Introduction¶
约 656 个字 3 行代码 11 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Abstract
- What, Why, How?
- What is a compiler?
- Why do we need to learn compilers?
- How to learn compilers?
- General Workflow of a Compiler
- Modules and Interfaces in Tiger
-
A compiler is a program to translate one language to another.

-
A compiler is a complex program.
-
Why
- Compilers are used in almost all forms of computing.
- The principles and techniques are applicable to so many other domains.
- Compiler construction touches upon other fields.
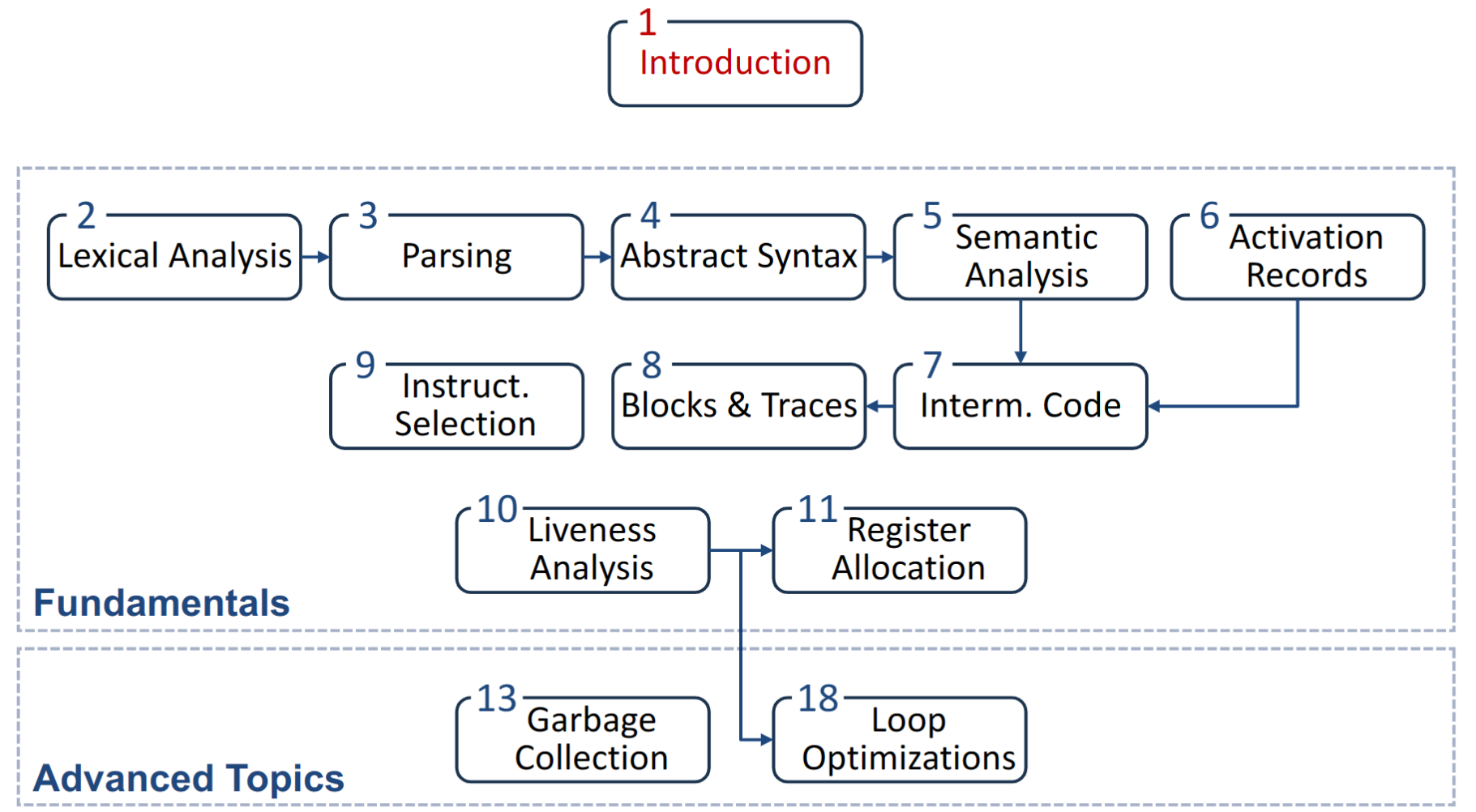
Typical Workflow of a Compiler¶
通用意义下的编译过程
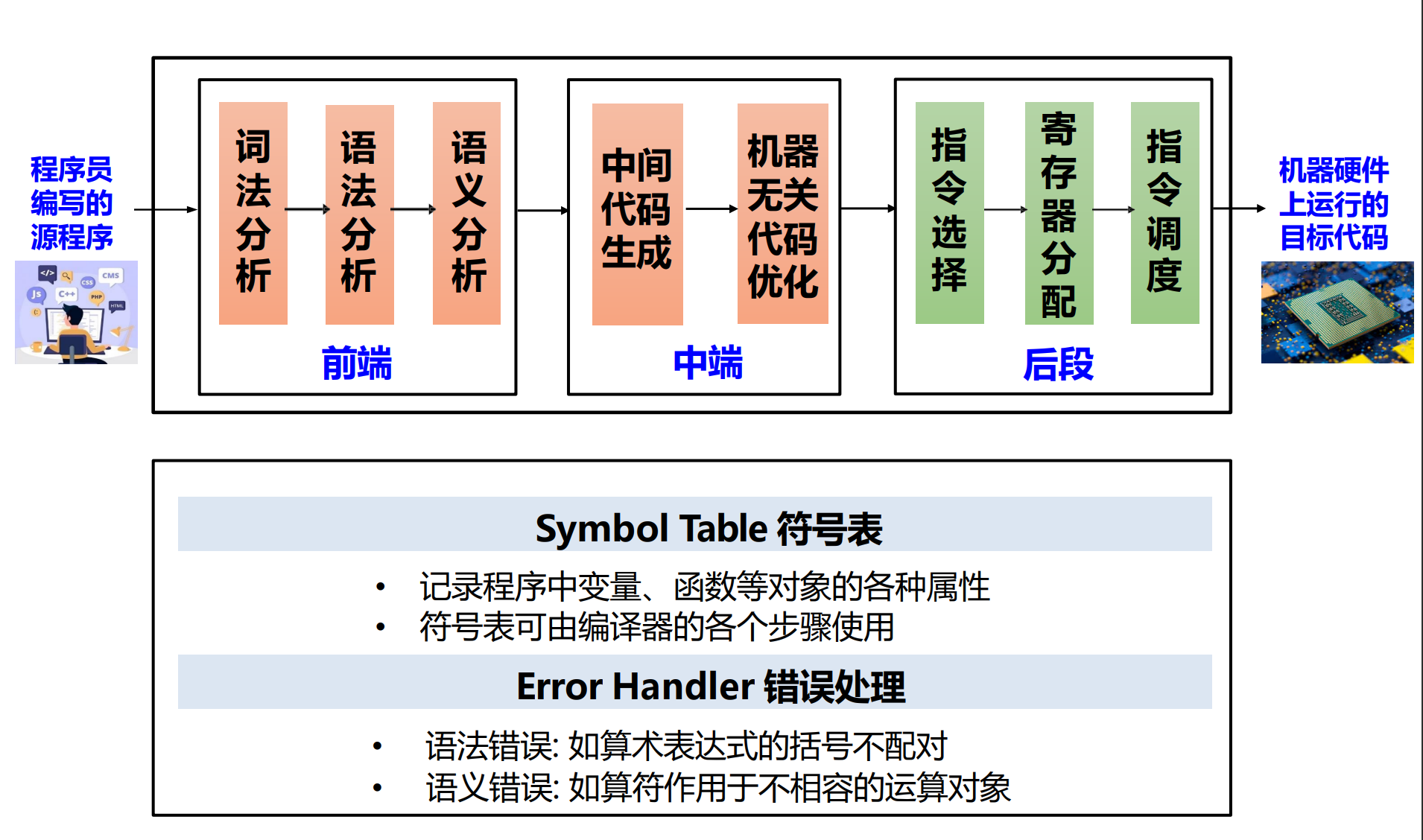
中端是为了剥离开前后端,与前端的语言、后端的硬件都是解耦的,让前端和后端可以独立发展。
贯穿整个过程:符号表、错误处理。
Two Important Concepts
-
Phases: one or more modules operating on different abstract “languages”.
