clk [remove_from_collection [all_inputs] [get_ports clk]],set_output_delay 2.5 –clock clk [all_outputs],注意这里输入端口要去除时钟端口。 -
另一种方式,定义输入输出 delay,并建模输入的 transitions 和输出的电容:
set_max_delay 5 –from [remove_from_collection [all_inputs] [get_ports clk]] set_max_delay 5 –to [all_outputs] set_driving_cell –cell [get_lib_cells MYLIB/INV4] –pin Z [remove_from_collection [all_inputs] [get_ports clk]] set_load $CIN_OF_INV [all_outputs]- input delay: 时钟上升沿过去多久后,数据到达输入端口。
- output delay: 模块输出到下一级模块需要多少延迟,也可以理解为在捕获沿到来时,数据已经存在的时间。
- 模拟输入驱动和输出负载,可以视为电阻或电容模型。

Timing Exceptions¶
- 有时我们需要定义特殊的 path,让 STA 特殊对待,例如 false path。
set_false_path命令用于指定设计中某些路径不会影响时序分析的结果。这通常用于那些不依赖于时钟周期或不需要满足特定时序要求的路径,例如复位路径、异步信号路径或某些测试路径。set_false_path through [get_pins mux1/I0] through [get_pins mux2/I0]表示 mux1 的输入引脚 I0 到 mux2 的输入引脚 I0 之间的路径是 false path。
-
还有跨时钟域的时钟约束,我们可以通过
set_false_path –from F1/CP –to F2/D的方式设置 false path。Example

也可以通过给时钟分组的方式
set_clock_groups –logically_exclusive –group [get_clocks C1] –group [get_clocks C2] -
set_multicycle_path命令用于指定某些特定的时序路径可以超过一个时钟周期来完成数据的建立(setup)或保持(hold) 。
Case Analysis¶
set_case_analysis命令用于指定一个信号或端口在综合或时序分析期间的固定逻辑值。这个命令通常用于模拟某些特定的设计状态,例如测试模式或配置模式,而不需要实际改变硬件的物理连接。- 例如
set_case_analysis 0 [get_ports TEST_MODE]表示分析时我们假设端口TEST_MODE端口始终输出逻辑 0,这个值可以传播到整个设计中。 (例如 0 是 AND 门的一个输入,那么 AND 门的输出时钟 0,实际上也成为了 false path)
Design Rule Violations¶
- You can set specific design rules that should be met, for example:
- Maximum transition through a net.
set_max_transition $MAX_TRAN_IN_NS - Maximum Capacitive load of a net.
set_max_capacitance $MAX_CAP_IN_PF - Maximum fanout of a gate.
set_max_fanout $MAX_FANOUT
- Maximum transition through a net.
