Image Classificatin¶
约 1266 个字 6 张图片 预计阅读时间 4 分钟
Data-driven approach¶
-
图像分类的问题:存在 semantic gap,计算机没有那种直觉,只能看到像素(数字
) 。- fine-grained categories,例如不同类的猫。
- background clutter,背景可能和物体有聚合在一起。
- illumination changes,例如同类物体在不同亮度下。
- Occlusion,要识别的东西看你无法看不见全貌。
-
Machine Learning: Data-Driven Approach
- Collect a dataset of images and labels
- Use ML to train a classifier
- Evaluate the classifier on new images
- 不是用 human knowledge,而是 data-driven. 通常我们的模型会有 2 个 API:
- train 返回某些统计模型。
- predict 利用模型预测新图像。
-
Image Classification Datasets
-
MNIST
- 10 classes(0 to 9)
- 28*28 grayscale image
- 50k training images, 10k test images
Results from MNIST often do not hold on more complex datasets.
MNIST 数据集比较简单,在这个数据集上表现很好并不足以说明这个模型足够好。 -
CIFAR-10
- 10 classes
- 50k training images(5k per class)
- 10k testing images(1k per class)
这个数据集比较 challenging,因为很难识别。
-
ImageNet
- ~1.3M training images (~1.3K per class)
- 50K validation images (50 per class)
- 100K test images (100 per class)
- test labels are secret!
-
performance metric: Top 5 accuracy Algorithm predicts 5 labels for each image; one of them needs to be right.
预测前五个只要有一个对了,就认为预测成功。
是图像分类的 gold standard.
-
MIT Places
- ~8M training images
- 18.25K val images (50 per class)
- 328.5K test images (900 per class)
- Omniglot
- 1623 categories: characters
- from 50 different alphabets
- 20 images per category
- Meant to test few shot learning
-
如何用更大的数据集来提高我们算法 robust 分类的能力。
First classifier: Nearest Neighbor¶
- Idea: Memorize all data and labels. Predict the label of the most similar training image.