阶段由不同的模块拼成。
-
Interfaces: information exchanged between modules of the compiler.
不同模块之间为了交互,需要定义接口,是交换信息的媒介。
-
Why breaking the compiler into multiple phases
- Easier to understand and implement
-
Allow for reusing the components
模块可以复用。
-
Workflow
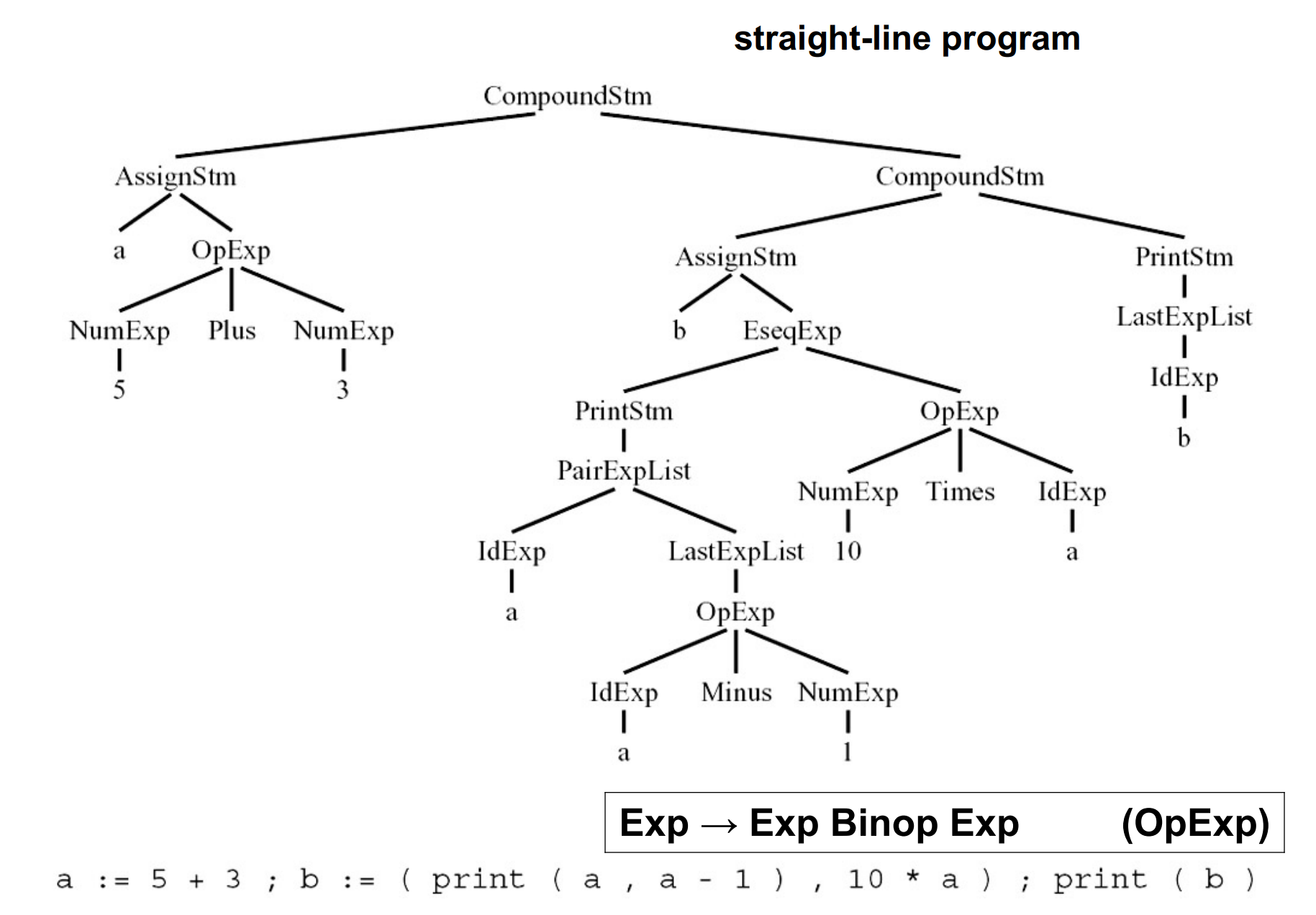
- Lexing/Scanning/Lexical Analysis 词法分析:将程序字符流分解为记号 (Token) 序列。
