Inheritance¶
约 728 个字 54 行代码 8 张图片 预计阅读时间 3 分钟
Abstract
- composition
- inheritance
Composition¶
Composition: reusing the implementation
- Composition: construct new object with existing objects
- It is the relationship of "has-a"
- Ways of inclusion
- Fully
- By reference (Inclustion by reference allows sharing)
e.g. an employee has
Embedded objects
- All embedded objects are initalized
- The default constructor is called if you donʼt supply the arguments, and there is a default constructor (or one can be built)
- Constructors can have initial
Note
If we wrote the constructor as (assuming we have the set accessors for the sub-objects):
SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount (
const char* name,
const char* address,
int cents ) {
m_saver.set_name( name );
m_saver.set_address( address );
m_balance.set_cents( cents );
}
对于嵌入对象,不用初始化列表,就必须有默认构造函数。
public vs private
It is common to make embedded objects private.
Inheritance¶
Reusing the interface
继承是要基于已有的类来设计新的类,新的类的对象可以被当作已有类的对象。
Inheritance is the ability to define the behavior or implementation of one class as a superset of another class.
Example¶
Source Code:
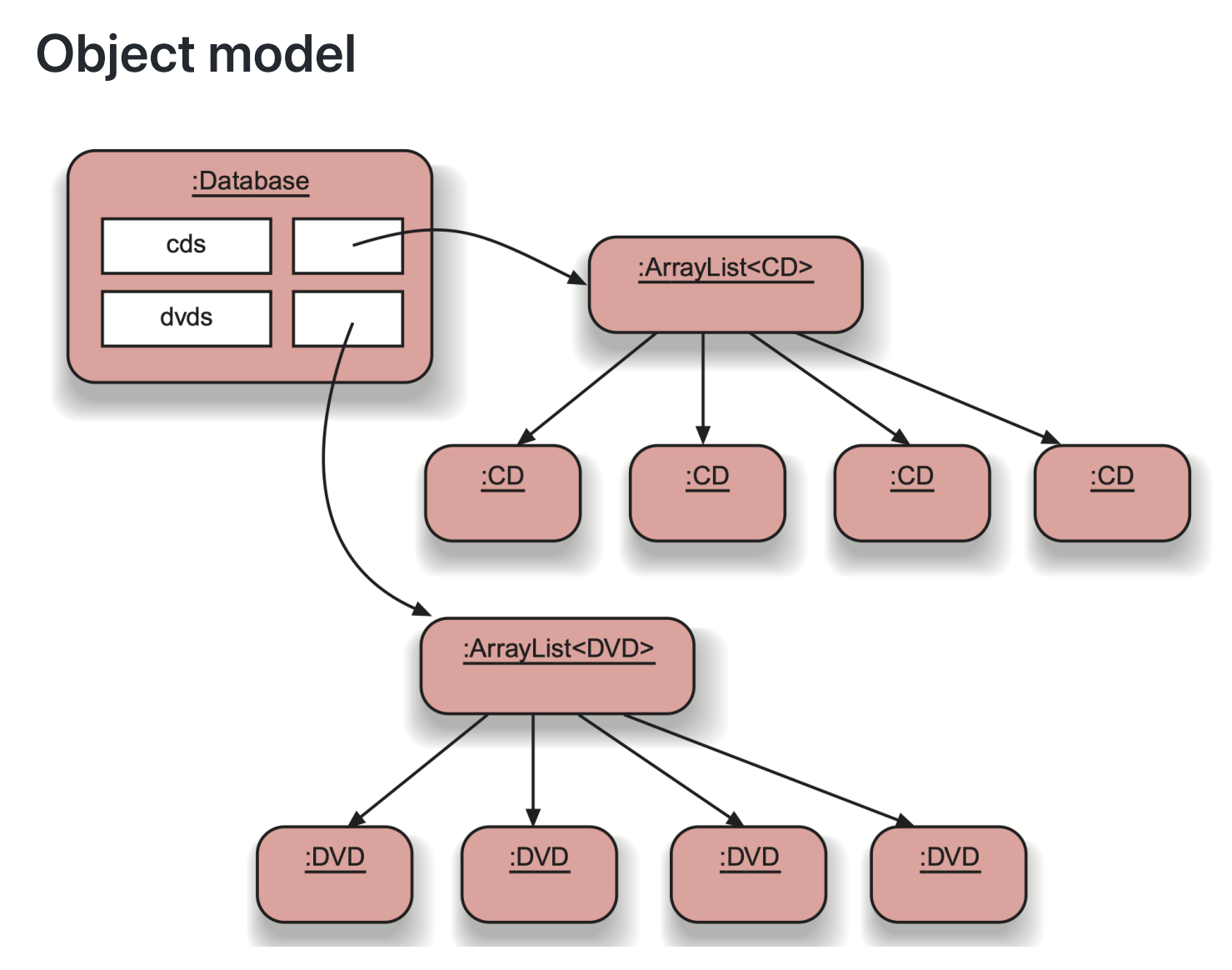
class Database {
vector<CD> cds;
vector<DVD> dvds;
public:
void addCD(CD &aCD);
void addDVD(DVD &aDVD);
void list() {
for (auto x:cds) { cd.print(); }
for (auto x:dvds) { x.print(); }
}
}
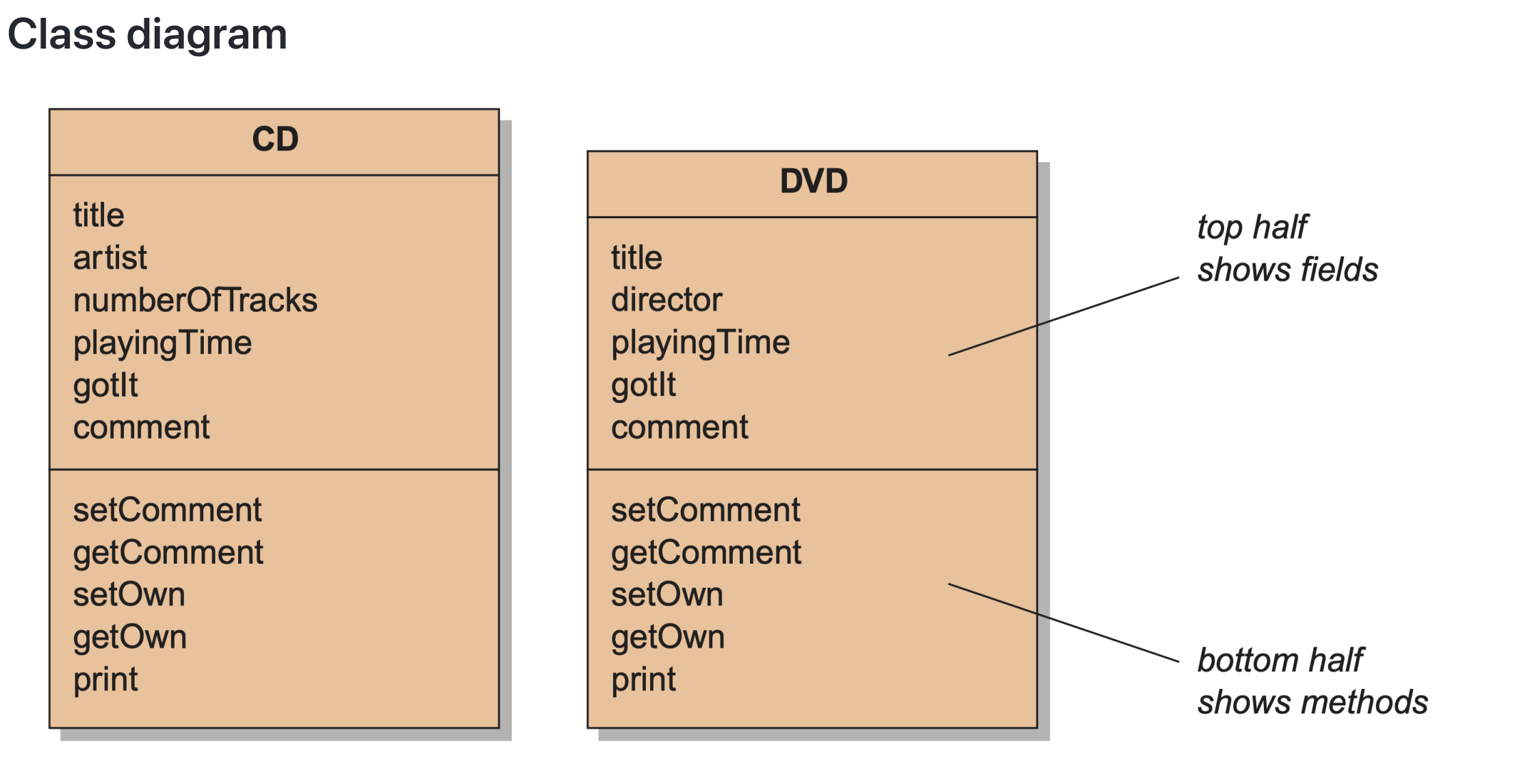
- code duplication
- CD and DVD classes very similar (large part are identical)
- makes maintenance difficult/more work
- introduces danger of bugs through incorrect maintenance
- code duplication also in Database class
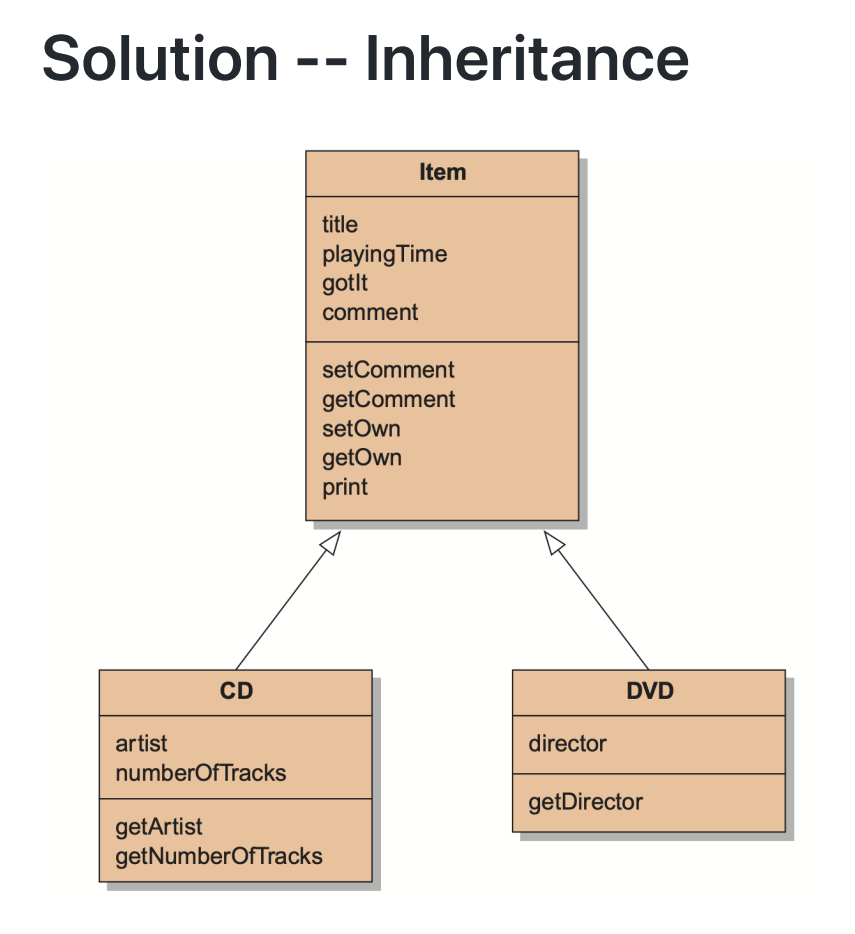
Inheritance allows us to define one class as an extension of another.