记住所有数据和标签。预测时进行比较,找到最相似的图像,返回其标签。 - Distance Metric
- L1 distance \(d_1(I_1-I_2)=\sum_p|I_1^p - I_2^p|\)
- Performance
- training: \(O(1)\)
-
testing: \(O(N)\) this is bad! we can afford slow training, but need fast testing.
实际上有算法计算近似的最近邻。
Problem
最近的邻居往往是视觉上比较类似的图像,但是这种方法在实际中并不总是有效的。

Nearest Neighbor Decision Boundaries¶
- 决策边界是两个分类区域的边界(can be noisy, affetecd by outliers)
-
为了平滑这些决策,我们采用 KNN 的方式。即选前 k 近邻,进行多数投票。
Example
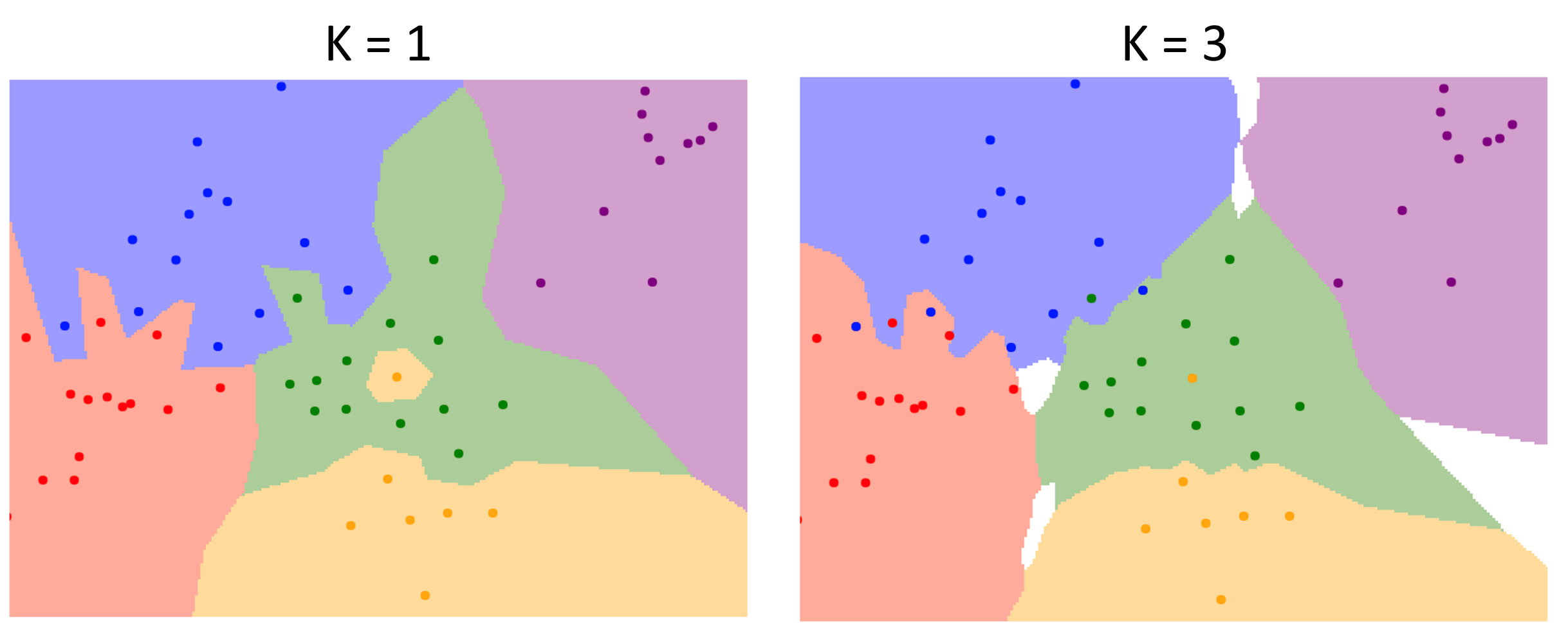
白色区域无法决定出结果(有 3 种不同颜色的点
) ,需要其他启发式的方法。 -
Distance Metric
不同的距离度量,决策边界有不同的性质。- L1 Manhattan
- L2 Euclidean \(d_2(I_1, I_2)=\sqrt{\sum\limits_p (I_1^p - I_2^p)^2}\)
如果距离度量选择正确,我们可以把 KNN 引用在任何类型的数据上
。 (虽然简单,但 robust)
Hyperparameters¶
-
超参数:我们需要在学习中做出的选择,不一定能从数据中学习,而是直接设置。
- What is the best value of K to use?
- What is the best distance metric to use?
Very problem-dependent. In general need to try them all and see what works best for our data / task. * Idea: - Choose hyperparameters that work best on the data (training set)
BAD: K=1 总是在数据集上最好的。(因为数据总是能找到相同的)-
Split data into train and test, choose hyperparameters that work best on test data.
BAD: 不知道算法会在新的数据上的表现(被测试集污染)
-
Split data into train, val, and test; choose hyperparameters on val and evaluate on test.
只有在测试的时候才接触你的测试集。
-
Cross-Validation: Split data into folds, try each fold as validation and average the results.
交叉验证,将数据分为不同块。
例如下面,我们可以用 1234 来训练,5 来验证;1235 来训练,4 来验证。etc.
Example

你可以为每个 fold 找到一个超参数的设置,然后平均得到结果。
但是成本昂贵,在小的数据集是可以的,but not used too frequently in deep learning.