- 删除字符串中不必要的部分(如空格
) 。 - 通常使用正则表达式匹配(DFA 定义
) 。
- 删除字符串中不必要的部分(如空格
- Parsing/Syntactic Analysis 语法分析:将记号序列解析为语法结构。
- 去除不必要的记号(例如括号
) 。 - 一般使用抽象语法树(AST)定义。
- 去除不必要的记号(例如括号
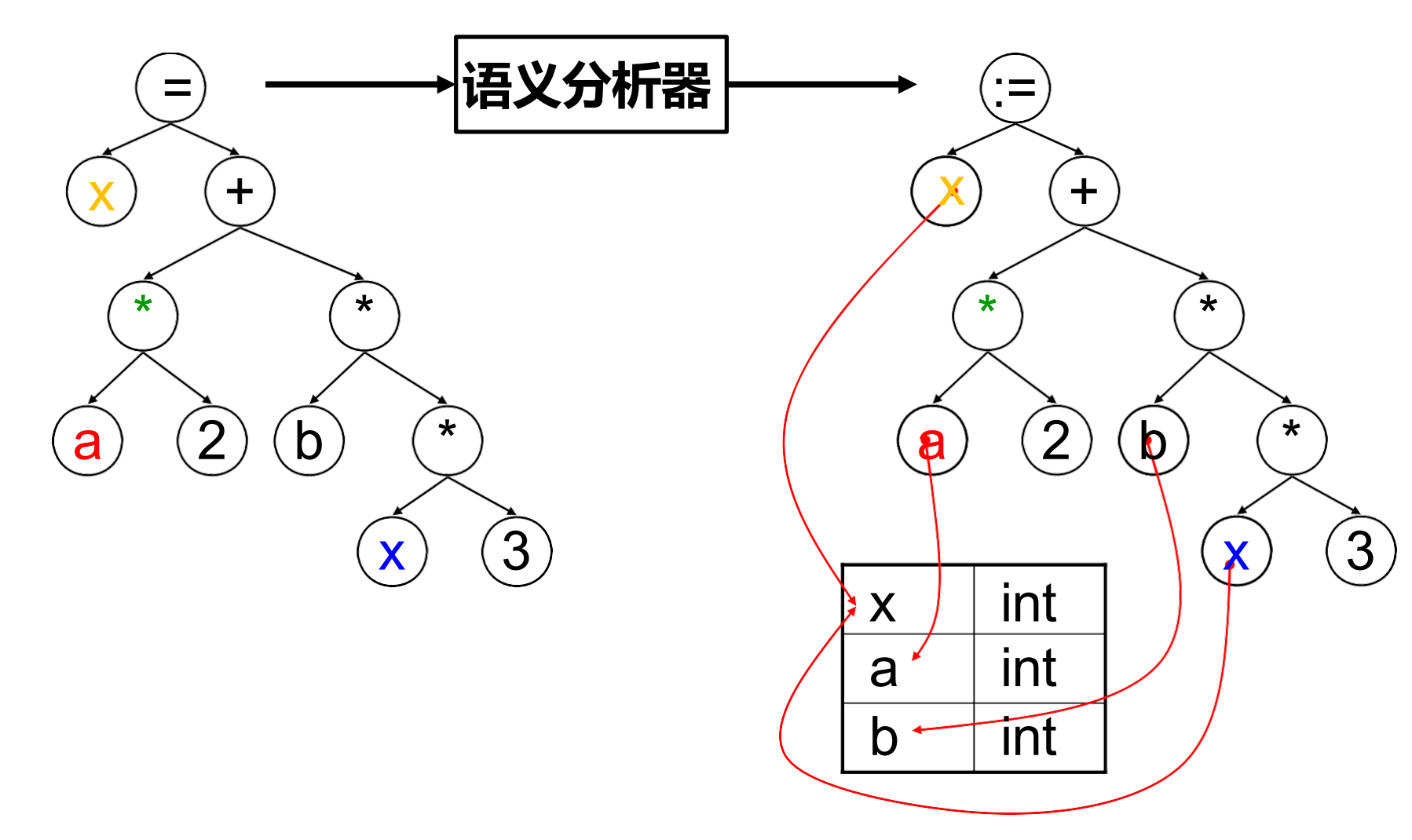
- Semantic Analysis 语义分析:决定语法结构的含义。
- e.g. 变量的类型?运算符的含义?读写变量是否合法?...
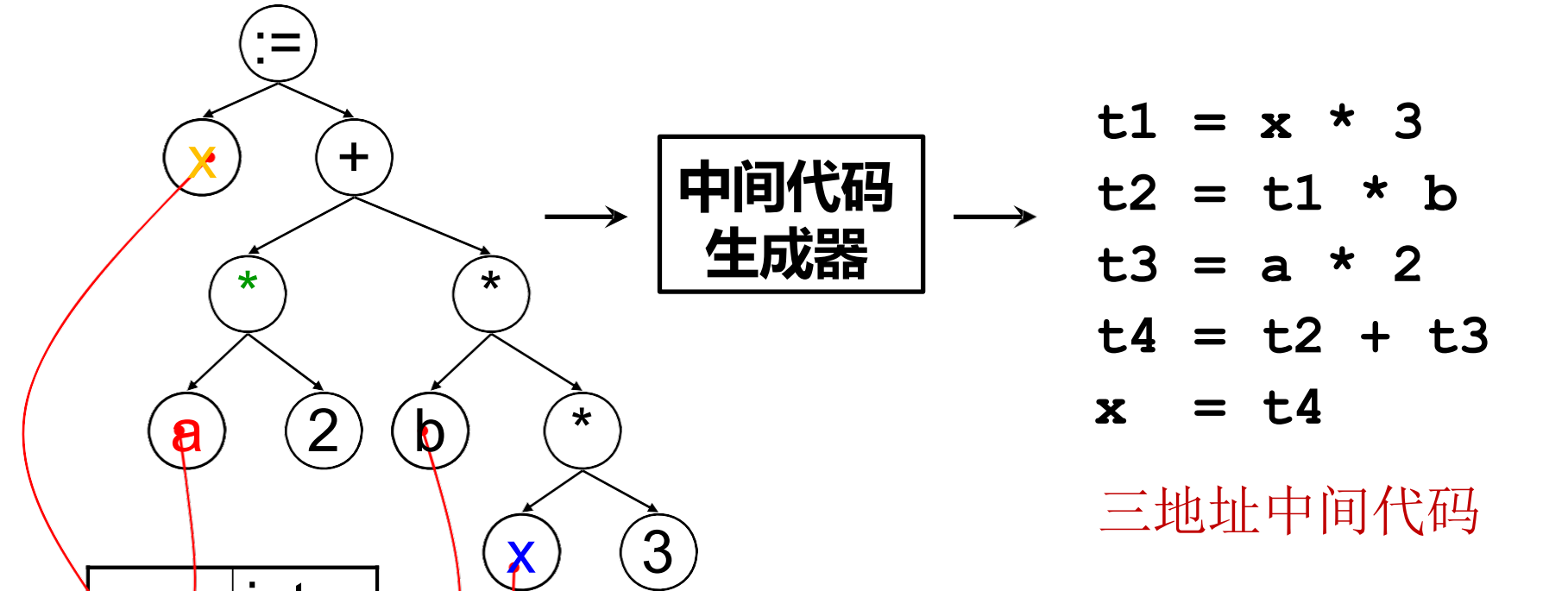
- 中间代码生成