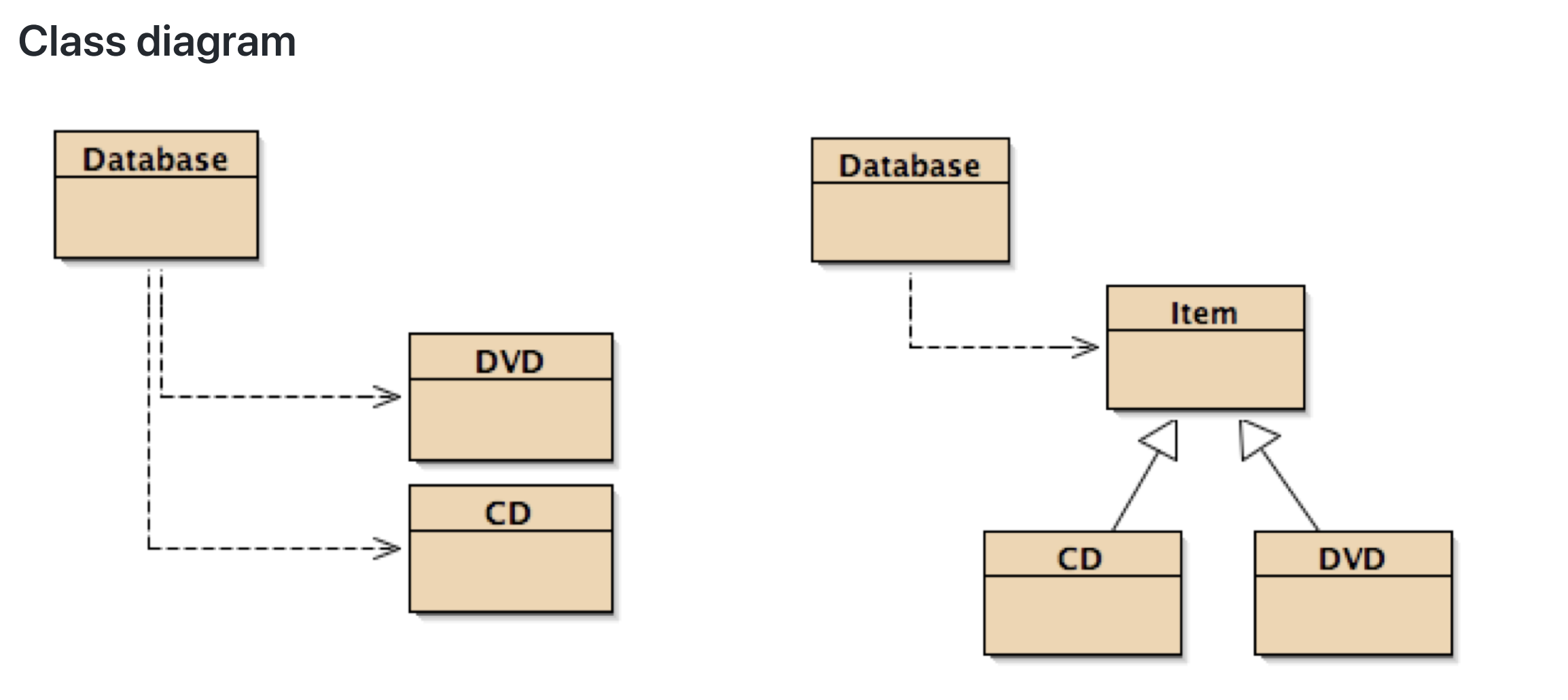

这时如果希望增加一个新的类型,如磁带,直接 class Tape: public Item 继承即可。
Inheritance¶
Advantages of inheritance
- Avoiding code duplication
- Code reuse
- Easier maintenance
可维护性,指代码修改后可以适应未来的变化。 - Extendibility
可扩展性,指代码不经修改就可以适应未来的变化。
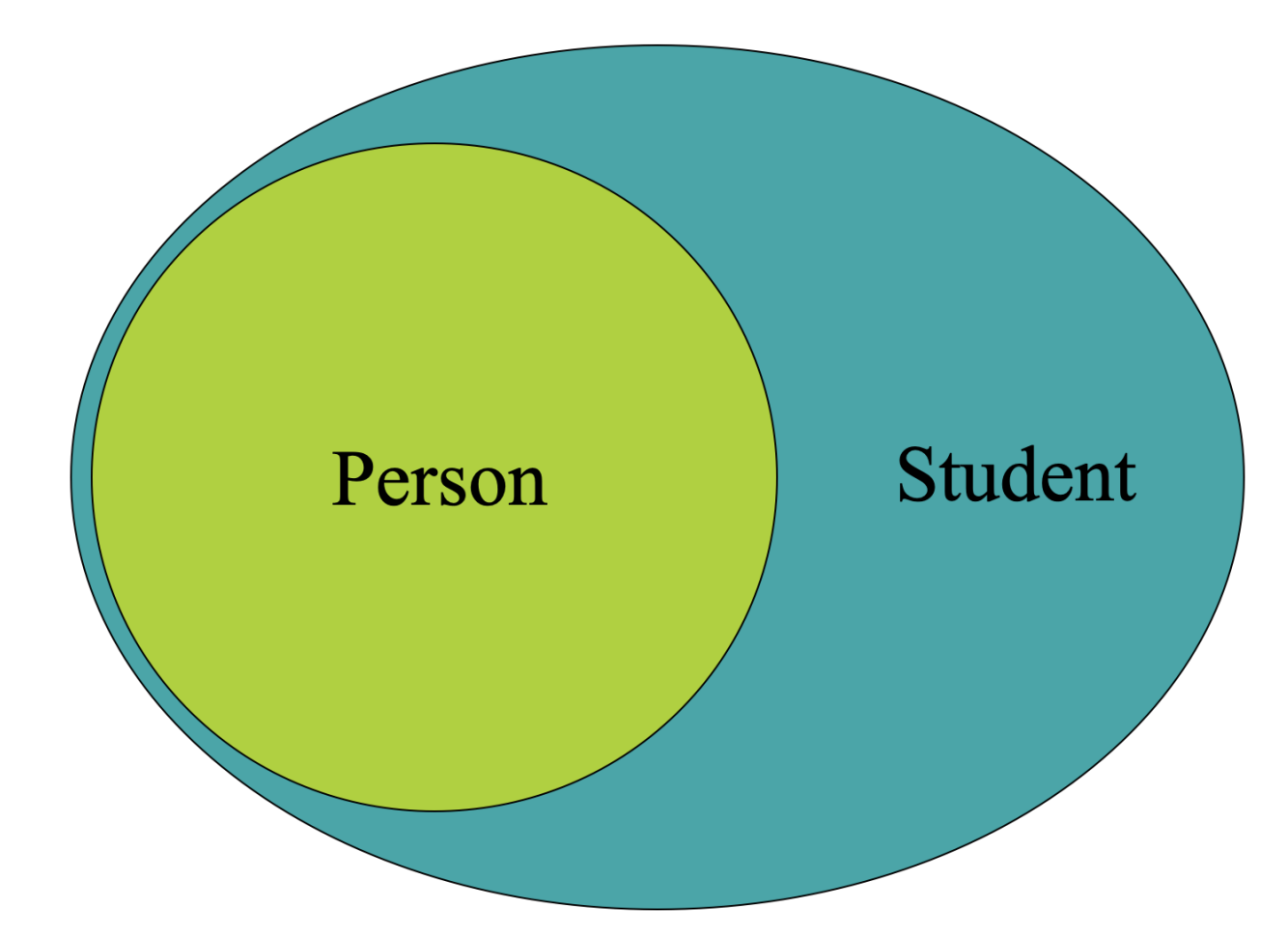
Class relationship: Is-A e.g. manager is an employee.
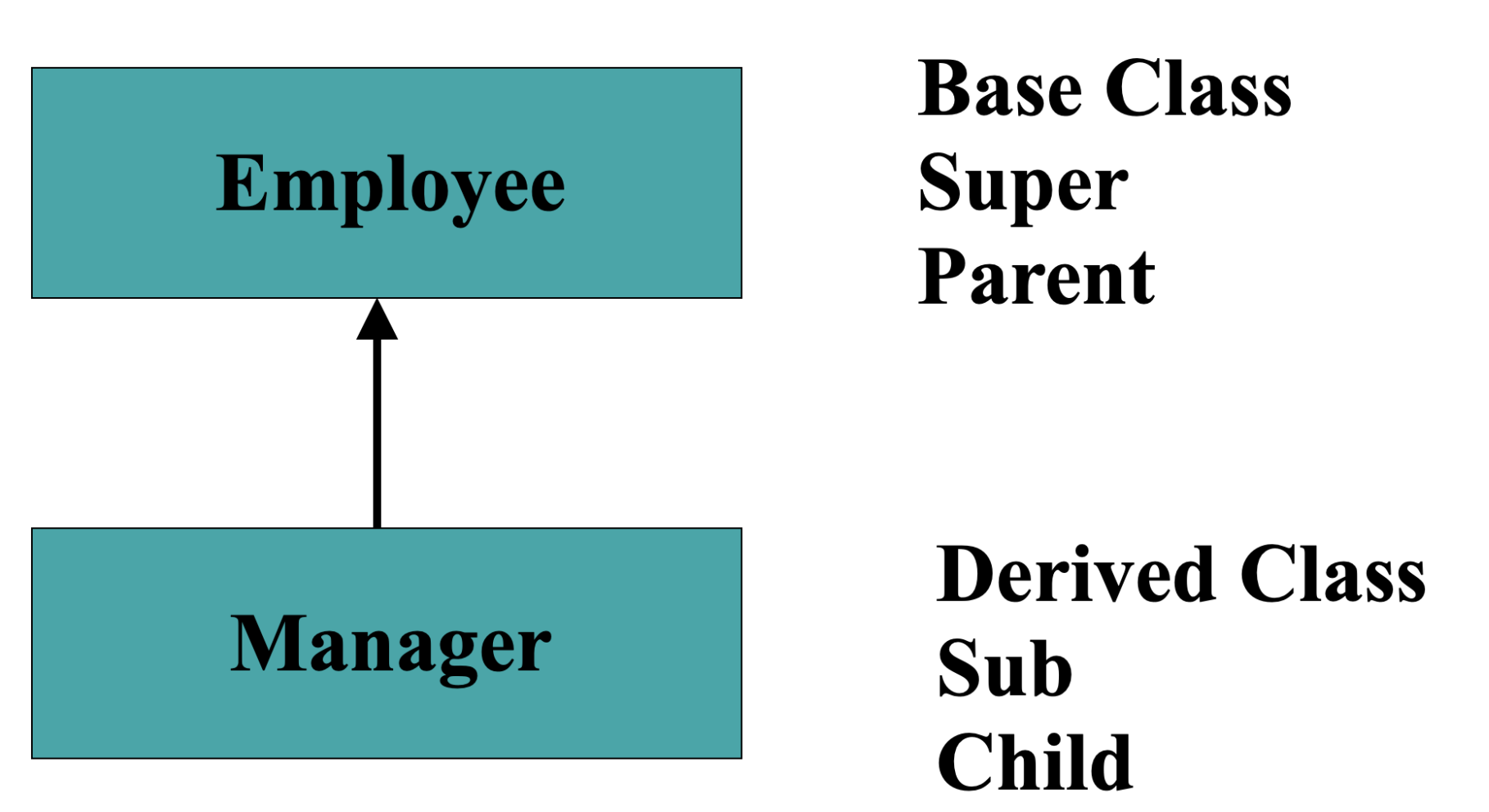
基类,超类,父类。派生类,子类。
Scopes and access in C++¶
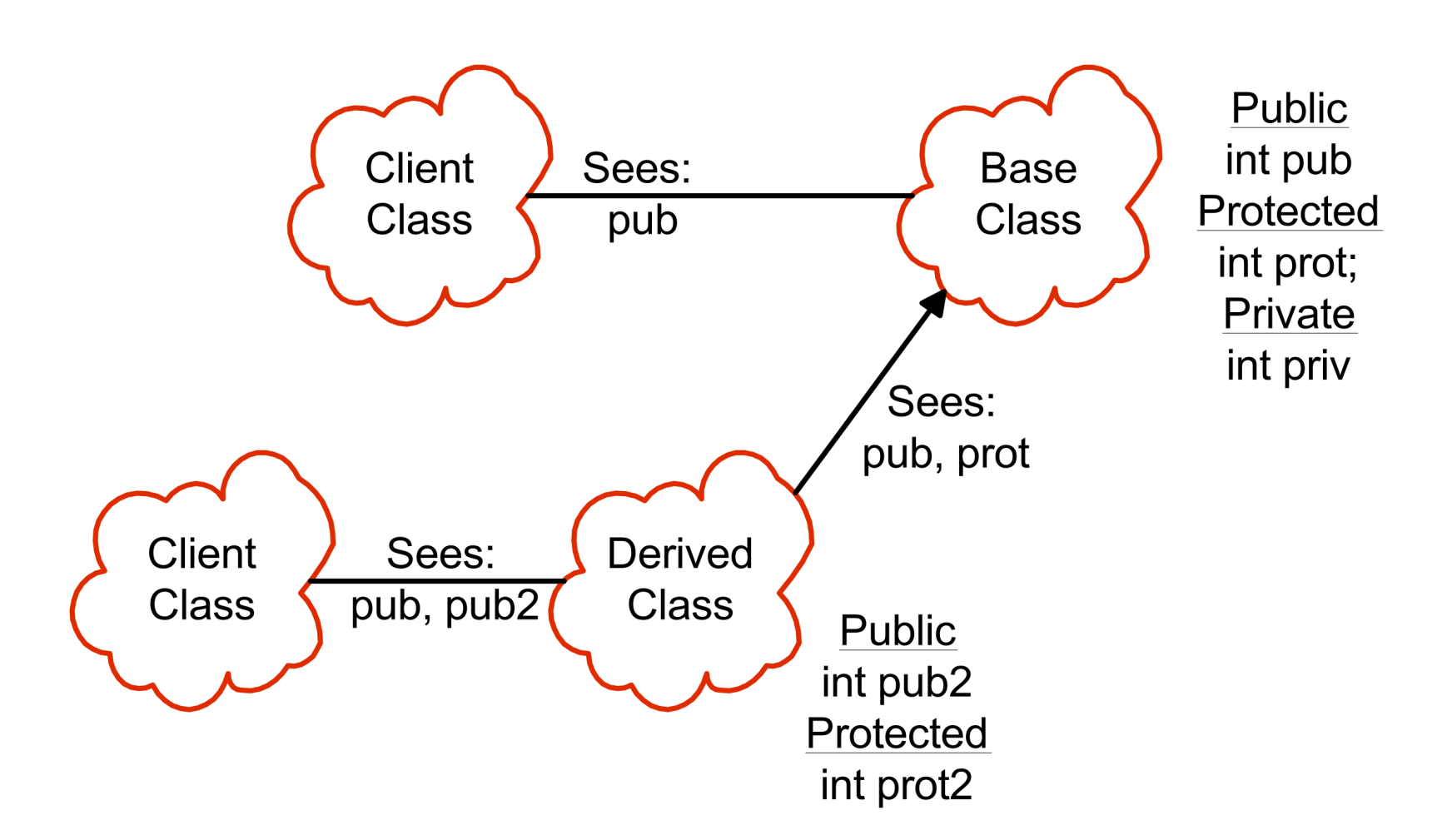
clint class 表示这个类要使用另一个类public)
能接受相同信息的对象可以被认为是同一个类型,因此子类的对象也可以认为是父类的对象。