交叉验证的结果

More about K-Nearest Neighbor¶
-
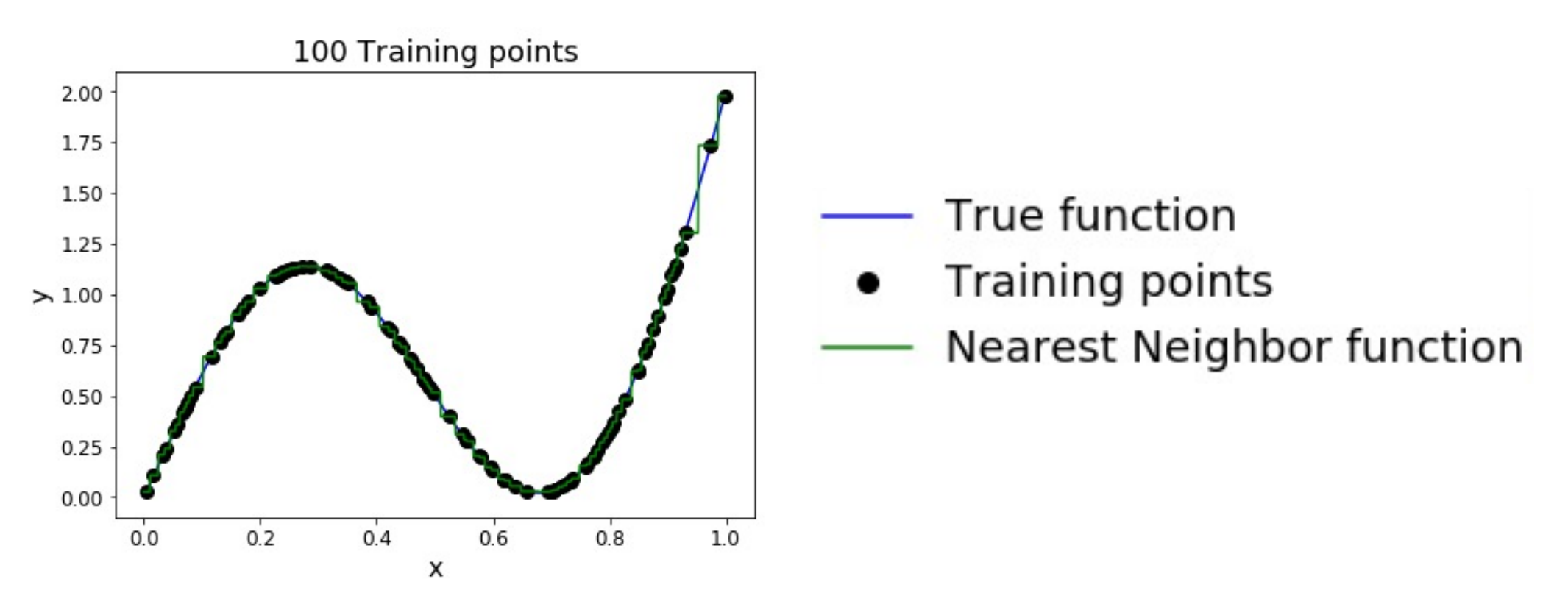
KNN 可以实现一个有趣的功能:Universal Approximation.
-
As the number of training samples goes to infinity, nearest neighbor can represent any(*) function!
可以近似于任何函数。
KNN 近似
-
-
Problem: Curse of Dimensionality
维数灾难。
For uniform coverage of space, number of training points needed grows exponentially with dimension.
为了让训练集覆盖整个空间,我们需要的数据集呈指数级增炸。Example
假设 1 维的时候有 4 个点,2 维就需要 4^2,3 维需要 4^3 个点才能实现相同的覆盖密度。
对于 CIFAR-10 的图像,我们要覆盖空间(32*32 维的
) ,需要 \(2^{32\times32}\approx 10^{308}\) 个图像。我们无法收集足够的数据。
-
KNN 在实际中很少用于像素。
- 预测慢。
- 无法获得足够的数据。
- 原始像素值的距离度量在语义上意义不大。
-
But Nearest Neighbor with ConvNet features works well!
不是用原始像素,而是神经网络提取出的特征向量。
Summary¶
Summary
- In Image classification we start with a training set of images and labels, and must predict labels on the test set
- Image classification is challenging due to the semantic gap: we need invariance to occlusion, deformation, lighting, intraclass variation, etc
- Image classification is a building block for other vision tasks
- The K-Nearest Neighbors classifier predicts labels based on nearest training examples
- Distance metric and K are hyperparameters
- Choose hyperparameters using the validation set; only run on the test set once at the very end!