- 中间代码 / 表示 (IR): 源语言与目标语言之间的桥梁。
- 机器无关代码优化:基于中间表示进行分析与变换。
- e.g. 降低执行时间,减少资源消耗等。
- 目标代码生成:把中间表示形式翻译到目标语言。
- e.g. 指令选择、寄存器分配、指令调度等。
- Lexing/Scanning/Lexical Analysis 词法分析:将程序字符流分解为记号 (Token) 序列。
Think As If You Were a Compiler
* 词法分析:把“字符串”分割成“单词”。 * 语法分析:“单词”组合成“句子”。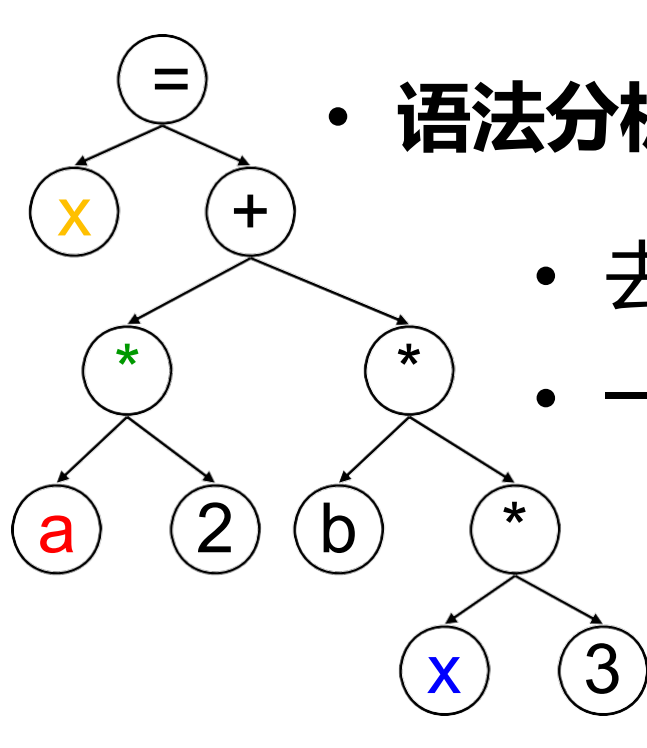
-
语义分析:解析“句子”的含义。
-
中间代码生成
-
机器无关代码优化

-
目标代码生成

Modules and Interfaces in Tiger¶

- AST ( 抽象语法树 ): 语法分析 + Parsing Actions 生成。
- IR Tree: 语义分析后按一定规则生成(树型中间表示
) 。 - Canonicalized IR Tree: 规范化 IR Tree(方便生成汇编
) 。 - Assem: 指令选择器生成(一种特殊的抽象汇编
) 。 - CFG (Control Flow Graph) 控制流图 : 方便进行数据流分析。
- 如活跃变量分析 (Liveness Analysis)。
- Interference Graph ( 冲突图 ): 由活跃变量分析结果构造,用于指导寄存器分配。