Polymorphism¶
约 1512 个字 123 行代码 6 张图片 预计阅读时间 7 分钟
Abstract
- Polymorphism
- virtual functions and override
- abstract functions and classes
- Multiple Inheritance
Virtual function¶
Subtyping¶
Objects of subclasses can be used where objects of supertypes are required. (This is called substitution)
Subclass object may be assigned to superclass pointr variables.
Conversions
- Public Inheritance should imply substitution
- If B isa A, you can use a B any where an A can be used.
- if B isa A, then everything that is true for A is also true of B.
- Be careful if the substitution is not valid!
- Given D is derived from B
D -> B
只把 D 内和 B 相同的地方赋值,不会把 D 特有的东西赋值。D* -> B*
换个眼光看待对象,并没有改变对象。D& -> B&
Upcasting¶
cast 在 OOP 里叫造型,不再是强制类型转换的意思。
Upcasting is the act of converting from a Derived reference or pointer to a base class reference or pointer.
我们是学生,现在让我们去搬砖,并没有改变我们的能力。但 对于 int i = (int)6.25; 这里必须强制改造,否则无法存进这个值 , 6.25 也被截断为 6.
upcasting: 向上造型,重新为对象想了一个造型,但并没有改变对象的值。因为 Manager 中一定有 Employee 的部分,而且一定在这部分的最上方。现在我们认为这块地址存放的是 Employee 的对象。
Example
Lose type information about the object:Example: A drawing program¶
operations: render, resize, move.
data: center.
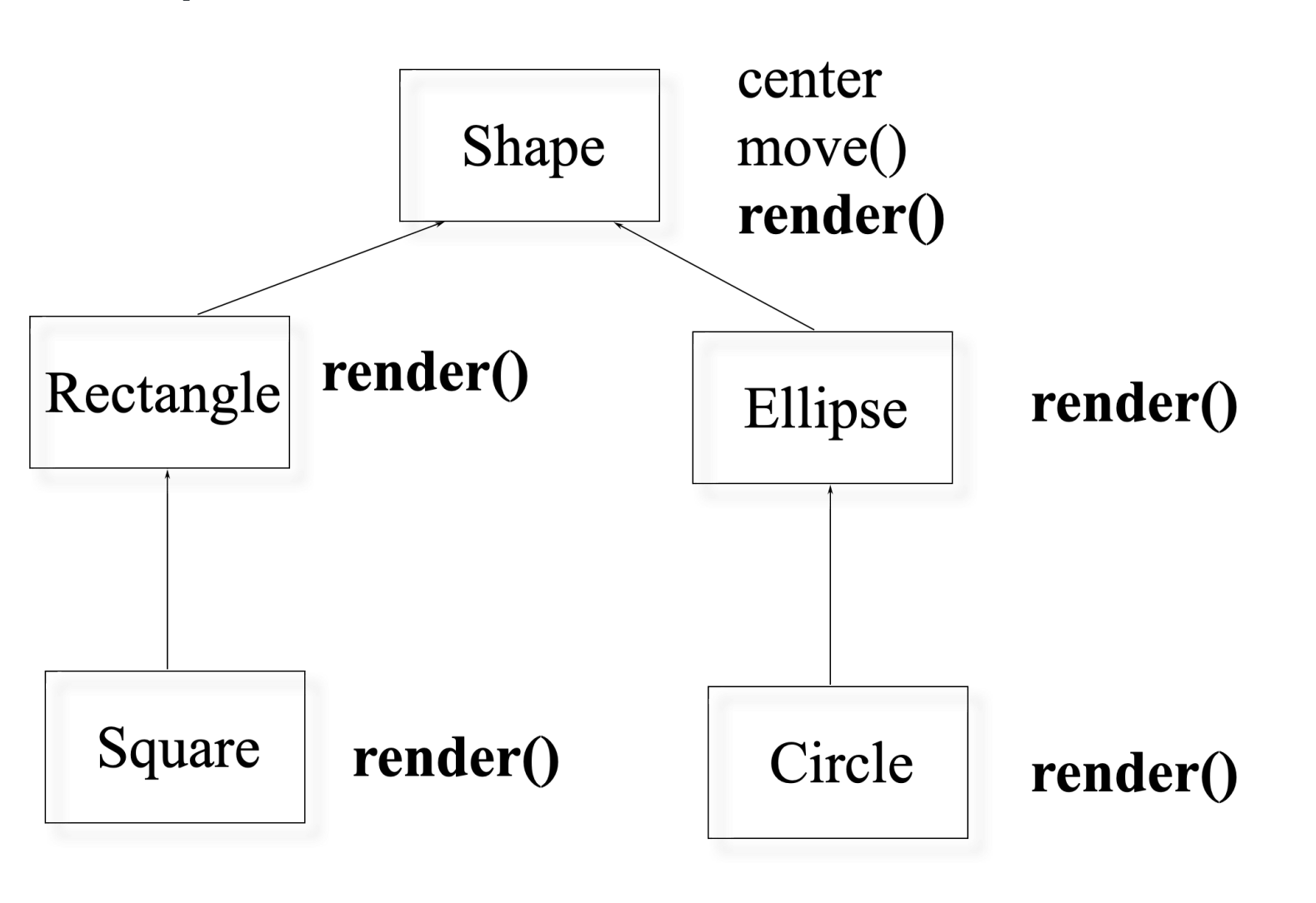
class XYPos{}
class Shape {
public:
Shape();
virtual ~Shape();
virtual void render();
void move (const XYPos&);
virtual void resize();
protected:
XYPos center;
}
virtual 定义了虚函数,意味着子类可能出现这个函数的新版本。告诉编译器通过指针访问这个函数时,要如何编译。
class Ellipse : public Shape {
public:
Ellipse(float maj, float minr);
virtual void render(); // will define own
protected:
float major_axis, minor_axis;
};
class Circle : public Ellipse {
public:
Circle(float radius) : Ellipse(radius, radius){}
virtual void render();
};
void render(Shape* p) {
p->render(); // calls correct render function
} // for given Shape! void func() {
Ellipse ell(10, 20);
ell.render(); // static -- Ellipse::render();
Circle circ(40);
circ.render(); // static -- Circle::render();
render(&ell); // dynamic -- Ellipse::render();