子类不能访问父类的私有变量,但私有变量存在于这个类中。
当调用构造函数时,我们不能调用父类的私有变量,只能用初始化列表的方式调用父类的构造函数。我们不能也不应该在子类对父类的变量做初始化 (code duplication)
Employee::Employee( const string& name, const string& ssn )
: m_name(name), m_ssn( ssn) {
// initializer list sets up the values!
}
class Manager : public Employee {
public:
Manager(const std::string& name, const std::string& ssn, const std::string& title);
const std::string title_name() const;
const std::string& get_title() const;
void print(std::ostream& out) const;
private:
std::string m_title;
};
Manager::Manager( const string& name, const string& ssn, const string& title = "" )
:Employee(name, ssn), m_title( title ) {
}
有什么是没有继承得到:
构造函数没有被继承,但父类的构造会被自动调用。析构同理。
赋值的运算符不会被继承。
Inheritance
- Public:
class Derived : public Base ... - Protected:
class Derived : protected Base ... - Private:
class Derived : private Base ...- default
| Inheritance Type (B is) | public | protected | private |
|---|---|---|---|
| public A | public in B | protected in B | hidden |
| private A | private in B | private in B | hidden |
| protected A | protected in B | protected in B | hidden |
private 继承:私生子,外界不能知道他的父亲是谁。即 B 的用户不能看到 A 的 public 函数。其实是一种组合,父类的函数、变量变为私有。
int main()
{
Employee p1("John");
Manager p2("Tom Jordan", );
p1.print();
p2.print();
p1.print("Welcome:");
//p2.print("Welcome:"); 报错
Employee *p = &p1;
p->print();
p = &p2;
p->print(); // 按 Employee 里面的函数输出,而不是 Manager
}
要调用父类的成员函数,要Employee::print() .
初始化列表是属于 body 的,要和 {} 一起。
父类的构造是在子类的构造之前。
子类重新定义了父类的某个函数,就会把其他 overloaded 的函数覆盖掉(C++ 独有,无法解释p2.print("welcome")会报错。
如果在 Employee 中的 print 函数加上virtual , p->print()就会输出。