render(&circ); // dynamic -- Circle::render()
我们认为 p 这个指针是一个 polymorphic variable 多态变量,有静态(声明)类型 Shape 又有动态类型。
Static and dynamic type¶
- The declared type of a variable is its static type.
- The type of the object a variable refers to is its dynamic type.
- The compilerʼs job is to check for static-type violations.
因此在编译时,如果我们去掉Shape()里的render函数,编译就会报错。这样无法通过静态检查,尽管我们知道我们并不会使用Shape的render函数。
Polymorphism¶
- Upcast: take an object of the derived class as an object of the base one.
e.g. Ellipse can be treated as a Shape - Binding: which function to be called
- Static binding: call the function as the code
- Dynamic binding: call the function of the object
virtual关键词是在告诉编译器,这个函数使用动态绑定。否则即使用指针,也是静态绑定。 e.g.g();Student a; a.f()是静态 ;Student &a; a.f();p->f();不一定是静态。
| call | type |
|---|---|
| free function | static |
object.fun() |
static |
ref.func() |
static |
p->func() |
static |
ref.vfunc() |
dynamic |
p->vfunc() |
dynamic |
Virtual functions¶
- Can be transparently overridden in a derived class
父类的函数定义为虚函数后,子类不需要再定义了,会传递下去。(? - Objects carry a pack of their virtual functions
- Compiler checks pack and dynamically calls the right function
- If compiler knows the function at compile-time, it can generate a static call
Polymorphic variables
- Pointers or reference variables of objects are polymorphic variables
- They can hold objects of the declared type, or of subtypes of the declared type.
只写了一句代码,但实际执行中可能会有多种执行方式,这就是多态。
How virtuals work in C++¶
这时 sizeof(A) == 4 但如果将 f 声明为虚函数 , sizeof(A)就变为 16. 如果去掉 int i; 后 sizeof(A) 变为 8.
一旦有虚函数声明,这里会在开头放一个指针VPTR , 指向一个表,里面放的是函数指针
Ellipse elly(20F, 40F);
Circle circ(60F);
elly = circ; // 10 in 5?
elly.render(); // Ellipse::render()
Ellipse* elly = new Ellipse(20F, 40F);
Circle* circ = new Circle(60F);
elly = circ;
elly->render(); // Circle::render()
References act like pointers.
Virtual destructors¶
p 的静态类型是 Shape, 如果不定义虚函数,那么 p 只会发生静态绑定,即调用 Shape 的析构函数,无法调用 Ellipse 的析构函数。
Overriding¶
Overriding redefines the body of a virtual function.
仍然可以在子类中调用父类的被 overide 的函数。
Return types relaxation
- Suppose D is publicly derived from B
D::f()can return a subclass of the return type defined inB::f()- Applies to pointer and reference types
Relaxation Example
指向子类的对象可以被看做是一个指向父类的对象。但是子类的对象和父类的对象是不同的。If you override an overloaded function, you must override all of the variants!
- Can't override just one
- If you don't override all, some will be hidden
Tips
- Never redefine an inherited non-virtual function
子类不要重新定义不是 virtual 的函数,这样无法形成 override 的关系。- Non-virtuals are statically bound
- No dynamic dispatch!
- Never redefine an inherited default parameter value
不要重新定义父类的默认参数值。- Theyʼre statically bound too!
- And what would it mean?
Example
这里会发生动态绑定。但是 VPTR 会在构造函数的 initialized list 里初始化。我们会执行 A 的构造函数,这个时候 VPTR 是 A 的,因此会调用 A 中的 f 函数。父类结束后回到 B 的构造函数,这时把 VPTR 改写为指向 B 的表,这时的动态绑定就变为 B 的 f 函数。Abstract classes¶
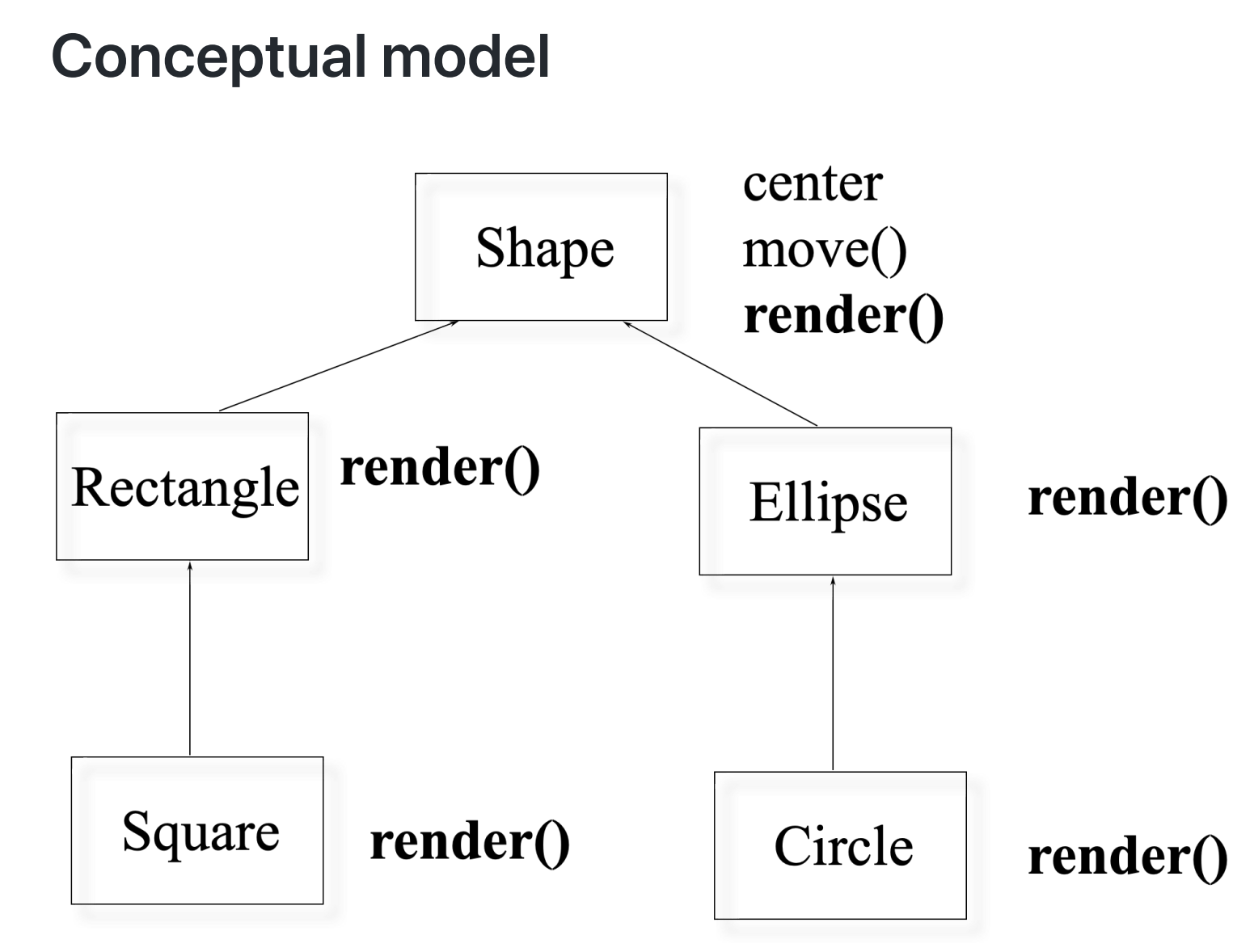
我们不应该制造 Shape 的对象,他的作用只在于提供一个抽象的概念和公共接口。
这个类中一旦有一个虚函数 =0( 纯虚函数 ), 那么这个类就不能被制造出对象,这样的类叫做抽象类。
Example
- An abstract base class has pure virtual functions
- Only interface defined
- No function body given
- Abstract base classes cannot be instantiated
- Must derive a new class (or classes)
- Must supply definitions for all pure virtuals before class can be instantiated
Multiple Inheritance¶
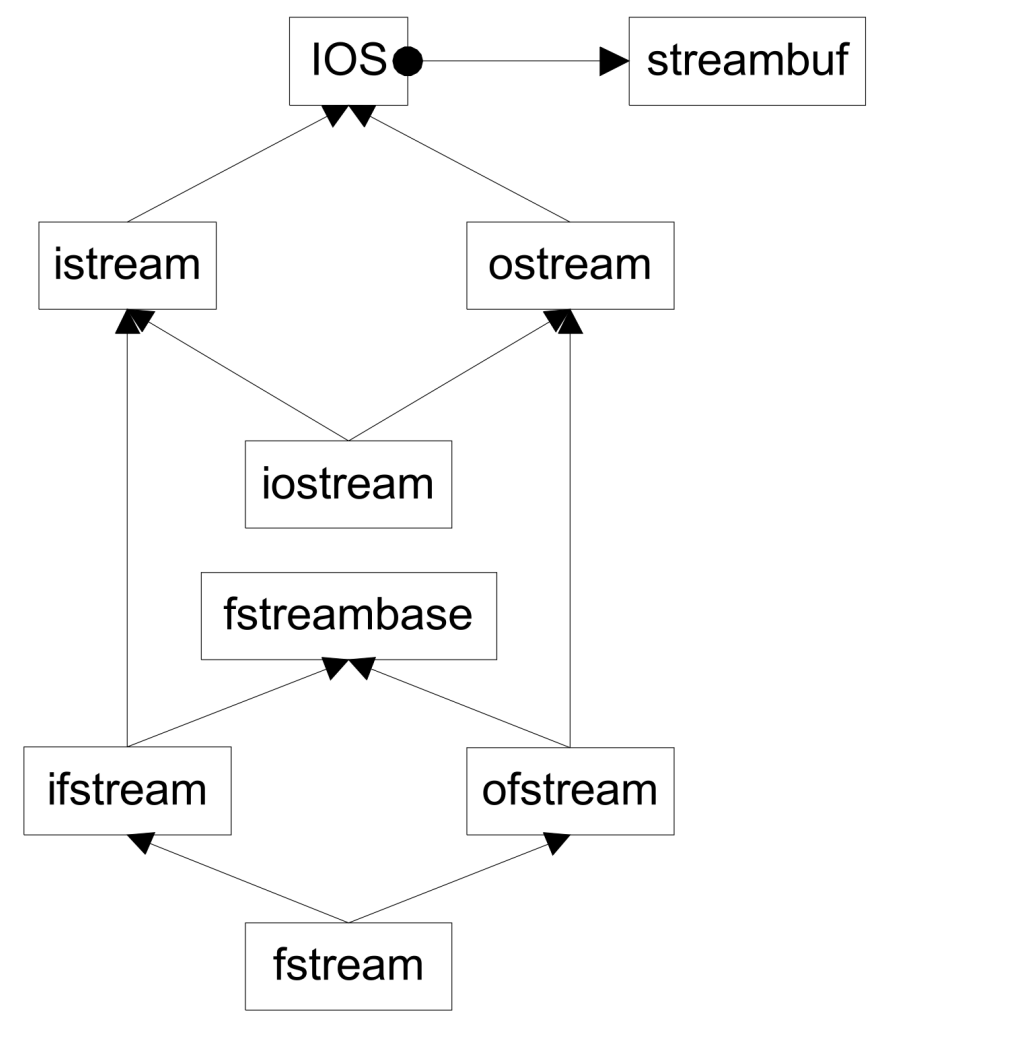
diamond inheritance. 孙子体内有两个爷爷。
Vanilla MI¶
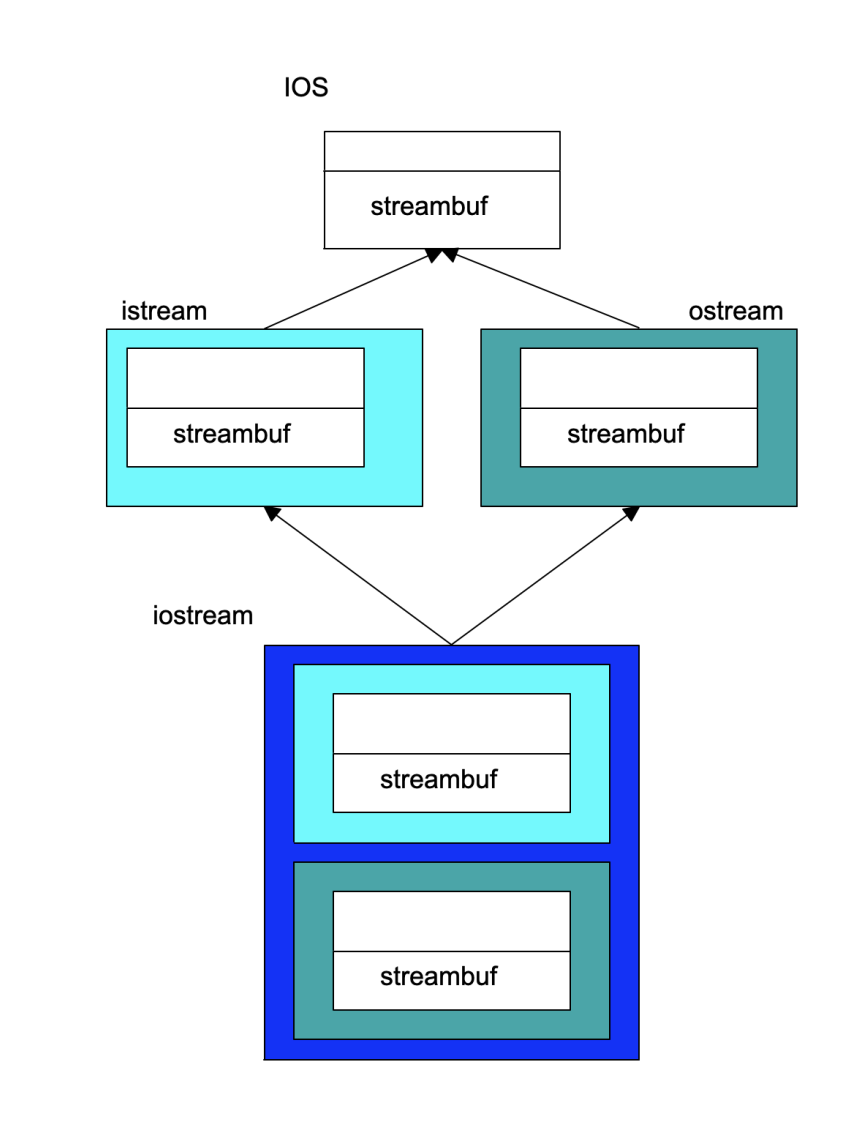
- Members are duplicated
- Derived class has access to full copies of each base class
- This can be useful!
- Multiple links for lists
- Multiple streambufs for input and output
class B1 { int m_i; };
class D1 : public B1 {};
class D2 : public B1 {};
class M : public D1, public D2 {};
void main() {
Mm; //OK
B1* p = new M; // ERROR: which B1
B1* p2 = dynamic_cast<D1*>(new M); // OK
}
Protocol classes¶
多继承:只有一个父类有成员变量(函数没关系)
Protocol classes 协议类,里面没有成员变量(除了 static, const)只有纯虚函数。这样的类可以安全地做多继承。
Abstract base class with
- All non-static member functions are pure virtual except destructor
- Virtual destructor with empty body
- No non-static member variables, inherited or otherwise may contain static members
Using virtual base classes¶
虚继承 virtual public 把父类的对象拿出来放在外面,子类指针指向外面的空间。从两个虚继承的类多继承,这时其中的两个爷爷类可以指向同一个地方。

class B1 { int m_i; };
class D1 : virtual public B1 {};
class D2 : virtual public B1 {};
class M : public D1, public D2 {};
void main() {
M m; //OK
m.m_i++; // OK, there is only one B1 in m.
B1* p = new M; // OK
}
建议:对多继承 say no.